Homage, tribute, allegiance, fealty, and obeisance each represent different expressions of respect or loyalty, ranging from formal loyalty to a sovereign to gestures of deep respect or submission. Understanding the nuances between these terms can clarify historical texts or social customs where these types of honor play a crucial role. Discover how these distinctions impact your interpretation of loyalty and respect by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
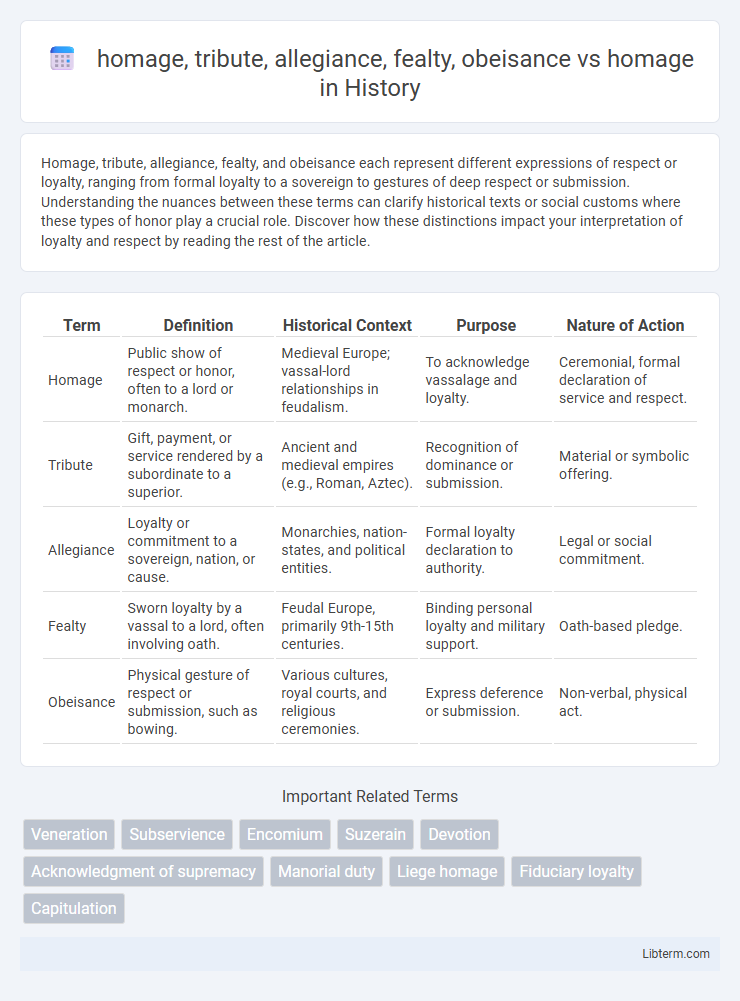
| Term | Definition | Historical Context | Purpose | Nature of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homage | Public show of respect or honor, often to a lord or monarch. | Medieval Europe; vassal-lord relationships in feudalism. | To acknowledge vassalage and loyalty. | Ceremonial, formal declaration of service and respect. |
| Tribute | Gift, payment, or service rendered by a subordinate to a superior. | Ancient and medieval empires (e.g., Roman, Aztec). | Recognition of dominance or submission. | Material or symbolic offering. |
| Allegiance | Loyalty or commitment to a sovereign, nation, or cause. | Monarchies, nation-states, and political entities. | Formal loyalty declaration to authority. | Legal or social commitment. |
| Fealty | Sworn loyalty by a vassal to a lord, often involving oath. | Feudal Europe, primarily 9th-15th centuries. | Binding personal loyalty and military support. | Oath-based pledge. |
| Obeisance | Physical gesture of respect or submission, such as bowing. | Various cultures, royal courts, and religious ceremonies. | Express deference or submission. | Non-verbal, physical act. |
Understanding Homage: A Historical Perspective
Homage historically refers to the formal public acknowledgment of allegiance or fealty by a vassal to a lord during the medieval feudal system, symbolizing loyalty and service. Tribute denotes payments or gifts given by a subordinate party to a superior as acknowledgment of dependence or submission. Obeisance involves physical gestures of respect or deference, while allegiance and fealty emphasize solemn loyalty and binding oaths to a sovereign or lord.
Defining Tribute: Expressions of Respect and Honor
Tribute represents intentional acts or statements conveying respect and honor towards a person, group, or idea, often serving as formal recognition of admiration or reverence. It differs from homage, which encompasses ceremonial or feudal acknowledgment of allegiance or fealty, primarily in a structured or hierarchical context. Obeisance and allegiance denote gestures or commitments signifying loyalty and submission, whereas tribute emphasizes expressive, sometimes artistic or symbolic, celebrations honoring the valued subject.
Allegiance Explained: Loyalty to Authority or Cause
Allegiance signifies a profound loyalty or commitment to a sovereign, nation, or cause, often formalized through oaths or pledges, underpinning political and social order. Unlike homage, which emphasizes public respect or honor typically toward a ruler or noble, allegiance carries a binding obligation of fidelity and support, crucial in contexts of governance and citizenship. Fealty and obeisance, related but distinct, focus respectively on sworn loyalty in feudal systems and ritualistic gestures of respect, while tribute denotes material offerings acknowledging subordination or alliance.
Fealty: Origins and Evolution of Sworn Loyalty
Fealty originated in the medieval feudal system as a solemn oath of loyalty sworn by a vassal to their lord, signifying a commitment to mutual defense and service. Unlike general homage or tribute, fealty involved a formalized, personal bond reinforced by ritualistic ceremonies, often including the symbolic act of kneeling or clasping hands. Over time, fealty evolved from a pragmatic military alliance into a broader expression of allegiance and political loyalty, influencing modern concepts of oath-taking and fiduciary responsibility.
Obeisance: Physical Demonstrations of Deference
Obeisance involves physical demonstrations of deference such as bowing, kneeling, or curtsying, symbolizing respect and submission to authority or tradition. Unlike homage or fealty, which emphasize verbal declarations of loyalty or service, obeisance primarily conveys allegiance through bodily gestures that communicate honor and recognition. This form of respect is deeply rooted in cultural and historical practices, reinforcing social hierarchies and relational dynamics through observable acts.
Homage vs. Tribute: Key Semantic Differences
Homage denotes a formal acknowledgment of respect or loyalty, often associated with feudal or ceremonial contexts, emphasizing personal allegiance and submission. Tribute refers to a payment, gift, or act made to show gratitude, respect, or submission, typically highlighting a material or symbolic offering rather than personal loyalty. The key semantic difference lies in homage's focus on expressive, ritualized respect and allegiance, while tribute centers on tangible acknowledgment or honor through offerings.
Allegiance vs. Fealty: Varied Forms of Loyalty
Allegiance and fealty represent distinct expressions of loyalty within hierarchical relationships, where allegiance signifies a broader, often civic or national loyalty, while fealty specifically denotes a personal, sworn loyalty to a lord or sovereign in a feudal context. Both terms imply fidelity and commitment but differ in scope and legal binding, with fealty requiring a formal oath and often military or service obligations. Understanding these variations clarifies medieval social structures and modern interpretations of loyalty in political and social contracts.
Obeisance vs. Homage: Contrasting Acts of Respect
Obeisance involves a physical gesture of respect, such as bowing or kneeling, signifying submission or reverence, while homage is a broader act of showing honor and loyalty, often through sworn allegiance or public acknowledgment. Homage typically encompasses formal ceremonies or pledges affirming fealty to a lord or sovereign, whereas obeisance can be a more spontaneous or informal expression of respect without legal obligation. Both acts reinforce social hierarchies and relationships but differ in formality and the nature of the commitment involved.
Modern Interpretations: Homage and Its Alternatives
Modern interpretations of homage emphasize a voluntary expression of respect or honor, often in cultural or artistic contexts. Alternatives such as tribute, allegiance, fealty, and obeisance vary in formality and context, with tribute being a public acknowledgment of admiration, allegiance signifying loyalty to a cause or leader, fealty involving formal vows of fidelity historically tied to feudal systems, and obeisance representing a physical act of deference or submission. Understanding the nuances between homage and its alternatives enhances clarity in contemporary discourse on respect and loyalty.
Choosing the Right Term: Semantic and Contextual Nuances
Choosing the right term between homage, tribute, allegiance, fealty, and obeisance depends on the specific historical and cultural context; homage often implies a formal acknowledgment of loyalty in feudal systems, while tribute denotes a regular payment or offering as a sign of submission or respect. Allegiance emphasizes a sworn loyalty to a sovereign or cause, whereas fealty refers to the oath of fidelity by a vassal to a lord. Obeisance highlights physical gestures of respect or submission, making careful understanding of each term essential for precise communication in legal, historical, or literary texts.
homage, tribute, allegiance, fealty, obeisance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com