Fealty refers to the sworn loyalty and allegiance a vassal owes to their lord, often in the context of medieval feudal systems. Understanding fealty helps you grasp the foundations of political and social relationships in historical societies. Explore the rest of this article to uncover the nuances and significance of fealty across time.
Table of Comparison
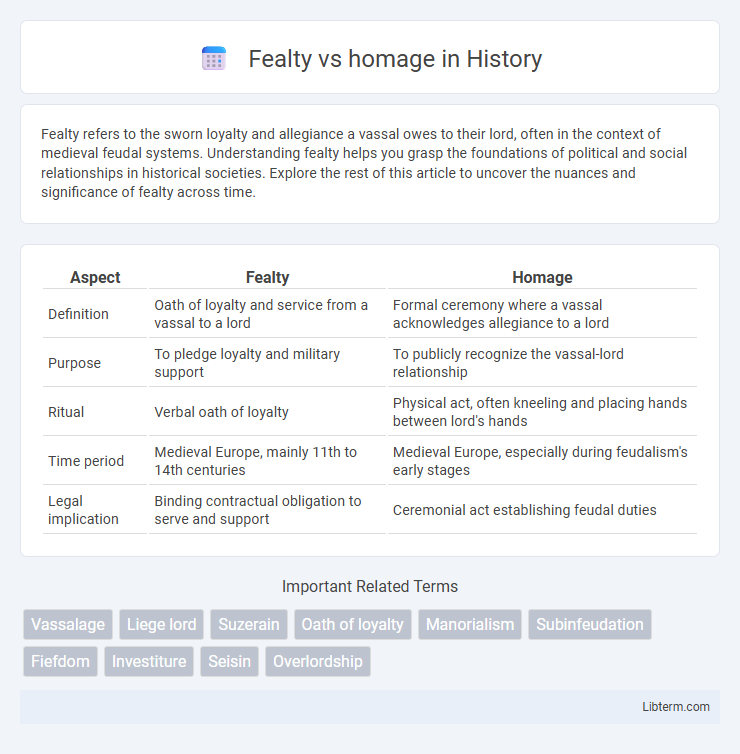
| Aspect | Fealty | Homage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oath of loyalty and service from a vassal to a lord | Formal ceremony where a vassal acknowledges allegiance to a lord |
| Purpose | To pledge loyalty and military support | To publicly recognize the vassal-lord relationship |
| Ritual | Verbal oath of loyalty | Physical act, often kneeling and placing hands between lord's hands |
| Time period | Medieval Europe, mainly 11th to 14th centuries | Medieval Europe, especially during feudalism's early stages |
| Legal implication | Binding contractual obligation to serve and support | Ceremonial act establishing feudal duties |
Understanding Fealty and Homage: Definitions
Fealty refers to a sworn loyalty or fidelity, typically a vassal's pledge of allegiance and service to a lord in a feudal system, emphasizing personal loyalty and military support. Homage is a formal ceremony in which a vassal publicly acknowledges the lord's authority and accepts the obligations of the relationship, symbolizing mutual respect and legal commitment. Both fealty and homage constitute foundational elements of medieval feudal bonds, defining the social structure and hierarchical duties between lords and vassals.
Historical Origins of Fealty and Homage
Fealty and homage originated in the medieval feudal system as mechanisms to establish loyalty and duty between a vassal and a lord. Fealty involved a sworn oath of allegiance emphasizing the vassal's duty of faithfulness, while homage was a ceremonial act symbolizing the vassal's submission and recognition of the lord's authority. Both customs emerged in early medieval Europe, particularly during the Carolingian Empire, shaping the socio-political hierarchy of the Middle Ages.
Key Differences Between Fealty and Homage
Fealty is a sworn loyalty to a lord, often involving a formal oath and promise of military support, whereas homage is a broader act of respect and acknowledgment of a lord's authority, typically performed through a ceremonial gesture. Fealty usually entails specific obligations such as service and protection, while homage emphasizes the personal bond and recognition of the lord-vassal relationship. The key difference lies in fealty's contractual nature with explicit duties versus homage's symbolic expression of allegiance and honor.
The Role of Fealty in Medieval Society
Fealty in medieval society primarily functioned as a sworn loyalty oath between a vassal and their lord, symbolizing a personal bond that obligated military service, counsel, and support. Unlike homage, which was a ceremonial acknowledgment of lordship involving physical acts like kneeling, fealty emphasized ongoing fidelity and trust integral to the feudal hierarchy. This pledge reinforced social structure by ensuring mutual responsibilities that maintained stability and governance within the medieval manorial system.
How Homage Shaped Feudal Relationships
Homage established a formal, public ceremony in medieval feudal society where vassals pledged loyalty and service to their lords, directly influencing fealty by embedding personal loyalty and mutual obligations within the feudal hierarchy. This ritual created binding social and legal ties that shaped the development of fealty as a more explicit and enduring oath of allegiance. Consequently, homage reinforced the structural foundation of feudal relationships, making fealty not just a duty but a solemn promise crucial for maintaining political stability and land tenure.
Legal and Social Implications of Fealty
Fealty, a sworn loyalty to a lord, established a legally binding relationship in medieval feudal law, often involving military service or counsel as obligations enforceable by court. Socially, fealty reinforced hierarchical structures, solidifying vassal-lord bonds and ensuring political stability through mutual responsibilities and protection. Unlike homage, which symbolized personal allegiance through public ceremony, fealty's legal implications included formal oaths that could be invoked in disputes or succession issues, highlighting its role in maintaining order within feudal societies.
Rituals and Ceremonies: Homage in Practice
Homage rituals involved a vassal kneeling before the lord, clasping hands in a symbolic gesture known as "the oath of fealty," signifying their personal loyalty and submission. The ceremony often included the vassal swearing an oath of allegiance while publicly acknowledging the lord's authority, accompanied by ceremonial acts such as kissing the lord's hand or boots. These formalized ceremonies reinforced the hierarchical relationship and legal obligations, distinguishing homage as a public affirmation of feudal bonds beyond the private promises of fealty.
Fealty vs Homage: Evolving Meanings Over Time
Fealty and homage both originated as medieval expressions of loyalty, with fealty signifying a sworn oath of fidelity by a vassal to a lord, emphasizing personal loyalty and military service. Homage initially involved a public ceremony where a vassal acknowledged the lord's sovereignty, symbolizing a deeper social and political bond beyond mere service. Over time, fealty evolved into a general pledge of allegiance, while homage's significance diminished, reflecting shifts in feudal structure and legal interpretations.
Fealty and Homage in Literature and Culture
Fealty in literature often symbolizes unwavering loyalty and servitude, reflecting medieval societal hierarchies and knightly codes of honor, while homage represents a public acknowledgment of allegiance and respect, frequently dramatized in ceremonial contexts. Fealty's portrayal emphasizes personal bonds between vassal and lord, highlighting themes of trust and duty in cultural narratives. Homage, on the other hand, is utilized in literary and cultural works to illustrate social structures and power dynamics through ritualized expressions of fealty and submission.
Modern Interpretations of Fealty and Homage
Modern interpretations of fealty emphasize loyalty and service within legal and organizational structures rather than medieval ceremonial bonds, reflecting contractual obligations in corporate and political contexts. Homage today is often symbolized through acts of allegiance or respect toward leaders or institutions, preserving its historical connotation of personal loyalty but adapted to contemporary diplomatic or cultural practices. Both concepts underscore the evolving nature of allegiance, blending tradition with modern notions of duty and respect in governance and social hierarchies.
Fealty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com