A villa offers an unparalleled blend of luxury, privacy, and comfort, making it an ideal choice for those seeking an exclusive living experience or a serene vacation retreat. These spacious homes often feature exquisite architecture, private pools, lush gardens, and modern amenities designed to elevate your lifestyle. Discover how selecting the perfect villa can transform your living experience by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
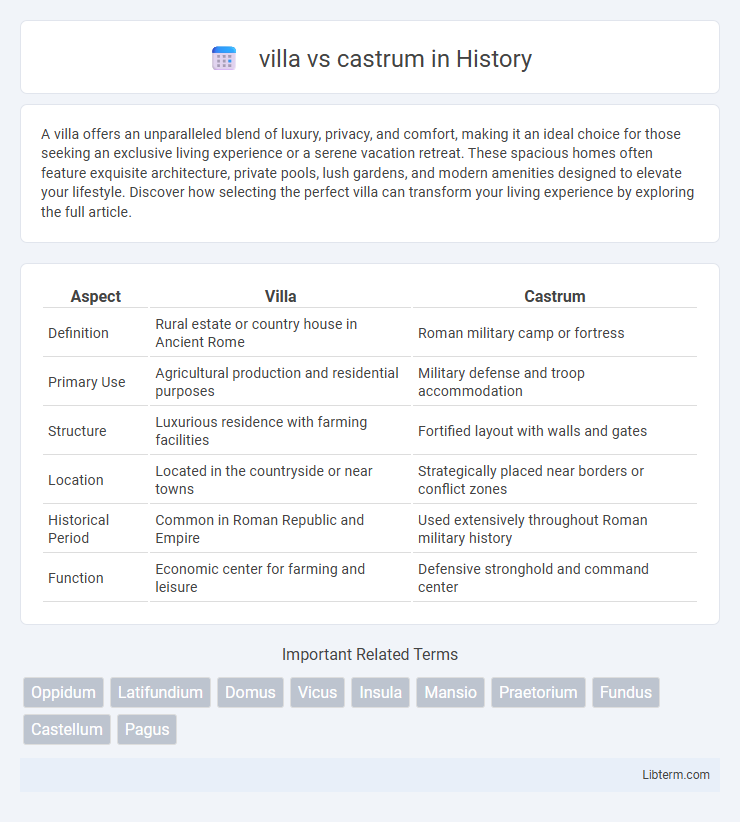
| Aspect | Villa | Castrum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rural estate or country house in Ancient Rome | Roman military camp or fortress |
| Primary Use | Agricultural production and residential purposes | Military defense and troop accommodation |
| Structure | Luxurious residence with farming facilities | Fortified layout with walls and gates |
| Location | Located in the countryside or near towns | Strategically placed near borders or conflict zones |
| Historical Period | Common in Roman Republic and Empire | Used extensively throughout Roman military history |
| Function | Economic center for farming and leisure | Defensive stronghold and command center |
Defining Villa and Castrum
A villa in antiquity was a countryside residence emphasizing agricultural production and leisure, typically comprising residential buildings, farm structures, and expansive lands. A castrum referred to a Roman military fortification designed for defense and housing troops, characterized by fortified walls, strategic positioning, and a structured internal layout including barracks and command areas. The villa served primarily as a private estate blending rural farming and luxury, while the castrum functioned as a secure military installation integral to Roman territorial control.
Historical Origins of Villas and Castra
Villas originated in the Roman Republic as large agricultural estates serving as rural residences for elite landowners, reflecting the socio-economic structure of ancient Rome. Castra were fortified military camps established to house Roman legions and control conquered territories, embodying the strategic and defensive needs of Roman expansion. While villas emphasized luxury and agrarian productivity, castra prioritized military organization and security, highlighting their distinct roles in Roman history.
Architectural Features: Villa vs Castrum
Villas typically feature spacious layouts with open courtyards, colonnaded gardens, and elaborate residential quarters designed for comfort and aesthetic appeal, reflecting Roman domestic architecture. Castra, by contrast, are characterized by a rigid, rectangular design with fortified walls, watchtowers, and barracks arranged in a grid pattern for military efficiency and defense. The villa's architectural focus is on luxury and leisure, while the castrum prioritizes security and tactical organization.
Geographic Locations and Distribution
Villas were predominantly found throughout the rural landscapes of the Roman Empire, especially in fertile regions such as Italy's Campania, Gaul, and North Africa, serving as agricultural estates and luxury residences. Castra, or Roman military forts, were strategically located along frontiers and in provinces like Britannia, Germania, and Dacia to protect territorial boundaries and facilitate military operations. The geographic distribution of villas reflects economic and social functions, while castra emphasize military control and territorial defense across diverse provincial environments.
Social and Economic Functions
Villas served as rural estates that functioned as centers of agricultural production and the residence of wealthy landowners, driving local economies through farming, livestock, and craft industries. Castra, originally military forts, evolved into fortified settlements that provided security and administrative control, supporting economic activities by protecting trade routes and local populations. While villas emphasized private wealth and social status among the elite, castra embodied collective organization and military authority, shaping social hierarchies and regional economic stability.
Military Significance of Castra
Castra served as fortified military camps, strategically designed to house Roman legions and maintain control over conquered territories, contrasting with villas that functioned primarily as domestic estates. The military significance of castra lay in their robust defensive structures, including walls, ditches, and watchtowers, which provided secure bases for troop deployment and rapid response to external threats. These forts were critical for maintaining Roman dominance, enabling efficient communication lines and supply routes across the empire's frontier regions.
Villas as Centers of Agriculture and Leisure
Villas functioned as multifunctional agricultural estates in Roman society, combining productive farming operations with luxurious residential amenities designed for relaxation and social gatherings. Unlike castra, which served primarily as military forts with strategic and defensive purposes, villas emphasized self-sufficiency through extensive cultivation of crops like olives, grapes, and grains, alongside livestock rearing. Wealthy landowners invested in villas not only to manage agricultural production efficiently but also to enjoy leisure activities such as hunting, bathing in private baths, and hosting elite guests in elegant surroundings.
Evolution Through Roman History
The Roman villa evolved from a simple rural farmhouse into a luxurious country estate, reflecting the expansion of wealth and social status among the Roman elite. In contrast, the castrum originated as a fortified military camp designed for strategic defense and control during Roman conquests. Over time, some castra developed into permanent settlements, influencing urban planning, while villas remained centers of agricultural production and leisure, showcasing the dual facets of Roman life.
Legacy and Influence on Modern Architecture
The villa, originating as a luxurious rural estate in ancient Rome, significantly influenced modern residential architecture through its emphasis on comfort, symmetry, and integration with nature, inspiring the design of contemporary suburban homes and estates. The castrum, a fortified Roman military camp, contributed to the development of urban planning principles, showcasing systematic layouts with grid-like street patterns still evident in modern city design. Both structures reflect Roman ingenuity, shaping principles of spatial organization, security, and aesthetics that persist in modern architectural and urban planning practices.
Key Differences Between Villa and Castrum
A villa was a country residence primarily used for agricultural production and leisure, characterized by residential buildings and farming facilities, often owned by wealthy Roman elites. In contrast, a castrum was a fortified military camp designed for defense and housing soldiers, featuring walls, ramparts, and a grid layout for organization. The villa emphasized domestic comfort and economic activity, while the castrum focused on strategic military function and protection.
villa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com