Cooperative businesses thrive on collective decision-making and shared responsibilities, fostering a sense of community and mutual benefit among members. These organizations prioritize member needs over profits, ensuring equitable distribution and sustainable growth. Explore the full article to discover how your involvement in a cooperative can create lasting positive impact.
Table of Comparison
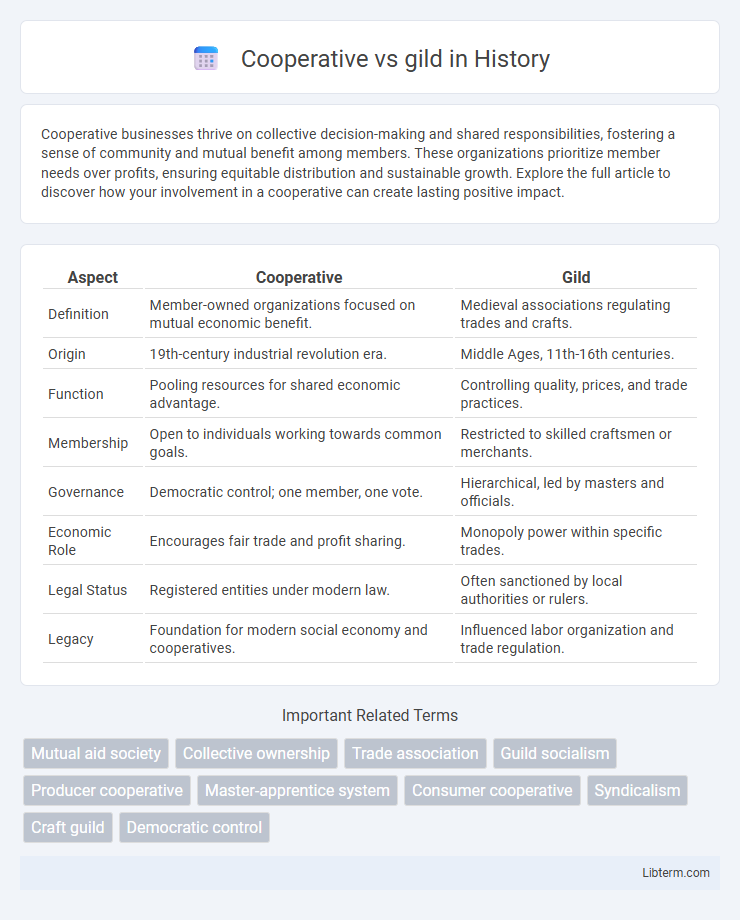
| Aspect | Cooperative | Gild |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Member-owned organizations focused on mutual economic benefit. | Medieval associations regulating trades and crafts. |
| Origin | 19th-century industrial revolution era. | Middle Ages, 11th-16th centuries. |
| Function | Pooling resources for shared economic advantage. | Controlling quality, prices, and trade practices. |
| Membership | Open to individuals working towards common goals. | Restricted to skilled craftsmen or merchants. |
| Governance | Democratic control; one member, one vote. | Hierarchical, led by masters and officials. |
| Economic Role | Encourages fair trade and profit sharing. | Monopoly power within specific trades. |
| Legal Status | Registered entities under modern law. | Often sanctioned by local authorities or rulers. |
| Legacy | Foundation for modern social economy and cooperatives. | Influenced labor organization and trade regulation. |
Introduction to Cooperative and Guild Models
Cooperatives are member-owned organizations that prioritize collective decision-making and profit-sharing among all participants, often focused on serving the members' common economic, social, or cultural needs. Guilds, historically rooted in medieval craft and trade groups, function as associations of professionals or artisans who regulate standards, skills, and market access within their specific industry. Both models emphasize collaboration, but cooperatives center on democratic ownership while guilds focus on maintaining quality and professional standards.
Defining Cooperatives: Key Features and Principles
Cooperatives are member-owned organizations emphasizing democratic control, economic participation, and mutual benefit, contrasting with traditional guilds that historically regulated trade practices and maintained professional standards. Key principles of cooperatives include voluntary and open membership, member economic participation, autonomy, independence, education, cooperation among cooperatives, and concern for community. These features promote equitable decision-making, shared profits, and community-oriented goals, differentiating cooperatives from the exclusive, often hierarchical nature of guilds.
Understanding Guilds: Origins and Structure
Guilds originated in medieval Europe as associations of artisans or merchants who regulated production, maintained quality standards, and protected mutual economic interests within specific trades. Their hierarchical structure typically included apprentices, journeymen, and masters, providing a clear path for skill development and market control. Unlike cooperatives, which emphasize democratic member control and profit sharing, guilds functioned more as exclusive bodies enforcing trade regulations and professional standards.
Historical Context: Evolution of Cooperatives and Guilds
Cooperatives and guilds both emerged in medieval Europe, but cooperatives evolved as member-owned organizations promoting economic democracy and mutual aid, whereas guilds were exclusive associations regulating trades, maintaining quality, and controlling market entry. The cooperative movement gained momentum in the 19th century during the Industrial Revolution, addressing worker exploitation and fostering collective ownership, while guilds declined due to industrialization and the rise of free-market capitalism. Historical records highlight cooperatives' emphasis on egalitarian governance, contrasting with guilds' hierarchical structure and monopoly control over crafts and trade practices.
Membership and Governance Differences
Cooperatives operate with open membership, allowing anyone who meets the criteria to join and participate in decision-making through a one-member, one-vote system that ensures democratic governance. Guilds, in contrast, restrict membership to skilled practitioners of a specific trade or craft and often feature hierarchical governance structures led by masters or elected officers. The cooperative model emphasizes equal ownership and collective control, while guilds prioritize skill levels and apprenticeship progression within their governance framework.
Economic Impact: Cooperatives vs Guilds
Cooperatives generate economic impact by promoting shared ownership and democratic decision-making, leading to equitable profit distribution and community wealth building. Guilds historically controlled trade practices and maintained quality standards, imposing restrictions that limited market competition and innovation. The cooperative model fosters inclusive growth and resilience, whereas guilds often reinforced monopolistic behaviors, affecting economic dynamism differently.
Community Engagement and Social Responsibility
Cooperatives emphasize democratic member participation, fostering deep community engagement by allowing members to influence decisions and share benefits equitably. Guilds historically served as trade unions protecting craftsmen's interests but maintained hierarchical structures limiting broader community involvement. Social responsibility in cooperatives is embedded through collective ownership and sustainable practices, while guilds prioritized skill preservation and economic control within specific crafts.
Challenges Faced by Cooperatives and Guilds
Cooperatives face challenges such as member coordination difficulties, limited access to capital, and governance issues due to diverse stakeholder interests. Guilds often struggle with maintaining exclusivity while adapting to changing industry standards and technology, leading to resistance to innovation. Both entities encounter hurdles in balancing tradition with modernization to sustain relevance and growth.
Modern Applications and Case Studies
Cooperatives emphasize member ownership and democratic control, making them effective in modern sectors like agriculture, renewable energy, and shared services where community benefits are prioritized. Guilds, historically centered on skill preservation and quality standards, are reemerging in digital economies through professional networks and freelancer associations that regulate access and maintain expertise quality. Case studies in platform cooperatives showcase how cooperative models foster equitable profit distribution and user participation, while modern guild-inspired groups support niche craftsmanship and knowledge exchange in specialized industries.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right model between a cooperative and a guild depends on factors such as member ownership, governance structure, and purpose. Cooperatives emphasize democratic control and profit-sharing among members, making them ideal for businesses prioritizing equitable participation and economic benefits. Guilds focus on skill development, standards enforcement, and professional networking, suitable for trades or crafts seeking collective expertise and quality assurance.
Cooperative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com