Knighthood represents a historic tradition of honor, bravery, and chivalry deeply rooted in medieval culture and warfare. It embodies a code of conduct emphasizing loyalty, courage, and service to others, often celebrated through ceremonial rites and symbolic armor. Explore the rich history and cultural significance of knighthood to understand its lasting impact on society and your appreciation of noble ideals.
Table of Comparison
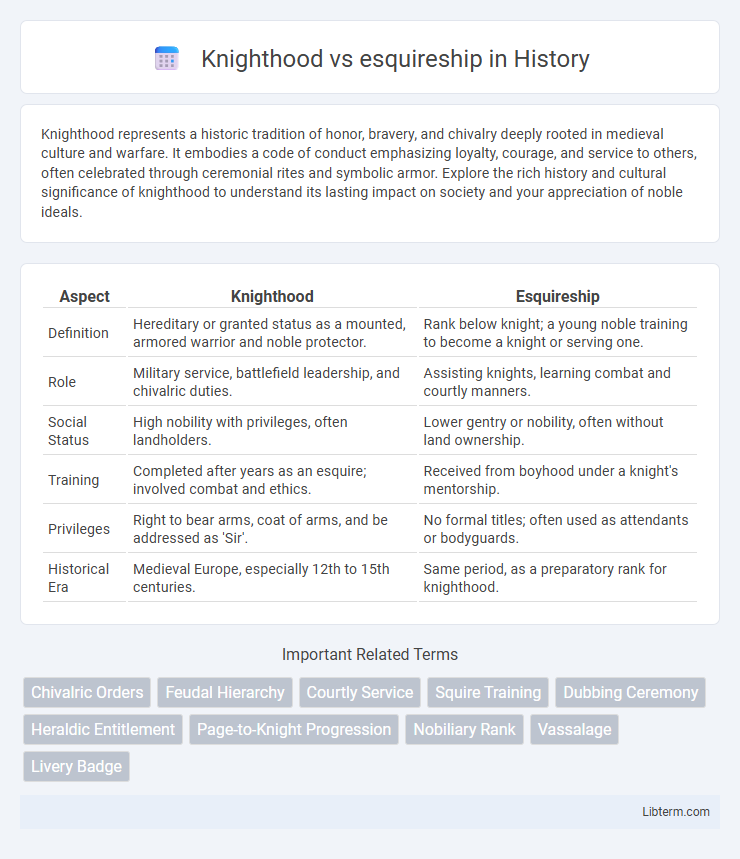
| Aspect | Knighthood | Esquireship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hereditary or granted status as a mounted, armored warrior and noble protector. | Rank below knight; a young noble training to become a knight or serving one. |
| Role | Military service, battlefield leadership, and chivalric duties. | Assisting knights, learning combat and courtly manners. |
| Social Status | High nobility with privileges, often landholders. | Lower gentry or nobility, often without land ownership. |
| Training | Completed after years as an esquire; involved combat and ethics. | Received from boyhood under a knight's mentorship. |
| Privileges | Right to bear arms, coat of arms, and be addressed as 'Sir'. | No formal titles; often used as attendants or bodyguards. |
| Historical Era | Medieval Europe, especially 12th to 15th centuries. | Same period, as a preparatory rank for knighthood. |
Defining Knighthood and Esquireship
Knighthood is a formal rank granted by a sovereign or a noble, symbolizing a warrior's valor, chivalry, and loyalty, often accompanied by ceremonial dubbing and the right to bear specific heraldic arms. Esquireship denotes a social status below knighthood, historically associated with landed gentry or attendants to knights, serving as a transitional rank preparing men for knighthood or administrative roles. The distinction between knighthood and esquireship lies in their respective roles within the feudal hierarchy, with knighthood emphasizing military service and honorable conduct, while esquireship focuses on service, landholding, and social prestige without the full martial responsibilities of a knight.
Historical Origins of Knighthood
Knighthood originated in medieval Europe during the early Middle Ages as a distinct social class of mounted warriors who served feudal lords in exchange for land or protection. Esquireship evolved as a transitional status where young noblemen trained under knights, learning combat, chivalry, and courtly manners before being formally knighted. The historical development of knighthood reflects the militarization of the European aristocracy and the codification of martial and social duties within feudal society.
The Emergence of the Esquire Title
The esquire title emerged in medieval England as a rank below knighthood, originally designating a young nobleman serving as a knight's attendant or shield-bearer. Unlike knights who earned formal recognition through ceremonial dubbing and military achievements, esquires held a social status linked to landownership, administrative duties, and potential future knighthood. The distinction between knights and esquires became crucial in hierarchical structures, influencing legal privileges, military responsibilities, and noble lineage documentation.
Roles and Responsibilities: Knight vs Esquire
Knighthood involves direct combat roles, leadership on the battlefield, and upholding chivalric codes, whereas esquireship serves as a preparatory stage focusing on training, assisting knights, and managing weapons and armor. Knights bear the responsibility of protecting the realm and leading troops, while esquires support knights by performing duties such as attending to horses and learning martial skills. The transition from esquire to knight signifies a shift from apprenticeship and service to full military and social responsibilities.
Pathways to Knighthood
Pathways to knighthood traditionally began with becoming an esquire, serving a knight or noble while learning martial skills, chivalry, and courtly manners. Training included rigorous combat practice, horsemanship, and participation in tournaments to demonstrate valor and skill. Upon proving loyalty and competence, an esquire could be ceremonially dubbed a knight, often in recognition of bravery in battle or outstanding service to a lord or monarch.
Duties and Daily Life of an Esquire
Esquires primarily assisted knights by maintaining armor, tending to horses, and serving during tournaments and battles, reflecting their role as knights-in-training. Their daily life involved rigorous physical training, weapons practice, and learning courtly manners to prepare for eventual knighthood. Administrative duties included managing the knight's equipment and serving as a retainer, ensuring readiness for both martial and noble responsibilities.
Social Status and Prestige Comparison
Knighthood represented a higher social status and greater prestige than esquireship, signifying martial valor and royal favor, often accompanied by land grants and command responsibilities. Esquires functioned as attendants to knights or nobles, holding a lower rank within the feudal hierarchy with limited rights and social influence. The distinction was marked by ceremonial roles and the exclusive privileges knights enjoyed in medieval society.
Symbols and Insignia of Each Rank
Knighthood is symbolized by the iconic suit of armor, a sword, and the ceremonial tabard bearing a coat of arms, representing valor and noble duty. Esquireship is identified by the silver belt and smaller, less ornate badges signifying their role as attendants or apprentices to knights. Both ranks use heraldic symbols, but knights display more elaborate insignia indicative of their higher social and military status.
Modern Relevance of Knighthood and Esquireship
Knighthood in modern times serves primarily as an honorary title awarded for exceptional contributions to society, often recognizing achievements in fields such as arts, science, and public service, while esquireship remains a traditional courtesy title reflecting social status with limited formal privileges. The evolution of knighthood has transformed it into a prestigious emblem of national recognition, particularly in countries like the United Kingdom where honors such as the Order of the British Empire maintain cultural significance. In contrast, esquireship today functions mainly within legal and heraldic contexts, with esquires occasionally referenced in formal address or historical documentation rather than active societal roles.
Legacy and Cultural Impact
Knighthood established a lasting legacy symbolizing valor, honor, and chivalric ideals that profoundly influenced medieval and modern cultural narratives, including literature, art, and national identity. Esquireship acted as a vital preparatory rank, shaping future knights by instilling discipline and loyalty, thus sustaining the hierarchical and social structures of the time. Together, these roles contributed to a cultural framework that celebrated martial prowess and aristocratic duty, embedding the ideals of knighthood deeply into Western heritage.
Knighthood Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com