Oral tradition preserves cultural heritage by passing stories, beliefs, and customs through spoken word across generations. This method ensures that history and values remain alive even without written records. Explore the rest of the article to discover how oral tradition shapes communities and storytelling.
Table of Comparison
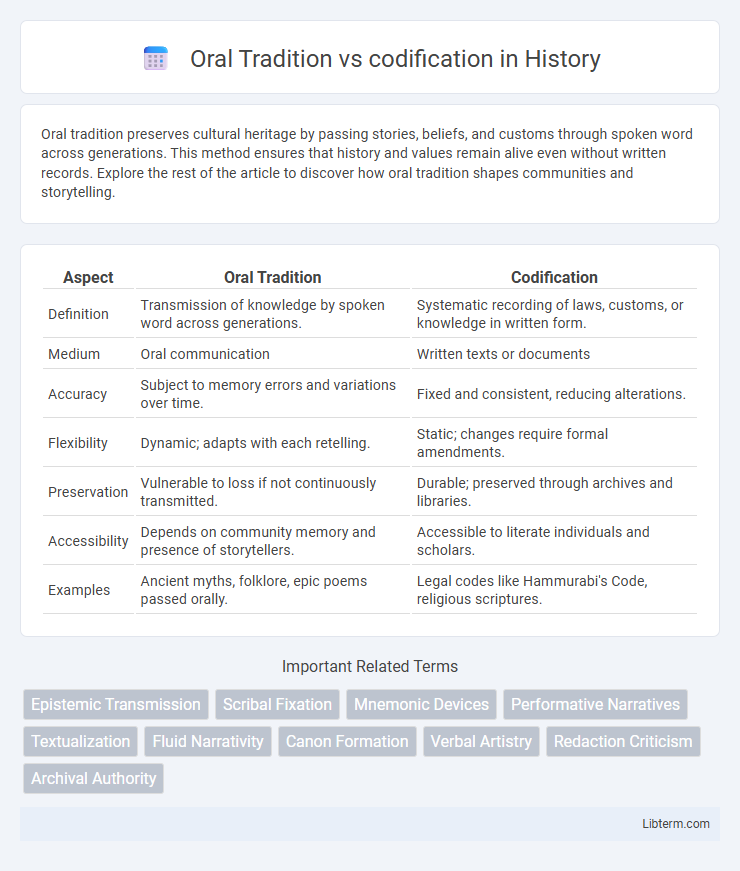
| Aspect | Oral Tradition | Codification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transmission of knowledge by spoken word across generations. | Systematic recording of laws, customs, or knowledge in written form. |
| Medium | Oral communication | Written texts or documents |
| Accuracy | Subject to memory errors and variations over time. | Fixed and consistent, reducing alterations. |
| Flexibility | Dynamic; adapts with each retelling. | Static; changes require formal amendments. |
| Preservation | Vulnerable to loss if not continuously transmitted. | Durable; preserved through archives and libraries. |
| Accessibility | Depends on community memory and presence of storytellers. | Accessible to literate individuals and scholars. |
| Examples | Ancient myths, folklore, epic poems passed orally. | Legal codes like Hammurabi's Code, religious scriptures. |
Introduction to Oral Tradition and Codification
Oral tradition serves as the earliest method of knowledge transmission, relying on spoken word and memory to preserve cultural narratives, laws, and customs across generations. Codification transforms these unwritten traditions into formal, written codes, ensuring consistency, accessibility, and legal authority in societies. This shift from oral to codified systems revolutionizes communication by establishing standardized records that support governance, education, and cultural preservation.
Historical Origins of Oral Tradition
The historical origins of oral tradition date back to prehistoric times when societies transmitted knowledge, history, and cultural values through spoken word rather than written records. Oral tradition relies on memory, storytelling, and communal participation to preserve and pass down information across generations, making it a dynamic and adaptive source of historical knowledge. In contrast to codification, which systematizes and fixes information in written form, oral tradition emphasizes fluidity and collective ownership of cultural narratives.
The Process of Codification Explained
The process of codification involves systematically organizing and recording laws, customs, or knowledge into written form, ensuring consistency and accessibility across generations. Unlike oral tradition, which relies on memorization and verbal transmission vulnerable to alteration, codification creates a fixed legal or cultural framework that can be referenced authoritatively. This transformation from fluid oral narratives to structured written codes enhances the preservation, interpretation, and enforcement of established norms in societies worldwide.
Key Differences Between Oral and Written Systems
Oral tradition relies on memory and spoken language to transmit knowledge, often evolving with each retelling, whereas codification involves fixing information in written form, enabling consistency and permanence. Oral systems emphasize communal participation and flexibility, while written systems prioritize accuracy, standardization, and long-term preservation. The key difference lies in the mode of transmission--dynamic and adaptable oral narratives versus stable, exact written records.
Advantages of Oral Tradition
Oral tradition preserves cultural heritage through storytelling, songs, and rituals, ensuring knowledge transmission across generations without reliance on written materials. This dynamic and adaptable method allows communities to modify and enrich their histories in response to social changes, fostering collective memory and identity. It also promotes communal participation and memorization skills, strengthening social bonds and enhancing the authenticity of shared experiences.
Limitations of Oral Tradition
Oral tradition faces significant limitations such as the risk of distortion and loss of information over generations due to reliance on human memory. The absence of a fixed written record makes it difficult to verify accuracy and maintain consistency in cultural narratives and laws. Furthermore, oral transmission limits the scope of dissemination, often confining knowledge to specific communities and hindering widespread accessibility.
Benefits of Codification in Modern Societies
Codification in modern societies provides legal clarity and consistency by systematically organizing laws into accessible written codes, reducing ambiguity and disputes. It enhances the enforcement of rules by offering a stable reference point for judges, lawyers, and citizens, supporting the rule of law and equal treatment under legal frameworks. Codification also facilitates legal education and reforms, allowing societies to adapt laws efficiently in response to social, economic, and technological changes.
Cultural Impact: Preserving Heritage vs Standardizing Knowledge
Oral tradition plays a vital role in preserving cultural heritage by transmitting stories, customs, and values through generations, ensuring the diversity and richness of cultural identities. Codification, on the other hand, standardizes knowledge by recording laws, beliefs, and practices in written form, which promotes consistency and broader dissemination but may limit the fluidity of cultural expression. The balance between oral tradition and codification shapes how societies retain their unique identities while adapting to evolving social frameworks.
Oral Tradition and Codification in Legal Systems
Oral tradition in legal systems relies on the transmission of laws, customs, and judicial decisions through spoken word, enabling flexibility and adaptability within communities lacking formal literacy. Codification involves systematically compiling and writing down laws into legal codes, promoting consistency, clarity, and accessibility in governance. Oral traditions often preserve cultural values and precedents, while codification institutionalizes laws for broader applicability and enforceability across diverse populations.
Future Trends: Bridging Oral and Codified Knowledge
Future trends highlight the increasing integration of oral tradition with codified knowledge through digital archiving and AI-driven transcription, preserving ephemeral narratives in accessible formats. Emerging technologies enable real-time documentation and semantic analysis of oral histories, enhancing cultural preservation and academic research. This convergence fosters a hybrid knowledge ecosystem where traditional storytelling enriches formalized databases, supporting diverse epistemologies.
Oral Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com