Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and scripts, essential for interpreting historical documents and understanding cultural contexts. Experts analyze letter forms, materials, and writing styles to date manuscripts and authenticate their origins. Explore the article to discover how paleography unlocks the secrets of the past through deciphering old texts.
Table of Comparison
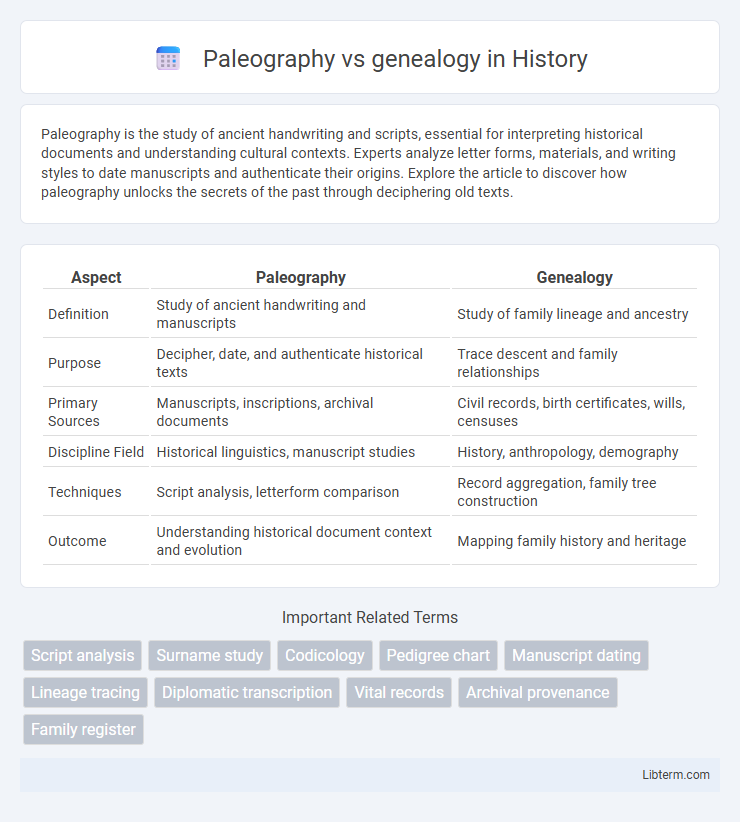
| Aspect | Paleography | Genealogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of ancient handwriting and manuscripts | Study of family lineage and ancestry |
| Purpose | Decipher, date, and authenticate historical texts | Trace descent and family relationships |
| Primary Sources | Manuscripts, inscriptions, archival documents | Civil records, birth certificates, wills, censuses |
| Discipline Field | Historical linguistics, manuscript studies | History, anthropology, demography |
| Techniques | Script analysis, letterform comparison | Record aggregation, family tree construction |
| Outcome | Understanding historical document context and evolution | Mapping family history and heritage |
Understanding Paleography and Genealogy
Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and scripts, essential for accurately interpreting historical documents, while genealogy involves researching family histories and lineage based on records such as birth, marriage, and death certificates. Mastery of paleography enhances genealogical research by enabling the deciphering of old manuscripts, church registers, or census records, which are often written in challenging scripts or archaic language. Understanding both disciplines allows researchers to construct accurate family trees and comprehend historical contexts, preserving ancestral heritage through documented evidence.
The Origins of Paleography
The origins of paleography trace back to ancient civilizations where the need to decipher and interpret historical manuscripts emerged, particularly in Egypt and Mesopotamia, enabling scholars to understand early writing systems like cuneiform and hieroglyphics. Paleography focuses on the study of ancient handwriting, scripts, and inscriptions to date and authenticate documents, whereas genealogy centers on tracing family lineages and ancestral relationships through historical records. Understanding the development of paleography enhances the analysis of historical documents critical to both historical research and genealogical investigations.
Defining Genealogy: Tracing Family Histories
Genealogy involves tracing family histories by systematically researching lineage and ancestral records to establish relationships and heritage over generations. It relies heavily on documents such as birth certificates, marriage licenses, census data, and oral histories to construct detailed family trees and uncover historical contexts. Paleography, by contrast, specializes in analyzing ancient handwriting and manuscripts to interpret historical documents, which often aids genealogists in deciphering old records crucial for accurate family history research.
Key Differences Between Paleography and Genealogy
Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and manuscript analysis, focusing on deciphering, dating, and authenticating historical documents. Genealogy centers on tracing family lineage and ancestry through records such as birth certificates, censuses, and oral histories. The key difference lies in paleography's emphasis on document interpretation and script evolution, whereas genealogy prioritizes constructing family histories and understanding hereditary connections.
How Paleography Supports Genealogical Research
Paleography enhances genealogical research by enabling the accurate reading and interpretation of ancient manuscripts, such as birth, marriage, and death records, which are often written in old or unfamiliar scripts. Understanding handwriting styles, abbreviations, and historical writing conventions allows genealogists to extract precise data from archival documents that may otherwise be illegible. This skill bridges gaps in family histories by unlocking original sources crucial for verifying lineage and constructing accurate genealogies.
Essential Skills for Paleographers and Genealogists
Paleographers require essential skills such as deciphering ancient scripts, understanding historical languages, and analyzing manuscripts to accurately interpret historical texts. Genealogists must excel in researching archival records, verifying lineage through vital records, and utilizing DNA analysis to construct accurate family trees. Both disciplines demand meticulous attention to detail, critical thinking, and proficiency in historical research methods for accurate documentation and interpretation.
Common Tools Used in Paleography vs Genealogy
Paleography primarily uses tools such as magnifying glasses, ultraviolet lights, and digital imaging software to analyze ancient manuscripts and handwriting styles. Genealogy relies more on databases, archival records, DNA testing kits, and online family tree platforms to trace lineage and ancestral connections. Both disciplines utilize specialized software, but paleography emphasizes document examination while genealogy focuses on data aggregation and lineage mapping.
Challenges Faced in Paleography and Genealogy
Paleography challenges include deciphering ancient handwriting styles that vary by region and era, often impaired by document deterioration and inconsistent spelling conventions. Genealogy faces difficulties in verifying lineage due to incomplete records, common names, and migration that obscure familial connections. Both fields require meticulous cross-referencing of historical data to overcome ambiguities and reconstruct accurate historical narratives.
Real-World Applications of Paleography and Genealogy
Paleography enables researchers to analyze historical manuscripts, decipher ancient scripts, and authenticate documents for academic and legal purposes. Genealogy allows individuals to trace family lineages, construct detailed family trees, and uncover inherited medical conditions through DNA analysis and archival records. Both disciplines contribute to historical research, with paleography providing the tools to read original documents and genealogy applying that information to map ancestral connections.
Integrating Paleography and Genealogy for Deep Research
Integrating paleography and genealogy enhances deep research by combining the analysis of ancient handwriting with family history reconstruction, enabling accurate interpretation of historical documents. Paleographic expertise facilitates deciphering and dating manuscripts, while genealogy contextualizes this information within familial lineages, enriching the understanding of ancestral connections. This interdisciplinary approach uncovers hidden clues in archival records, transforming fragmented data into comprehensive narratives.
Paleography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com