Acculturation involves the process of cultural and psychological change that occurs when individuals or groups from different cultures come into continuous firsthand contact. This adaptation can affect language, customs, values, and social behaviors, influencing identity formation and intercultural relationships. Discover how acculturation shapes societies and impacts your experience in diverse cultural settings by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
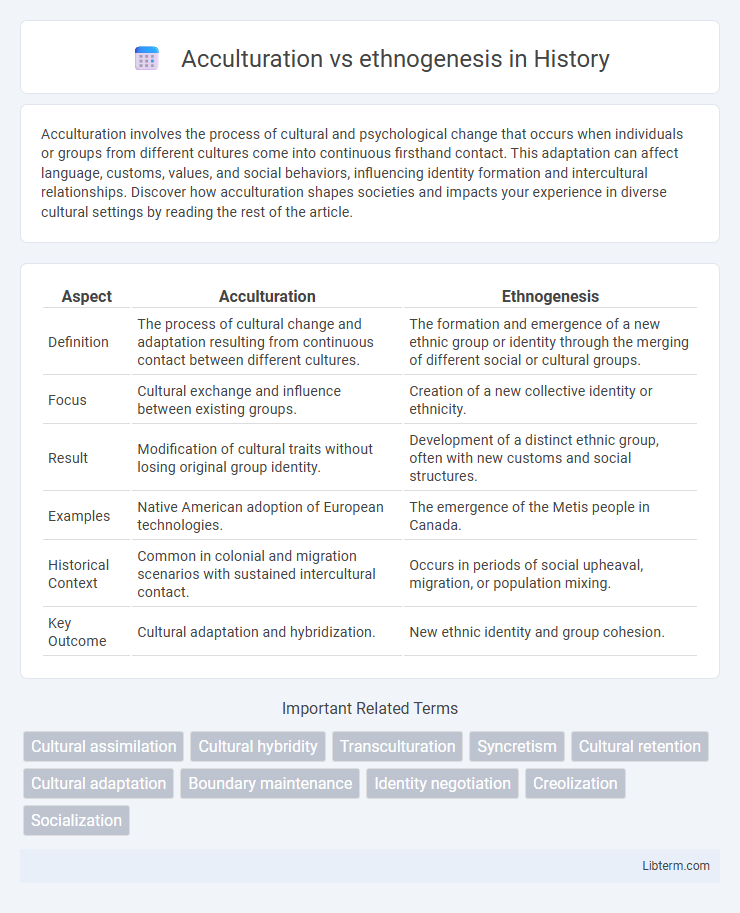
| Aspect | Acculturation | Ethnogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of cultural change and adaptation resulting from continuous contact between different cultures. | The formation and emergence of a new ethnic group or identity through the merging of different social or cultural groups. |
| Focus | Cultural exchange and influence between existing groups. | Creation of a new collective identity or ethnicity. |
| Result | Modification of cultural traits without losing original group identity. | Development of a distinct ethnic group, often with new customs and social structures. |
| Examples | Native American adoption of European technologies. | The emergence of the Metis people in Canada. |
| Historical Context | Common in colonial and migration scenarios with sustained intercultural contact. | Occurs in periods of social upheaval, migration, or population mixing. |
| Key Outcome | Cultural adaptation and hybridization. | New ethnic identity and group cohesion. |
Introduction to Acculturation and Ethnogenesis
Acculturation refers to the process through which groups adopt cultural traits or social patterns of another group, often resulting from sustained contact or interaction. Ethnogenesis is the formation and development of a new ethnic group, typically emerging when distinct populations merge or redefine their identity in response to social, political, or environmental changes. Understanding the dynamics of acculturation and ethnogenesis reveals how cultural integration and identity transformation shape social cohesion and diversity in human societies.
Defining Acculturation: Processes and Mechanisms
Acculturation involves the exchange and adaptation of cultural traits between groups through direct contact, often resulting in changes in language, customs, and social practices. Key mechanisms include assimilation, integration, separation, and marginalization, which determine the extent and direction of cultural transformation. This dynamic process shapes identity formation and social cohesion in multicultural environments.
Understanding Ethnogenesis: Origins and Development
Ethnogenesis refers to the process through which distinct ethnic groups emerge, often resulting from social, cultural, or political transformations that promote new group identities. This development involves the consolidation of shared myths, language, rituals, and historical narratives that differentiate the group from others. Unlike acculturation, which emphasizes cultural exchange and adaptation between groups, ethnogenesis centers on the creation of a unique collective identity and heritage.
Key Differences Between Acculturation and Ethnogenesis
Acculturation involves the exchange and adoption of cultural traits between groups, often leading to changes in language, customs, and social norms without creating a new ethnic identity. Ethnogenesis refers to the formation of a distinct ethnic group through shared experiences, identity, and cultural synthesis, often emerging from historical events or social transformations. Key differences lie in acculturation's emphasis on cultural adaptation and interaction, while ethnogenesis centers on the creation of new group identity and collective ethnicity.
Historical Examples of Acculturation
The historical examples of acculturation include the Roman Empire's assimilation of diverse cultures across Europe, where local customs blended with Roman law, language, and architecture, creating a unified cultural identity. Similarly, the spread of Islam through the Middle East and North Africa exemplifies acculturation, as indigenous populations adopted Islamic religious practices while retaining pre-existing social structures. The Columbian Exchange also represents acculturation, with European settlers and indigenous peoples exchanging agricultural products, technologies, and cultural traditions, resulting in profound societal transformations.
Case Studies Highlighting Ethnogenesis
Case studies highlighting ethnogenesis reveal how distinct cultural identities emerge through dynamic processes rather than mere assimilation. The Metis of Canada exemplify ethnogenesis as a distinct group formed from European and Indigenous ancestry, blending languages, customs, and social structures that differ from their parent cultures. Similarly, the Garifuna people of Central America illustrate ethnogenesis by developing a unique Afro-Indigenous identity through the fusion of African, Carib, and Arawak cultural elements following the forced migration and social upheavals of colonialism.
Sociocultural Factors Influencing Acculturation
Sociocultural factors influencing acculturation include language proficiency, social networks, and cultural attitudes that shape individuals' adaptation to a new cultural environment. The presence of supportive community institutions and intercultural contact also plays a critical role in facilitating or hindering acculturation processes. These factors interact dynamically, affecting the degree to which immigrants retain original cultural identities or integrate new cultural elements, often contrasting with the formation of new ethnic identities in ethnogenesis.
The Role of Identity in Ethnogenesis
The role of identity in ethnogenesis centers on the dynamic process through which groups construct and assert a distinct social and cultural self-definition, often in response to external pressures or internal transformations. Identity functions as a core element in ethnogenesis by providing symbolic markers, shared narratives, and collective memory that differentiate emerging ethnic groups from others. This contrasts with acculturation, where cultural exchange may alter practices without necessarily producing a new ethnic identity.
Impacts on Minority and Indigenous Populations
Acculturation often leads to the gradual assimilation of minority and indigenous populations, resulting in loss of cultural practices and languages. In contrast, ethnogenesis fosters the creation of new cultural identities that can empower these groups by reinforcing social cohesion and resilience. Both processes impact community continuity, with acculturation risking cultural erosion while ethnogenesis promotes cultural adaptation and survival.
Contemporary Relevance: Acculturation vs Ethnogenesis
Acculturation involves the process of cultural exchange and adaptation between groups, often resulting in shifts in language, customs, and social practices, which is crucial in understanding migration dynamics and multicultural integration today. Ethnogenesis refers to the formation and development of new ethnic identities, highlighting how groups redefine themselves in response to social, political, and historical changes, a phenomenon evident in contemporary diasporas and indigenous movements. Both concepts illuminate the ongoing evolution of identity and cultural boundaries in a globalized world marked by increased interaction and hybridization.
Acculturation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com