Military aristocracy represents a ruling class whose power is derived from military service and hereditary status, shaping governance and social hierarchy throughout history. This elite group often controls land, wealth, and political influence, maintaining authority through both martial prowess and lineage. Explore how military aristocracy has influenced societies and your understanding of historical power dynamics in the full article.
Table of Comparison
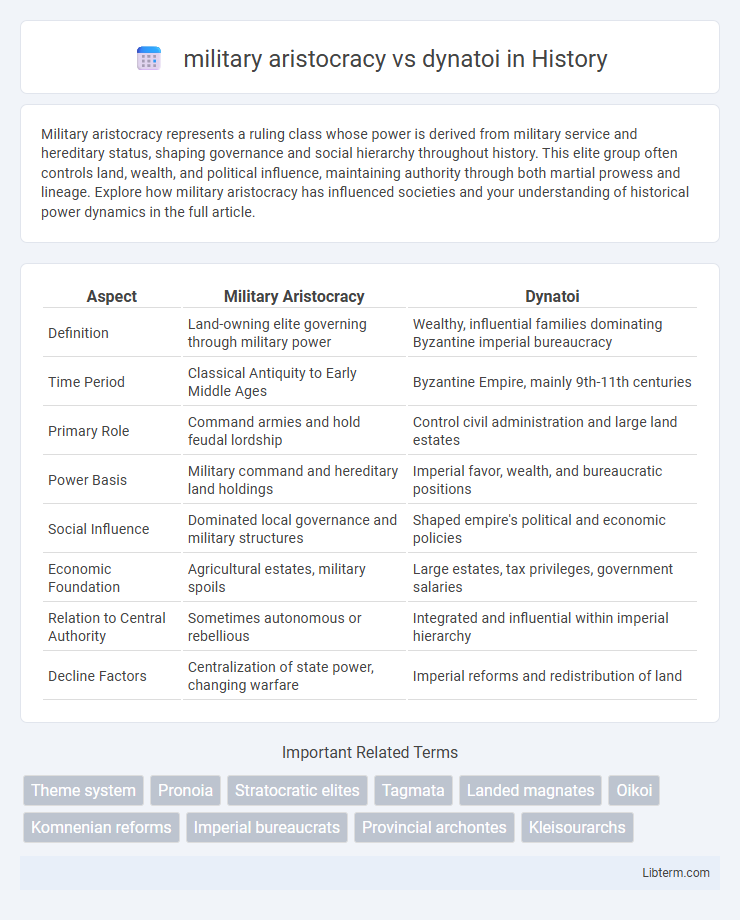
| Aspect | Military Aristocracy | Dynatoi |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Land-owning elite governing through military power | Wealthy, influential families dominating Byzantine imperial bureaucracy |
| Time Period | Classical Antiquity to Early Middle Ages | Byzantine Empire, mainly 9th-11th centuries |
| Primary Role | Command armies and hold feudal lordship | Control civil administration and large land estates |
| Power Basis | Military command and hereditary land holdings | Imperial favor, wealth, and bureaucratic positions |
| Social Influence | Dominated local governance and military structures | Shaped empire's political and economic policies |
| Economic Foundation | Agricultural estates, military spoils | Large estates, tax privileges, government salaries |
| Relation to Central Authority | Sometimes autonomous or rebellious | Integrated and influential within imperial hierarchy |
| Decline Factors | Centralization of state power, changing warfare | Imperial reforms and redistribution of land |
Understanding Military Aristocracy: Definition and Origins
Military aristocracy refers to a social class composed of hereditary warriors and landowners who held key military and political power in ancient and medieval societies. Originating in the early feudal and classical periods, this group distinguished itself through land ownership granted in exchange for military service, solidifying a ruling elite that controlled both the army and governance. Unlike the broader class of dynatoi--wealthy individuals with administrative roles--military aristocrats specifically derived authority from their martial prowess and hereditary obligations to defend the state.
Who Were the Dynatoi?: Social and Economic Profile
The Dynatoi were a class of wealthy landowners and powerful military aristocrats who emerged in the Byzantine Empire during the 10th and 11th centuries, dominating both the economic and social landscape. They held vast estates and leveraged their military roles to amass significant political influence, often overshadowing smaller landowners and local officials. Their control over land and military resources enabled them to shape imperial policies and maintain elite status within Byzantine society.
The Rise of the Military Aristocracy in Byzantine Society
The rise of the military aristocracy in Byzantine society marked a significant shift by consolidating power among the dynatoi, wealthy landowners and military elites who controlled vast estates and held key military commands. This elite class leveraged their economic resources and strategic positions to influence imperial policies and strengthen their social standing against the traditional bureaucratic aristocracy. Their increasing dominance contributed to the militarization of Byzantine politics and shaped the empire's administrative and military structures from the 9th to the 11th centuries.
Dynatoi vs Military Aristocrats: Key Differences
Dynatoi were powerful landowners in Byzantine society with significant political influence, often holding military titles but primarily wielding wealth and authority through land control. Military aristocrats, by contrast, derived their status chiefly from their roles and achievements in the army, emphasizing battlefield prowess and command over troops. While dynatoi could dominate civil administration and economy, military aristocrats focused on defense and military leadership, highlighting a key distinction between wealth-based aristocracy and merit-based military hierarchy.
Political Influence and Governance
Military aristocracy and dynatoi both wielded significant political influence in Byzantine governance, with the military aristocracy deriving power from land ownership and control of regional armies, thereby shaping imperial policies through direct military support. The dynatoi, often wealthy landowners and high-ranking officials, asserted influence by occupying key bureaucratic positions and leveraging economic resources to sway court decisions. Their roles intersected, with dynatoi sometimes evolving from military aristocracy, creating a complex power dynamic that affected administrative centralization and provincial authority.
Economic Foundations of Power
Military aristocracy derived economic power primarily from extensive landholdings and the revenues generated through serfdom, enabling them to sustain private armies and control local governance. Dynatoi, a class of wealthy landowners ascending in the Byzantine Empire, consolidated power through large estates (pronoia grants) and tax-exempt privileges, which amplified their wealth and influence over provincial administration. The economic foundations of both groups rested on agricultural surplus control and the capacity to mobilize military resources, underpinning their dominant roles in political and military hierarchies.
Military Roles and Strategic Importance
Military aristocracy, predominantly composed of hereditary nobles, held key command positions in medieval armies, leveraging their extensive landholdings to maintain private military forces and influence battlefield outcomes. The dynatoi, emerging as a class of wealthy military elites in the Byzantine Empire, integrated both administrative authority and military leadership, supporting imperial strategies with their professionalized and well-equipped troops. Their strategic importance lay in their ability to secure border regions, contribute to the empire's defense logistics, and serve as a reliable power base for imperial governance and military campaigns.
Conflicts and Rivalries Between the Groups
Military aristocracy and dynatoi often clashed over political influence and control of land in Byzantine society. The military aristocracy prioritized military power and territorial command, while the dynatoi leveraged wealth and administrative positions to consolidate authority. Rivalries intensified as both groups competed for imperial favor, undermining centralized power and contributing to internal instability.
Impact on Byzantine Stability and Decline
The military aristocracy, composed of landed elites controlling provincial armies, significantly influenced Byzantine stability by reinforcing regional power bases and defending key borders during the empire's peak. The dynatoi, powerful noble families who amassed vast estates, often undermined central authority, contributing to bureaucratic corruption and weakening imperial cohesion. This concentration of wealth and military power in aristocratic hands accelerated decline by fostering internal conflicts and reducing the effectiveness of centralized military command.
Legacy and Historical Significance
The military aristocracy established enduring legacies through their direct influence on political power and battlefield leadership during Byzantium's formative centuries. In contrast, the dynatoi wielded historical significance by consolidating wealth and land, transforming imperial administration and social hierarchies in the later Byzantine era. Both groups shaped the evolution of Byzantine governance, with the military aristocracy embodying martial dominance, while the dynatoi symbolized economic and bureaucratic authority.
military aristocracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com