Union plays a vital role in fostering collective strength and ensuring workers' rights are protected in the workplace. It enables employees to negotiate better wages, benefits, and working conditions through collective bargaining. Discover how unions can impact your professional life by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
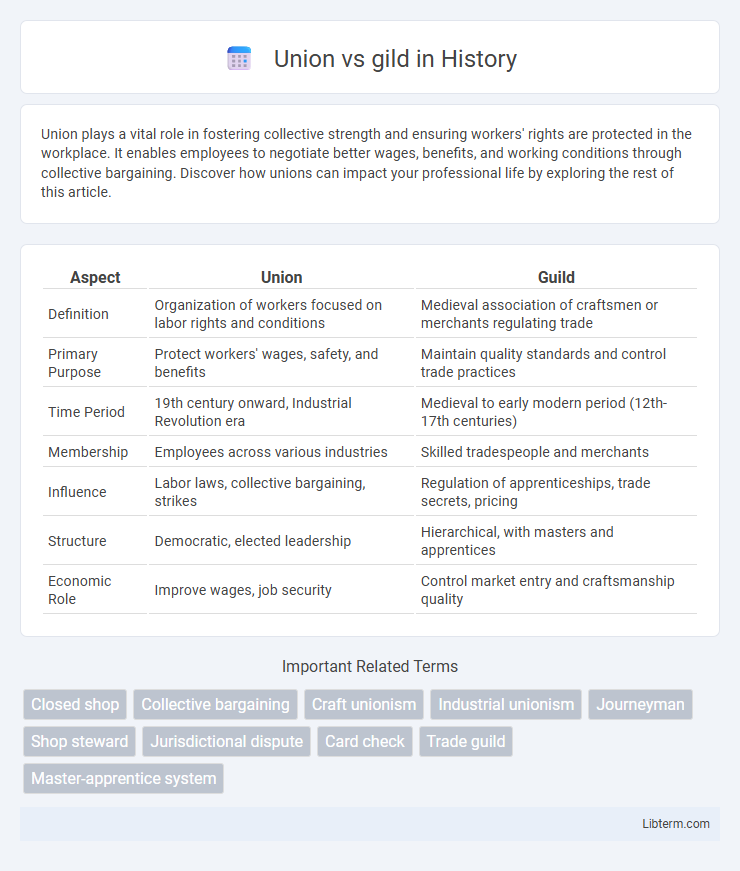
| Aspect | Union | Guild |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organization of workers focused on labor rights and conditions | Medieval association of craftsmen or merchants regulating trade |
| Primary Purpose | Protect workers' wages, safety, and benefits | Maintain quality standards and control trade practices |
| Time Period | 19th century onward, Industrial Revolution era | Medieval to early modern period (12th-17th centuries) |
| Membership | Employees across various industries | Skilled tradespeople and merchants |
| Influence | Labor laws, collective bargaining, strikes | Regulation of apprenticeships, trade secrets, pricing |
| Structure | Democratic, elected leadership | Hierarchical, with masters and apprentices |
| Economic Role | Improve wages, job security | Control market entry and craftsmanship quality |
Understanding Unions and Guilds: Definitions and Core Concepts
Unions are organizations formed by workers to protect their rights, improve wages, and secure better working conditions through collective bargaining. Guilds, historically rooted in medieval Europe, are associations of artisans or merchants that regulate trade standards, provide training, and preserve quality in specific crafts. Both entities emphasize collective action, but unions primarily address labor rights across industries, while guilds focus on maintaining professional standards within specialized trades.
Historical Evolution of Unions and Guilds
Unions and guilds both originated as forms of collective worker organization, with guilds emerging in medieval Europe to regulate trades, maintain quality, and protect members' economic interests within specific crafts. Unions evolved later, particularly during the Industrial Revolution, as a response to the rise of factory labor and the need to address broader worker rights, wages, and working conditions across industries. The historical shift from guilds to unions reflects changing economic structures, from artisanal and localized production to industrial and mass employment.
Structure and Organization: How Unions and Guilds Operate
Unions operate through a hierarchical structure with elected representatives, collective bargaining units, and local chapters that coordinate labor negotiations and member services. Guilds typically function as specialized professional organizations with a focus on maintaining industry standards, offering certification, and protecting craft-specific knowledge. Both structures emphasize member representation but differ in scope, with unions addressing broad labor rights and wages while guilds prioritize skill development and professional ethics.
Membership Criteria: Joining a Union vs Joining a Guild
Unions generally require employees to work in a specific industry or occupation and often mandate dues payment as a condition of membership, focusing on collective bargaining rights and labor protections. Guilds typically emphasize professional skill, craftsmanship, or trade mastery, requiring demonstration of expertise or apprenticeship completion for admission. The membership criteria for unions prioritize workplace representation, while guilds center on professional standards and skill validation.
Representation and Advocacy Roles
Unions serve as organized labor groups that negotiate collective bargaining agreements to enhance wages, benefits, and working conditions for their members. Guilds primarily represent skilled professionals, focusing on maintaining standards, offering training, and protecting the craft's integrity. While unions emphasize broad worker rights advocacy, guilds prioritize professional development and artistic freedom within specific trades.
Economic Impacts: Wages, Benefits, and Job Security
Unionized workers typically experience higher wages, improved benefits, and greater job security compared to non-unionized counterparts, due to collective bargaining power that secures better compensation packages and workplace protections. Gilds, as historical craft organizations, influenced economic impacts by controlling trade standards and apprenticeship systems, thereby stabilizing wages and ensuring skill-based job security within specific trades. The economic influence of unions expands across industries by reducing wage disparities and enhancing employment stability, whereas gilds primarily affected localized trades with a focus on maintaining economic exclusivity and quality control.
Legal Framework: Rights and Regulations
Unions operate under federal laws such as the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), which grants employees the right to organize, bargain collectively, and engage in concerted activities for mutual aid. Gilds, historically more informal and guild-like associations, often lacked consistent legal recognition and specific regulations protecting member rights. Modern labor law frameworks prioritize unions, providing structured mechanisms for dispute resolution, collective bargaining agreements, and protections against employer retaliation.
Influence in Modern Industries
Unions have significantly shaped labor standards and collective bargaining processes in modern industries, ensuring fair wages and improved working conditions. Gilds, as historical precursors, laid the foundational framework for worker organization and skill regulation that influences today's trade unions and professional associations. The legacy of both unions and gilds persists in modern corporate governance and labor law, impacting productivity, employee rights, and industry standards globally.
Key Differences and Similarities
Unions and guilds both serve as organizations that protect workers' rights and improve labor conditions, yet unions typically represent a wide range of industries, while guilds focus on specific trades or crafts. Both entities negotiate wages, ensure workplace safety, and provide collective bargaining power, but guilds often maintain stricter membership criteria and oversee skill standards within their craft. Despite differences, both unions and guilds share the core objective of advocating for their members' economic and professional interests.
Choosing Between a Union or Guild: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a union and a guild depends on factors such as the industry, scope of representation, and specific member benefits. Unions typically represent a broader range of workers focusing on collective bargaining, job security, and wages, while guilds often emphasize professional standards, networking, and artistic interests within creative fields. Evaluating workplace priorities, career goals, and the support services offered can guide individuals toward the most suitable affiliation.
Union Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com