Hermeticism, rooted in ancient Greek and Egyptian traditions, explores the mystical teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, focusing on spiritual transformation and the interconnectedness of the universe. This esoteric philosophy emphasizes principles such as mental alchemy, the correspondence between microcosm and macrocosm, and the pursuit of hidden knowledge to achieve enlightenment. Discover how Hermetic wisdom can deepen your understanding of reality and guide your inner journey by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
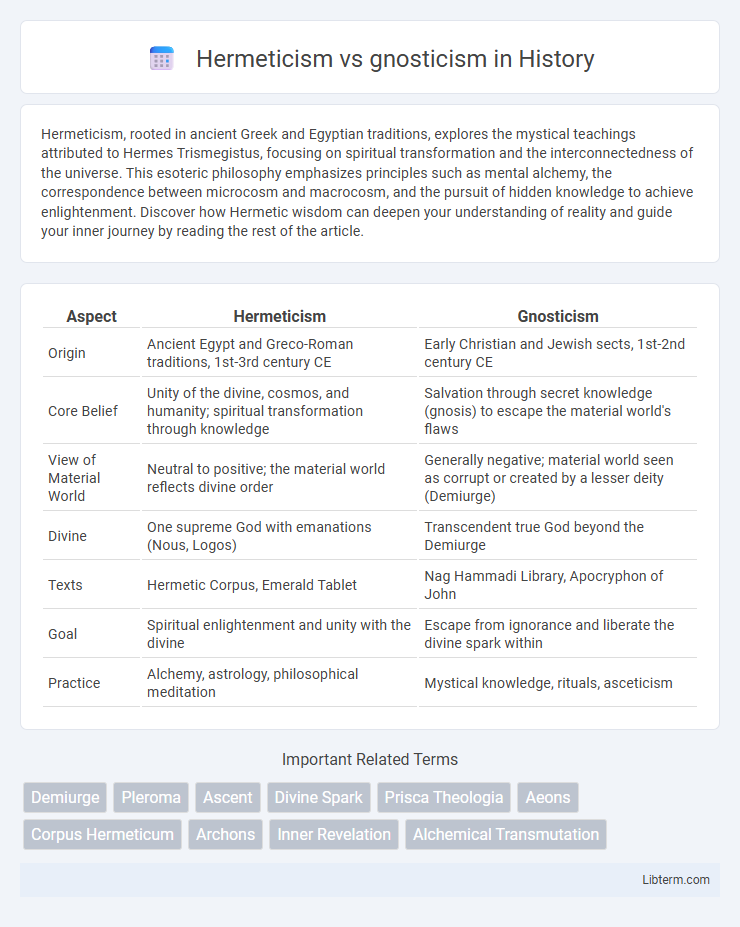
| Aspect | Hermeticism | Gnosticism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Egypt and Greco-Roman traditions, 1st-3rd century CE | Early Christian and Jewish sects, 1st-2nd century CE |
| Core Belief | Unity of the divine, cosmos, and humanity; spiritual transformation through knowledge | Salvation through secret knowledge (gnosis) to escape the material world's flaws |
| View of Material World | Neutral to positive; the material world reflects divine order | Generally negative; material world seen as corrupt or created by a lesser deity (Demiurge) |
| Divine | One supreme God with emanations (Nous, Logos) | Transcendent true God beyond the Demiurge |
| Texts | Hermetic Corpus, Emerald Tablet | Nag Hammadi Library, Apocryphon of John |
| Goal | Spiritual enlightenment and unity with the divine | Escape from ignorance and liberate the divine spark within |
| Practice | Alchemy, astrology, philosophical meditation | Mystical knowledge, rituals, asceticism |
Introduction to Hermeticism and Gnosticism
Hermeticism is a philosophical and spiritual tradition based on writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, emphasizing the pursuit of divine knowledge (gnosis), alchemy, astrology, and the unity of the cosmos. Gnosticism is an ancient religious movement characterized by the belief in secret knowledge for salvation, a distinction between a supreme, unknowable God and a demiurge creator responsible for the material world. Both traditions explore metaphysical dualism and the quest for spiritual enlightenment but differ in cosmology and the nature of the divine.
Historical Origins and Development
Hermeticism emerged in the early centuries of the Common Era, rooted in Greco-Egyptian syncretism and attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, blending elements of Hellenistic philosophy, Egyptian religion, and Platonic thought. Gnosticism developed contemporaneously in the 1st and 2nd centuries CE as a diverse set of religious movements emphasizing secret knowledge (gnosis) for salvation, influenced by Jewish, Christian, and Hellenistic traditions. Both systems evolved through interactions with early Christian communities and mystical traditions, shaping esoteric doctrines and mystical cosmologies in late antiquity.
Core Beliefs and Philosophical Foundations
Hermeticism centers on the pursuit of divine knowledge through the teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, emphasizing the unity of the cosmos, the principle of "as above, so below," and the transformation of the soul. Gnosticism focuses on the dualistic struggle between the material world, created by a lesser deity called the Demiurge, and the spiritual realm, highlighting salvation through secret gnosis and inner enlightenment. Both systems value esoteric wisdom but diverge in their cosmology, with Hermeticism promoting cosmic harmony and Gnosticism stressing liberation from material ignorance.
Concept of Divinity and the Divine
Hermeticism presents divinity as a singular, transcendent source often identified with the All or the One, emphasizing the soul's potential to reunite with this divine essence through knowledge and spiritual practice. Gnosticism delineates divinity into a complex hierarchy, distinguishing the true, ineffable God from the flawed creator demiurge, with salvation achieved by awakening to secret knowledge (gnosis) that reconnects the divine spark within humans to the higher God. Both systems explore the divine nature through esoteric wisdom but diverge in their ontology, with Hermeticism stressing unity and Gnosticism focusing on dualism and cosmic differentiation.
Cosmology: Structure of the Universe
Hermeticism and Gnosticism both present complex cosmologies with layered universe structures but differ in their cosmic hierarchy and divine emanations. Hermetic cosmology describes a harmonious, interconnected cosmos emanating from the One, where divine intellects and spiritual spheres govern matter and spirit integration. Gnostic cosmology centers on a flawed material world created by a lesser deity, the Demiurge, with salvation achieved through gnosis to transcend the ignorance binding the soul to the physical realm.
Human Nature and Spiritual Purpose
Hermeticism views human nature as a divine spark trapped within the material world, emphasizing the pursuit of gnosis to achieve spiritual rebirth and unity with the All. Gnosticism asserts that human beings possess a hidden divine essence imprisoned by a flawed creator, stressing salvation through secret knowledge to transcend the material realm. Both traditions prioritize inner enlightenment but differ in cosmology and the nature of the divine human self.
Knowledge and Salvation Pathways
Hermeticism emphasizes gnosis through inner alchemical transformation and divine revelation, promoting self-knowledge as the path to spiritual ascent and unity with the divine mind. Gnosticism centers on salvific knowledge (gnosis) that reveals the soul's entrapment in the material world, with salvation achieved by awakening to hidden truths and transcending the demiurge's cosmic prison. Both traditions prioritize esoteric wisdom but diverge in cosmology and the metaphysical nature of salvation, where Hermeticism aligns with cosmic harmony and Gnosticism with liberation from material corruption.
Rituals, Practices, and Texts
Hermeticism centers on alchemical rituals, meditation, and the study of the Hermetic Corpus, with a focus on cosmic unity and divine knowledge. Gnosticism emphasizes secret knowledge (gnosis) attained through rituals like baptism, sacramental meals, and visionary practices recorded in texts such as the Nag Hammadi library. Both traditions utilize esoteric scriptures and rituals to transcend material existence, but Hermeticism often integrates astrology and magic, whereas Gnosticism prioritizes spiritual dualism and liberation from the material world.
Influence on Western Esotericism
Hermeticism and Gnosticism profoundly shaped Western Esotericism, with Hermeticism emphasizing divine knowledge through the teachings of Hermes Trismegistus, influencing Renaissance magic and alchemical traditions. Gnosticism introduced dualistic cosmology and the concept of hidden spiritual knowledge (gnosis), impacting Christian mysticism and occult philosophies. Both systems contributed to the development of mystical, alchemical, and philosophical currents central to Western esoteric thought.
Comparative Summary and Modern Relevance
Hermeticism emphasizes the unity of all existence and the pursuit of spiritual knowledge through divine revelation, while Gnosticism centers on dualism and the belief in secret knowledge to escape material ignorance. Both systems influence contemporary esoteric practices, with Hermeticism shaping Western occult traditions and Gnosticism impacting modern spiritual movements that question institutional religion. Their teachings continue to resonate in modern metaphysical philosophy, alternative spirituality, and psychological interpretations of self-awareness.
Hermeticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com