Typing speed and accuracy significantly impact your productivity and communication efficiency. Mastering proper typing techniques reduces errors and strain, allowing you to work faster and more comfortably. Explore the rest of the article to discover expert tips and tools to enhance your typing skills.
Table of Comparison
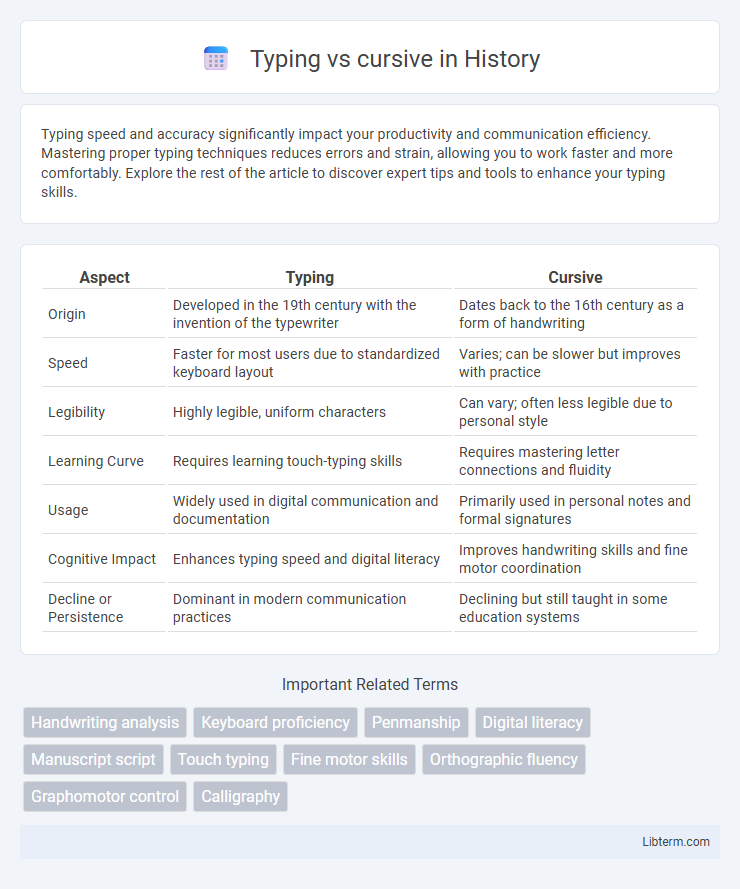
| Aspect | Typing | Cursive |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Developed in the 19th century with the invention of the typewriter | Dates back to the 16th century as a form of handwriting |
| Speed | Faster for most users due to standardized keyboard layout | Varies; can be slower but improves with practice |
| Legibility | Highly legible, uniform characters | Can vary; often less legible due to personal style |
| Learning Curve | Requires learning touch-typing skills | Requires mastering letter connections and fluidity |
| Usage | Widely used in digital communication and documentation | Primarily used in personal notes and formal signatures |
| Cognitive Impact | Enhances typing speed and digital literacy | Improves handwriting skills and fine motor coordination |
| Decline or Persistence | Dominant in modern communication practices | Declining but still taught in some education systems |
Introduction to Typing and Cursive
Typing involves using a keyboard to input text electronically, enhancing speed and accuracy in digital communication, while cursive refers to a style of penmanship where letters are joined in a flowing manner for faster writing by hand. Mastering typing skills improves efficiency in modern academic and professional environments, whereas cursive handwriting supports fine motor skills development and personal expression. Both serve distinct purposes: typing is essential for digital fluency, and cursive maintains traditional writing techniques valued in various educational curricula.
Historical Evolution of Writing Methods
The historical evolution of writing methods traces a clear transition from cursive writing, which dominated for centuries due to manual penmanship and elegant script styles, to typing as technology advanced with the invention of the typewriter in the 19th century and later the computer keyboard. Cursive served important cultural and educational roles, emphasizing personalized handwriting skills, while typing revolutionized efficiency and standardization in written communication. Modern writing practices now blend these methods, reflecting both historical legacies and digital era demands.
Cognitive Benefits of Typing vs Cursive
Typing enhances cognitive processing speed and memory recall by engaging motor skills linked to digital interfaces, fostering faster information acquisition. Cursive writing improves fine motor coordination and strengthens neural connections related to language and creativity, promoting better reading comprehension and retention. Studies show typing supports multitasking and editing efficiency, while cursive nurtures deeper cognitive engagement through sensory-motor integration.
Speed and Accuracy: Comparing Both Skills
Typing generally offers faster input speeds, with average typing rates ranging from 40 to 80 words per minute, while cursive writing typically averages between 15 to 40 words per minute. Accuracy in typing is often enhanced by tools such as spell checkers and autocorrect features, reducing errors significantly compared to cursive, which relies on manual precision and can be prone to legibility issues. Research indicates that proficiency in typing correlates with higher productivity, whereas cursive supports fine motor skills and cognitive development but lags in speed and error correction.
Impact on Learning and Memory Retention
Typing engages visual and motor skills through keyboard interaction, facilitating faster information entry but often reducing deep cognitive processing compared to cursive writing. Cursive writing activates neural pathways by requiring complex hand movements, which enhances memory retention and learning through multisensory integration. Studies show that students who practice cursive demonstrate improved comprehension and recall, linking handwriting's motor activity with stronger cognitive connections.
Relevance in Modern Education
Typing proficiency offers practical advantages in modern education due to the widespread use of digital devices and online assessments. While cursive writing supports fine motor skills and cognitive development, its relevance has diminished as keyboard skills become essential for academic and professional success. Educational curricula increasingly emphasize typing to prepare students for technology-driven learning environments and future workplaces.
Professional Applications and Requirements
Typing skills are essential in most professional environments due to the increasing reliance on digital communication, data entry, and document creation, offering speed and accuracy unmatched by cursive writing. Cursive handwriting, while less common in modern workplaces, is still valued in professions requiring personalized signatures, legal documents, and artistic or historical documentation where traditional scripts hold significance. Mastery of typing aligns with contemporary job demands, making it a critical skill for efficiency and effective digital collaboration across industries.
Handwriting Legibility and Communication
Typing produces consistently clear and legible text, enhancing communication by minimizing misinterpretation caused by poor handwriting. Cursive handwriting, while stylistically unique, often varies in legibility depending on individual skill, which can hinder quick and accurate comprehension. Advances in digital communication favor typing for its uniform readability and efficiency in conveying messages.
Technological Advancements Influencing Writing
Technological advancements have dramatically shifted writing preferences from cursive to typing, with keyboards and touchscreens enabling faster text input and easier editing. Digital tools such as word processors incorporate spell check, grammar suggestions, and autocomplete features that enhance typing accuracy and efficiency. The rise of smartphones and tablets further accelerates this transition, as typing becomes the dominant mode of writing in both personal and professional contexts.
Future of Typing and Cursive in a Digital Age
The future of typing remains dominant as digital communication and touchscreen technology continue to evolve, making keyboard skills essential for efficient information processing and online interaction. While cursive writing faces decline in everyday use, it maintains cultural and educational value by enhancing fine motor skills and reinforcing memory retention in early learning stages. Emerging digital tools integrate handwriting recognition, suggesting a complementary coexistence where cursive supports cognitive development alongside the speed of typing.
Typing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com