Landsknechts were renowned German mercenary soldiers during the 15th and 16th centuries, known for their distinctive colorful clothing and formidable combat skills with pikes and swords. Their role significantly influenced European warfare, combining aggressive tactics with a strong sense of camaraderie and discipline. Discover how the Landsknechts shaped military history and what lessons their legacy holds for your understanding of Renaissance battles in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
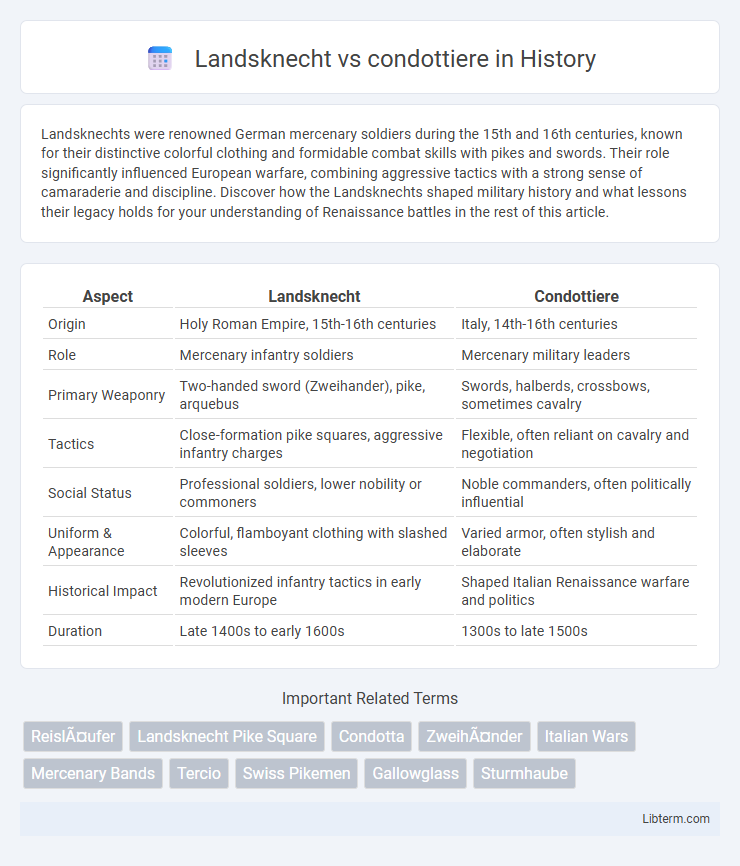
| Aspect | Landsknecht | Condottiere |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Holy Roman Empire, 15th-16th centuries | Italy, 14th-16th centuries |
| Role | Mercenary infantry soldiers | Mercenary military leaders |
| Primary Weaponry | Two-handed sword (Zweihander), pike, arquebus | Swords, halberds, crossbows, sometimes cavalry |
| Tactics | Close-formation pike squares, aggressive infantry charges | Flexible, often reliant on cavalry and negotiation |
| Social Status | Professional soldiers, lower nobility or commoners | Noble commanders, often politically influential |
| Uniform & Appearance | Colorful, flamboyant clothing with slashed sleeves | Varied armor, often stylish and elaborate |
| Historical Impact | Revolutionized infantry tactics in early modern Europe | Shaped Italian Renaissance warfare and politics |
| Duration | Late 1400s to early 1600s | 1300s to late 1500s |
Origins of the Landsknecht and Condottiere
The Landsknecht originated in late 15th-century Holy Roman Empire as highly disciplined infantry mercenaries specializing in pike and sword combat, born from the need to counter Swiss pikemen's effectiveness. The Condottiere emerged during the 14th century in Italy as leaders of mercenary bands hired by city-states, evolving from medieval knightly armies into professional soldiers under contractual agreements known as condotte. Both groups played pivotal roles in shaping Renaissance warfare but reflected distinct military traditions and political contexts within the Holy Roman Empire and Italian peninsula.
Historical Context and Emergence
Landsknechts emerged in the late 15th century as highly disciplined German mercenary infantry, primarily armed with pikes and halberds, during the Italian Wars and the broader European conflicts following the decline of medieval knight warfare. Condottieri were Italian mercenary captains who dominated the fragmented city-states of Renaissance Italy from the 14th to the 16th century, relying on cavalry and personal retinues to conduct warfare amidst political fragmentation and shifting alliances. Both groups arose from the increasing professionalization and commercialization of warfare in early modern Europe, reflecting the transition from feudal levies to contract-based armies.
Recruitment and Composition of Forces
Landsknechts were primarily recruited through state-sponsored levies and voluntary enlistment within the Holy Roman Empire, emphasizing infantry and pikemen armed with halberds and zweihander swords. Condottieri forces, on the other hand, consisted largely of professional mercenaries contracted by Italian city-states, comprising a mix of cavalry, infantry, and specialized troops tailored to contractual needs. The recruitment of Landsknechts emphasized mass infantry with standardized equipment, while condottieri relied on flexible, elite units shaped by negotiation and regional expertise.
Weapons and Armor: Comparative Analysis
Landsknechts wielded distinctive Zweihander swords and carried halberds, complemented by steel plate armor and colorful slashed garments, emphasizing both protection and intimidation. Condottieri favored lighter armor such as brigandine and helmets, prioritizing mobility while using a mix of pikes, swords, and early firearms to adapt to evolving battlefield tactics. The contrast in weaponry and armor between Landsknechts and Condottieri reflects their differing tactical roles: heavily armored, shock infantry versus agile, versatile mercenary leaders.
Tactics and Battlefield Strategies
Landsknechts employed tightly packed pike squares combined with arquebusiers to maximize defensive and offensive capabilities in open-field battles, emphasizing disciplined formations and coordinated volley fire. Condottieri favored flexible, cavalry-centered tactics with a mix of infantry and mercenary forces, utilizing terrain advantage and guerrilla-style ambushes to outmaneuver opponents. The Landsknecht's reliance on rigid, massed infantry contrasts with the condottiere's more adaptive and fluid approach to battlefield strategy.
Leadership Structure and Command
Landsknecht mercenaries operated under a hierarchical leadership structure with a colonel (Obrist) commanding regiments, supported by captains and lieutenants who led companies and squads, ensuring disciplined ranks and coordinated battlefield maneuvers. Condottieri, on the other hand, functioned as independent military contractors often heading autonomous mercenary bands under a condottiere leader who combined both strategic command and business negotiation roles, leading to a more flexible but less standardized command system. The rigid, military-style chain of command among Landsknechts contrasted with the personalized, contract-based leadership of condottieri, shaping their distinct operational effectiveness and adaptability.
Influence on Renaissance Warfare
Landsknechts, known for their disciplined pike formations and use of firearms, significantly advanced infantry tactics during Renaissance warfare, shaping European battlefields with their professional military structure. Condottieri, Italian mercenary leaders, influenced warfare through their emphasis on flexible cavalry maneuvers and strategic alliances, blending traditional chivalric combat with emerging Renaissance military innovations. Together, these forces transformed Renaissance warfare by introducing new organizational methods, tactical diversity, and increased reliance on professional soldiers.
Cultural Identity and Reputation
Landsknechts were German mercenary infantry known for their flamboyant dress and fierce loyalty, embodying the martial culture of the Holy Roman Empire during the late 15th and 16th centuries. Condottieri, Italian mercenary leaders primarily active during the Renaissance, were celebrated for their tactical ingenuity and political maneuvering within the fragmented city-states of Italy. While Landsknechts cultivated a reputation for brutality and discipline in battle, condottieri were often viewed as shrewd, adaptable commanders whose loyalty was tied to lucrative contracts rather than national identity.
Notable Battles and Campaigns
Landsknechts played a crucial role in the Battle of Pavia (1525), where their disciplined pike formations helped secure a decisive victory for the Holy Roman Empire against France. Condottieri were instrumental in the Italian Wars, particularly during the Battle of Fornovo (1495), where they commanded mercenary armies fighting for various Italian states. Both military groups shaped Renaissance warfare through their participation in key campaigns across Europe from the late 15th to early 16th centuries.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Military
Landsknechts, originating in 15th-century Germany, introduced innovative pike and musket tactics that influenced early modern European infantry formations, setting a precedent for disciplined professional armies. Condottieri, Italian mercenary leaders, shaped Renaissance warfare through their strategic use of hired troops and emphasis on cavalry and fortification techniques, impacting the evolution of military contracting and battlefield tactics. Both left lasting legacies by professionalizing military service and contributing to the transition from feudal levies to standing armies in early modern Europe.
Landsknecht Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com