A banquet is a large formal meal often held to celebrate special occasions or achievements, featuring multiple courses and elaborate settings. Banquets provide an opportunity for socializing, networking, and honoring guests with a memorable dining experience. Discover how to plan the perfect banquet to impress your guests and create lasting memories in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
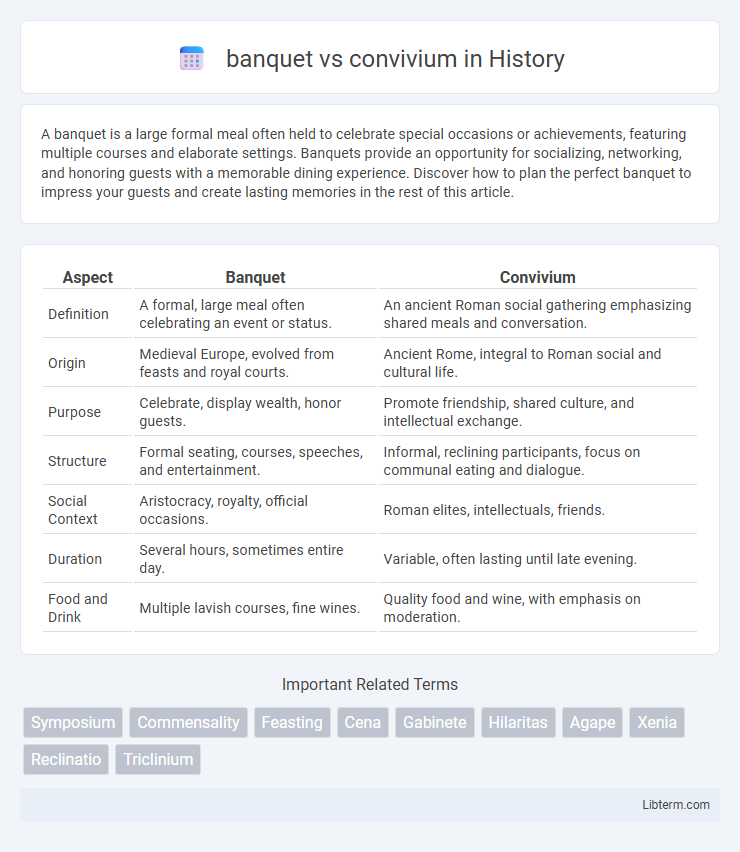
| Aspect | Banquet | Convivium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal, large meal often celebrating an event or status. | An ancient Roman social gathering emphasizing shared meals and conversation. |
| Origin | Medieval Europe, evolved from feasts and royal courts. | Ancient Rome, integral to Roman social and cultural life. |
| Purpose | Celebrate, display wealth, honor guests. | Promote friendship, shared culture, and intellectual exchange. |
| Structure | Formal seating, courses, speeches, and entertainment. | Informal, reclining participants, focus on communal eating and dialogue. |
| Social Context | Aristocracy, royalty, official occasions. | Roman elites, intellectuals, friends. |
| Duration | Several hours, sometimes entire day. | Variable, often lasting until late evening. |
| Food and Drink | Multiple lavish courses, fine wines. | Quality food and wine, with emphasis on moderation. |
Introduction to Banquet and Convivium
A banquet is a formal, lavish meal often held to celebrate significant events with multiple courses and elaborate settings emphasizing social status and ceremony. Convivium, rooted in ancient Roman tradition, refers to a more intimate and lively gathering centered on shared enjoyment, conversation, and companionship during the meal. Both concepts highlight communal dining but differ in scale, purpose, and cultural context, with banquets focusing on grandeur and convivium on social connection.
Historical Origins of Banquet and Convivium
The banquet and convivium both originated in ancient civilizations as social rituals centered around communal eating and celebration. The banquet, rooted in ancient Mesopotamian and Egyptian traditions, evolved into elaborate feasts marked by hierarchical seating and formalized courses. The convivium, emerging from Roman culture, emphasized equality, conviviality, and philosophical discourse, reflecting the Roman ideals of friendship and intellectual exchange.
Defining Banquet: Meaning and Characteristics
A banquet is a formal meal or feast characterized by a large number of guests, elaborate food presentation, and often a ceremonial or celebratory purpose. It typically involves multiple courses and is organized to honor a person, event, or occasion with an emphasis on grandeur and social hierarchy. Unlike a convivium, which emphasizes communal dining and social interaction, a banquet prioritizes structured formality and spectacle.
Understanding Convivium: Meaning and Features
Convivium, originating from Latin, refers to a social banquet emphasizing communal dining and shared experiences, distinct from a formal banquet that often centers on ceremony and hierarchy. Features of convivium include informal seating, interactive conversation, and a focus on bonding through food and drink. The concept highlights the cultural and social aspects of dining, fostering unity and genuine connection among participants.
Cultural Significance of Banquet
Banquets serve as grand ceremonial meals central to many cultures, symbolizing wealth, power, and social cohesion through elaborate rituals and formal settings. They often commemorate important events, reinforcing hierarchical structures and shared cultural values among participants. Unlike convivial conviviums, which emphasize informal socializing and communal enjoyment, banquets highlight status and tradition in their cultural significance.
Social and Cultural Importance of Convivium
Convivium, rooted in ancient Roman traditions, served as a platform for social bonding and cultural exchange, fostering a sense of community and shared identity among participants. Unlike a typical banquet, which often emphasized opulence and hierarchy, convivium prioritized egalitarian interaction, intellectual discourse, and the reinforcement of social networks. This cultural practice not only strengthened interpersonal relationships but also facilitated the transmission of values, customs, and collective memory within the society.
Key Differences Between Banquet and Convivium
A banquet is a formal, large-scale event typically organized to celebrate a specific occasion or honor guests, featuring elaborate food service and structured seating arrangements. In contrast, a convivium is an ancient Roman social gathering emphasizing communal dining, conversation, and shared enjoyment without strict formality or ceremonial aspects. Banquets prioritize ceremony and presentation, while convivia focus on social interaction and egalitarian participation around the meal.
Rituals and Traditions in Banquet vs. Convivium
Banquets traditionally feature formal rituals such as toasts, ceremonial courses, and hierarchical seating arrangements that emphasize status and protocol. Convivium, rooted in Roman customs, centers on communal sharing and interactive participation, with rituals including collective libations and informal exchanges that foster social bonding. These differing traditions highlight the banquet's structured formality versus the convivium's emphasis on egalitarian fellowship and shared experience.
Modern Adaptations of Banquet and Convivium
Modern adaptations of banquets emphasize large-scale, formal dining events featuring diverse cuisines and elaborate presentations, often incorporating technology such as digital menus and event management software to enhance guest experience. Convivium, rooted in the Roman tradition of intimate communal dinners, has evolved into smaller, interactive gatherings prioritizing social connection, shared dishes, and cultural storytelling, often seen in contemporary supper clubs and pop-up dining events. Both concepts reflect current trends in culinary arts and social dining, balancing tradition with innovation to create immersive and memorable experiences.
Conclusion: Banquet vs. Convivium in Contemporary Society
Banquet and convivium both serve as communal dining experiences, but banquets emphasize formal occasions with structured seating and elaborate menus, while convivium highlights informal, participatory meals fostering personal connections. In contemporary society, convivium aligns with modern values of inclusivity and shared creativity, promoting social bonding through collaborative food preparation and consumption. The banquet remains relevant for ceremonial events, yet convivium's flexible format better accommodates diverse cultures and evolving social dynamics.
banquet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com