Exploring the concept of aliens unveils intriguing possibilities about life beyond Earth and challenges our understanding of the universe. Scientific research and popular culture have fueled curiosity about extraterrestrial beings, making it a captivating topic for many. Dive into the rest of the article to discover fascinating insights about alien life and its implications for Your worldview.
Table of Comparison
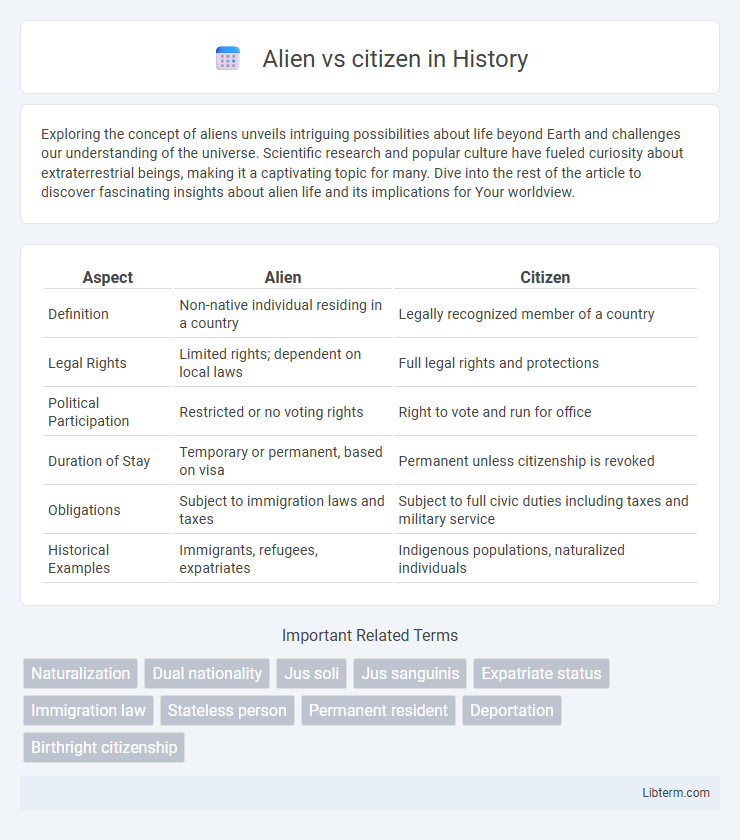
| Aspect | Alien | Citizen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-native individual residing in a country | Legally recognized member of a country |
| Legal Rights | Limited rights; dependent on local laws | Full legal rights and protections |
| Political Participation | Restricted or no voting rights | Right to vote and run for office |
| Duration of Stay | Temporary or permanent, based on visa | Permanent unless citizenship is revoked |
| Obligations | Subject to immigration laws and taxes | Subject to full civic duties including taxes and military service |
| Historical Examples | Immigrants, refugees, expatriates | Indigenous populations, naturalized individuals |
Definition of Alien vs Citizen
An alien refers to a person who is not a legal resident or citizen of a country and lacks certain rights and privileges granted to citizens, such as voting or holding public office. Citizens hold legal membership in a state, providing them with full rights, protections under the law, and responsibilities such as paying taxes and serving on juries. The distinction between alien and citizen is crucial for determining legal status, access to social benefits, and national identity.
Historical Context of Citizenship
The historical context of citizenship reveals a complex evolution from ancient city-states to modern nation-states, where distinctions between aliens and citizens became legally significant. Citizenship historically conferred rights, privileges, and responsibilities exclusive to members of a political community, while aliens remained outsiders subject to different regulations. Legal frameworks such as Roman law and later constitutional doctrines shaped the differentiation, influencing contemporary immigration and naturalization policies worldwide.
Legal Rights of Citizens vs Aliens
Citizens possess full constitutional rights, including voting rights, eligibility for federal employment, and protection under all federal laws, while aliens--both lawful permanent residents and non-immigrants--have limited rights that vary by immigration status. Legal protections for aliens include due process and equal protection under the law, but they lack certain privileges, such as voting and eligibility for specific government benefits. Enforcement of immigration laws can restrict aliens' rights more narrowly compared to citizens, particularly regarding detention, deportation, and access to social services.
Pathways to Citizenship
Pathways to citizenship for aliens typically include naturalization through lawful permanent residency, marriage to a U.S. citizen, or military service under the Immigration and Nationality Act. Eligibility requirements involve continuous residence, good moral character, and passing English language and civics tests. Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) recipients and asylum seekers may also pursue legal status adjustments leading to eventual citizenship.
Responsibilities and Duties: Citizen vs Alien
Citizens hold responsibilities such as voting in elections, serving on juries, and paying taxes to support government functions and community services. Aliens, or non-citizens, are generally required to obey local laws, pay taxes, and may have restrictions on voting or holding public office. Both citizens and aliens contribute to societal well-being through adherence to laws and financial obligations, but full civic duties and privileges are reserved mainly for citizens.
Voting Rights and Political Participation
Voting rights for aliens vary significantly across countries, with most democracies restricting electoral participation to citizens only, thereby limiting political influence for non-citizens. Some local jurisdictions in countries like the United States and New Zealand allow non-citizen residents to vote in municipal elections, enhancing their political engagement at the community level. Political participation among aliens often includes activism, advocacy, and involvement in non-governmental organizations to influence policies affecting immigrant populations despite restricted formal voting rights.
Social Integration and Identity
Alien status often challenges social integration by limiting access to citizenship rights and social benefits, affecting an individual's sense of belonging within the host society. Identity struggles emerge as non-citizens navigate cultural, legal, and social boundaries, balancing their original cultural identity with pressures to assimilate. Effective social integration policies promote inclusion and recognition of diverse identities, fostering a cohesive society where both aliens and citizens can coexist with mutual respect.
Economic Opportunities and Restrictions
Aliens often face limitations in accessing economic opportunities due to work permit requirements and restricted eligibility for government jobs, while citizens typically enjoy unrestricted access to the labor market and social benefits. Economic restrictions on aliens can include limitations on property ownership, business licensing, and participation in certain industries deemed strategic or sensitive. Citizens benefit from preferential treatment in employment, entrepreneurship, and social welfare programs, enhancing their economic stability and growth prospects.
Challenges Faced by Aliens
Aliens often face significant challenges such as legal barriers to employment, limited access to social services, and cultural integration difficulties. Language barriers and unfamiliarity with local customs can exacerbate feelings of isolation and hinder social acceptance. Navigating complex immigration laws and potential discrimination further complicates their ability to fully participate in society.
Impacts on Society and Policy
The distinction between alien and citizen status significantly influences social cohesion and access to resources, shaping public attitudes and community interactions. Policies regulating immigration, residency rights, and legal protections directly affect economic opportunities, healthcare access, and political participation for aliens, thereby affecting societal equity. Governments implement laws balancing national security with human rights, impacting social integration and shaping future demographic trends.
Alien Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com