Case law serves as a critical foundation in the legal system, guiding judicial decisions through precedents set by higher courts. Understanding how case law evolves and influences statutory interpretation can significantly impact your approach to legal challenges. Explore the rest of the article to discover how case law shapes legal outcomes and affects your rights.
Table of Comparison
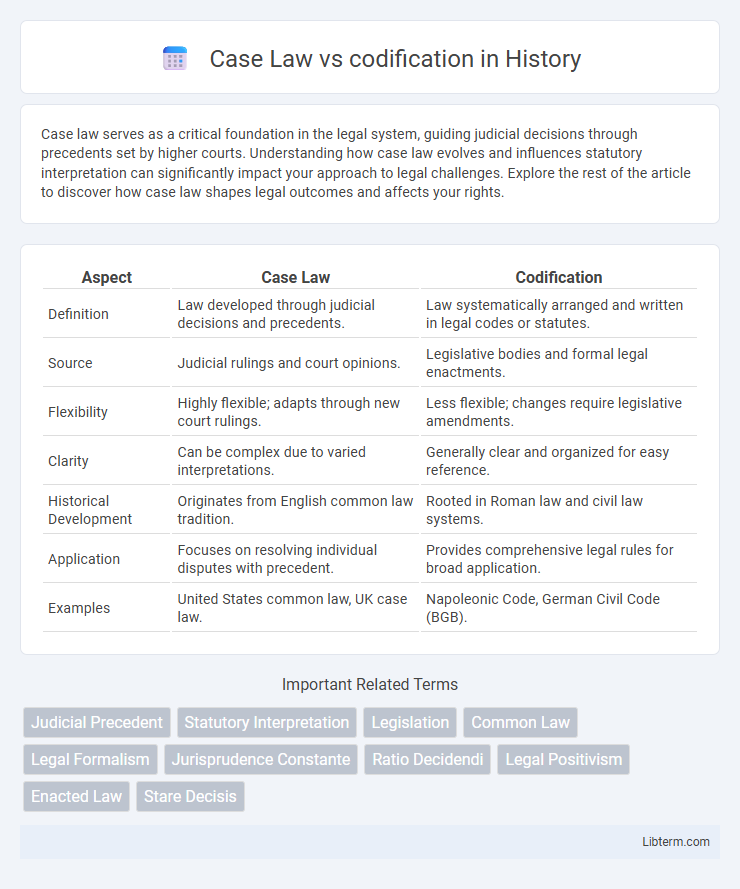
| Aspect | Case Law | Codification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law developed through judicial decisions and precedents. | Law systematically arranged and written in legal codes or statutes. |
| Source | Judicial rulings and court opinions. | Legislative bodies and formal legal enactments. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; adapts through new court rulings. | Less flexible; changes require legislative amendments. |
| Clarity | Can be complex due to varied interpretations. | Generally clear and organized for easy reference. |
| Historical Development | Originates from English common law tradition. | Rooted in Roman law and civil law systems. |
| Application | Focuses on resolving individual disputes with precedent. | Provides comprehensive legal rules for broad application. |
| Examples | United States common law, UK case law. | Napoleonic Code, German Civil Code (BGB). |
Introduction to Case Law and Codification
Case law, also known as judicial precedent, arises from decisions made by courts which interpret and apply legal principles to individual cases, creating binding rules for future cases. Codification involves the systematic compilation and organization of laws into comprehensive codes, providing a structured and accessible source of written legal rules. Understanding the distinction between case law's evolving nature and codification's fixed statutes is fundamental to grasping the sources and application of law in common law versus civil law systems.
Historical Evolution of Case Law
The historical evolution of case law traces back to the medieval English common law system, where judges' decisions formed binding precedents that shaped the legal landscape over time. Case law developed organically through judicial rulings, allowing the law to adapt to changing social and economic conditions without the need for formal legislative action. This judicial precedent system contrasts with codification, which involves systematic compilation of laws into written codes, emphasizing predictability and uniformity.
Origins and Development of Codification
Codification originated in ancient legal systems, notably with the Code of Hammurabi and later Roman Law, where laws were systematically arranged into written statutes to ensure clarity and consistency. The development of codification gained momentum during the 18th and 19th centuries, exemplified by the Napoleonic Code, which influenced many modern civil law systems by consolidating diverse legal principles into accessible, organized codes. This systematic approach contrasts with case law, which evolves through judicial decisions and precedent rather than fixed statutory compilations.
Key Differences Between Case Law and Codification
Case law, also known as judicial precedent, is developed through court decisions and relies on past rulings to guide future judgments, emphasizing interpretation and flexibility in legal application. Codification involves the systematic collection and organization of laws into written statutes or codes, providing clear, comprehensive, and accessible legal rules established by legislative bodies. The key differences lie in case law's adaptability and reliance on judicial reasoning versus codification's stability and predictability through formalized statutes.
Advantages of Case Law Systems
Case law systems provide flexibility by allowing courts to adapt legal principles based on evolving societal values and specific case circumstances. They offer detailed legal reasoning through judicial opinions, enhancing predictability and consistency in similar future cases. The precedent-driven nature of case law supports the development of nuanced interpretations, enabling the law to respond dynamically without waiting for legislative changes.
Benefits of Codified Legal Systems
Codified legal systems provide clarity and predictability by systematically organizing laws into comprehensive codes, reducing ambiguity in legal interpretation. These systems enhance accessibility for both legal professionals and the public, facilitating consistent application and enforcement of laws across jurisdictions. Codification also promotes legal stability and uniformity, minimizing discrepancies that often arise from disparate case law decisions.
Challenges in Case Law Jurisdictions
Case law jurisdictions face challenges including unpredictability due to reliance on judicial decisions, which can lead to inconsistent rulings and legal uncertainty. The volume and complexity of precedents complicate legal research and increase litigation costs. Furthermore, evolving societal norms may outpace judicial interpretation, creating gaps that codification in civil law systems aims to address.
Limitations of Codification
Codification streamlines legal norms but often lacks flexibility to adapt to complex or unforeseen circumstances, which case law addresses through judicial interpretation. Strict adherence to codified statutes can result in rigidity, limiting the legal system's ability to evolve with societal changes and nuanced disputes. Case law supplements these limitations by providing precedent-based rulings that fill gaps and clarify ambiguities in the codified legal framework.
Hybrid Legal Systems: Merging Case Law and Codification
Hybrid legal systems integrate case law and codification to create a dynamic legal framework that balances judicial precedent with statutory clarity. Countries like South Africa and Scotland exemplify these systems, where codified laws provide foundational rules, while case law fills gaps and adapts to evolving societal needs. This merger enhances legal adaptability, offering consistent interpretations while maintaining flexibility for judicial discretion.
Future Trends in Legal Systems and Jurisprudence
Future trends in legal systems indicate a growing integration of case law and codification, enhancing adaptability and consistency in jurisprudence. AI and legal tech platforms leverage vast databases of precedents and statutory codes to predict judicial outcomes and streamline legal analysis. This convergence fosters dynamic legal frameworks that can evolve rapidly while maintaining comprehensive statutory oversight.
Case Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com