Hetaerae were highly educated and cultured women in ancient Greece who played influential roles in social and intellectual circles. Unlike ordinary women of their time, hetaerae enjoyed greater freedom and were known for their wit, artistry, and companionship in symposiums. Discover more about the fascinating lives and societal impact of hetaerae in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
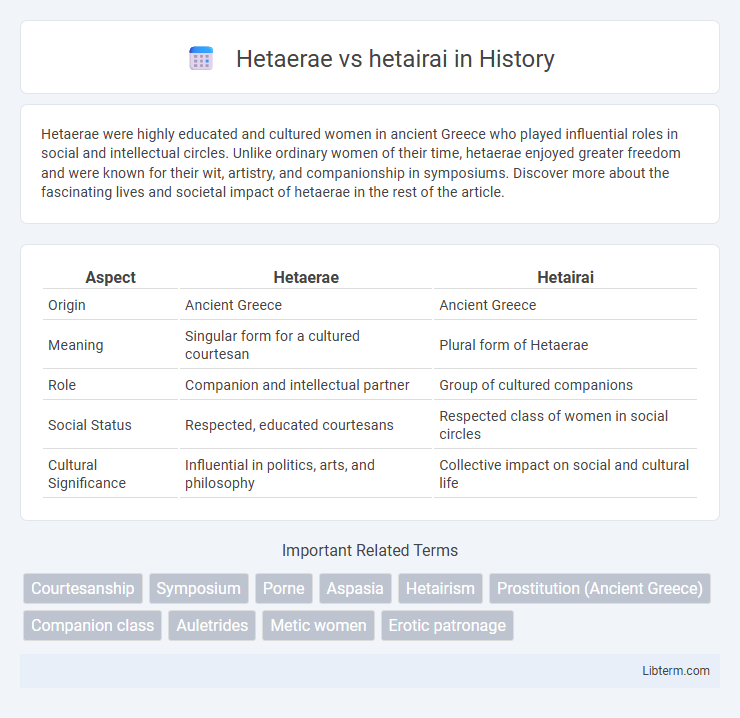
| Aspect | Hetaerae | Hetairai |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Greece | Ancient Greece |
| Meaning | Singular form for a cultured courtesan | Plural form of Hetaerae |
| Role | Companion and intellectual partner | Group of cultured companions |
| Social Status | Respected, educated courtesans | Respected class of women in social circles |
| Cultural Significance | Influential in politics, arts, and philosophy | Collective impact on social and cultural life |
Understanding the Terms: Hetaerae and Hetairai
Hetaerae and hetairai both refer to ancient Greek companion women but represent nuanced distinctions in language and context. Hetaerae is the Latinized plural form commonly used in scholarly texts, while hetairai is the original Greek plural, emphasizing the cultural and linguistic origins of these courtesans. These women were educated and influential, distinct from common prostitutes, serving as intellectual and social companions in classical Greek society.
Historical Context of Hetaerae and Hetairai
Hetaerae and hetairai both refer to courtesans in ancient Greek society, distinguished by their role and social status within historical context. Hetaerae were educated companions who participated in intellectual and social life, often attending symposia and influencing political discourse, while hetairai generally encompassed a broader range of female entertainers and companions. The distinction reflects the complex social dynamics of classical Greece, where hetaerae held a unique position blending companionship, cultural engagement, and economic independence.
Linguistic Differences: Hetaerae vs Hetairai
The terms "Hetaerae" and "Hetairai" both originate from the ancient Greek word etairai, referring to courtesans or companions, but differ primarily in their linguistic and transliteration conventions. "Hetaerae" is the traditional Latinized plural form often used in English texts, aligning with classical scholarship and older publications, while "Hetairai" reflects a more direct transliteration from the Greek plural, capturing modern academic preferences for phonetic accuracy. The distinction between these forms highlights the evolution of classical terminology through cultural transmission and scholarly interpretation in historical linguistics.
Social Roles of Hetaerae in Ancient Greece
Hetaerae, also known as hetairai, were elite companion courtesans in ancient Greece who played complex social roles beyond mere prostitution. They were educated, skilled in conversation, music, and arts, often participating in symposia alongside elite men, offering intellectual companionship and influencing political and cultural discussions. Unlike common prostitutes, hetaerae enjoyed a degree of social freedom, autonomy, and respect, acting as influential figures in Athenian society.
Cultural Significance of Hetairai
Hetairai were highly influential companion courtesans in ancient Greece, distinguished by their education, wit, and artistic talents, which set them apart from common prostitutes. Their cultural significance extended beyond physical companionship, as they often participated in intellectual discussions, symposia, and political circles, shaping social and cultural dynamics. Unlike Hetaerae, a general term sometimes misused, hetairai specifically embodied a respected social role that bridged entertainment and intellectual engagement in classical Greek society.
Key Distinctions Between Hetaerae and Hetairai
Hetaerae and hetairai both refer to ancient Greek courtesans but differ primarily in linguistic and cultural contexts, with "hetaerae" being the Latinized plural of the Greek "hetairai." Hetairai were highly educated companions in classical Athens, known for their intellectual and artistic skills, distinct from common prostitutes. The key distinction lies in the social and linguistic usage: "hetaerae" is a term used in Roman texts referencing these Greek figures, while "hetairai" specifically denotes the original Greek class of elite courtesans.
Misconceptions and Modern Interpretations
Hetaerae and hetairai are often confused due to their similar origins in ancient Greek society, but hetaerae referred specifically to high-status courtesans who were educated and influential, while hetairai is simply the plural form of hetaera. Modern interpretations frequently misrepresent hetaerae as mere prostitutes, overlooking their roles as intellectual companions and cultural participants in symposia and politics. Misconceptions stem from later historical biases and incomplete translations, which have blurred the nuanced social functions these women held in classical antiquity.
Influence on Art and Literature
Hetaerae and hetairai, both ancient Greek courtesans, significantly influenced art and literature by embodying ideals of beauty, intellect, and social power. Hetaerae were often portrayed in classical poetry and sculpture as symbols of elegance and wit, inspiring works by playwrights such as Aristophanes and poets like Anacreon. The hetairai's role in symposia and cultural gatherings enriched philosophical dialogues and theatrical themes, shaping the portrayal of women in classical Greek art and literary tradition.
Notable Figures Among Hetaerae and Hetairai
Notable figures among hetaerae and hetairai include Aspasia of Miletus, renowned for her intellect and association with Pericles, and Phryne, celebrated for her beauty and artistic patronage in ancient Athens. These courtesans often influenced politics, philosophy, and culture, with Hetairai like Lais of Corinth gaining fame for their wit and social connections. Their unique role in Greek society highlights the convergence of companionship, education, and influence beyond mere entertainment.
Lasting Legacy in Contemporary Culture
The terms Hetaerae and Hetairai, rooted in Ancient Greek society, refer to courtesans who combined companionship with intellectual influence, leaving a lasting legacy in contemporary culture through their depiction in art, literature, and feminist discourse. Modern interpretations highlight their role in challenging traditional gender norms and shaping early concepts of female agency and sexuality. Their nuanced portrayal continues to inspire discussions on autonomy and the complexity of social roles in historical and cultural studies.
Hetaerae Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com