A digest simplifies complex information into clear and concise summaries, making it easier for you to grasp essential points quickly. It enhances understanding by focusing on key details while eliminating unnecessary content. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to create effective digests for better information retention.
Table of Comparison
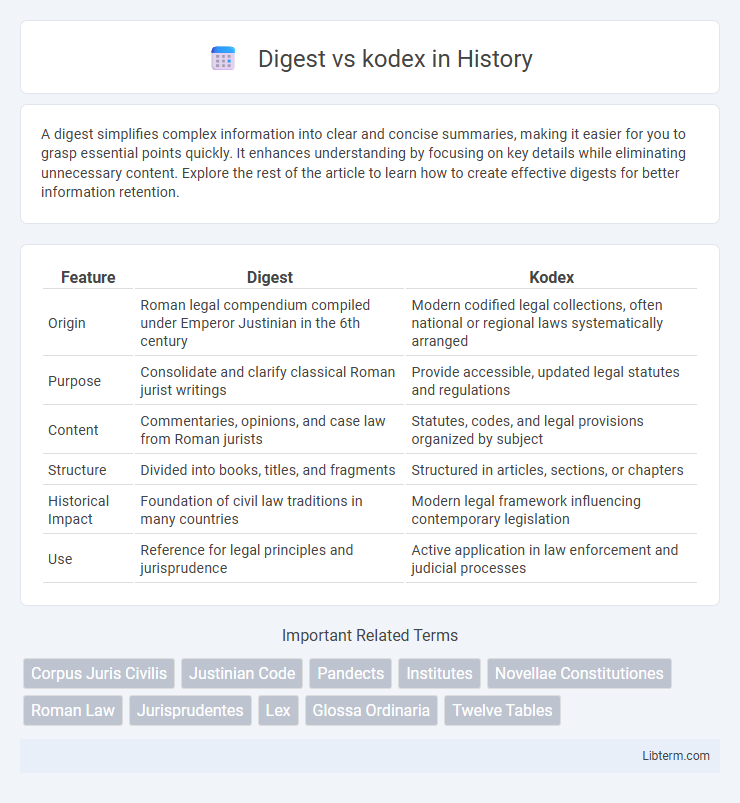
| Feature | Digest | Kodex |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Roman legal compendium compiled under Emperor Justinian in the 6th century | Modern codified legal collections, often national or regional laws systematically arranged |
| Purpose | Consolidate and clarify classical Roman jurist writings | Provide accessible, updated legal statutes and regulations |
| Content | Commentaries, opinions, and case law from Roman jurists | Statutes, codes, and legal provisions organized by subject |
| Structure | Divided into books, titles, and fragments | Structured in articles, sections, or chapters |
| Historical Impact | Foundation of civil law traditions in many countries | Modern legal framework influencing contemporary legislation |
| Use | Reference for legal principles and jurisprudence | Active application in law enforcement and judicial processes |
Introduction to Digest and Kodex
Digest is a comprehensive legal publication offering summarized case law and legislative updates tailored for quick reference by legal professionals. Kodex serves as a detailed legal commentary platform providing in-depth analysis and interpretation of statutes and case law for practitioners and scholars. Both Digest and Kodex enhance legal research efficiency, with Digest emphasizing concise summaries and Kodex focusing on thorough, contextual insights.
Historical Background of Digest and Kodex
The Digest, part of the Justinian Code, was compiled in the 6th century under Emperor Justinian I to consolidate Roman legal writings and opinions into a single comprehensive source. The Kodex, deriving from the Codex Justinianus, formed the core legal statute that compiled imperial constitutions and laws to provide clear governance guidelines. Both Digest and Kodex significantly shaped the foundation of civil law traditions by preserving and organizing Roman legal principles.
Origin and Development
Digest law originated in the Byzantine Empire under Emperor Justinian I in the 6th century, serving as a comprehensive compilation of Roman legal writings designed to unify and systematize existing legal principles. Kodex, rooted in Germanic legal traditions, evolved as a codified set of laws aimed at standardizing regional statutes and customs within various European states during the 19th century. Both Digest and Kodex represent pivotal developments in legal history, with Digest emphasizing classical Roman jurisprudence and Kodex reflecting the modern legislative codification movement.
Structure and Organization
Digest is structured as a curated compilation of summarized legal cases, organized by topics and jurisdictions to facilitate quick reference and comparative analysis. Kodex offers a comprehensive, systematic codification of statutes and regulations, arranged hierarchically with clear chapter and section delineations for exhaustive legal research. The organization of Digest emphasizes thematic categorization, while Kodex prioritizes a formal, legislative framework for easy navigation through statutory content.
Key Legal Principles
Digest and Kodex serve distinct roles in legal research; Digests compile case law summaries organized by legal issues, enabling quick identification of relevant judicial decisions. Kodex typically refers to systematic legal codes or statutes that establish foundational legal principles and statutory frameworks governing specific areas of law. Key legal principles in Digests rely on judicial interpretation and precedent, whereas Kodex principles are grounded in codified laws enacted by legislative authorities.
Influence on Modern Law
Digest, part of Justinian's Corpus Juris Civilis, serves as a foundational compilation of Roman juristic writings that deeply influenced the development of civil law systems across Europe. Kodex, often referring to codified legal texts like the German Burgerliches Gesetzbuch (BGB), offers a systematic and comprehensive legal framework that shapes modern statutory law and legal interpretation. The Digest provided historical legal principles that underpin modern concepts of equity and justice, while the Kodex establishes precise legislative authority and uniformity in contemporary legal practice.
Comparative Analysis: Digest vs Kodex
Digest offers a comprehensive, user-friendly platform with advanced search capabilities tailored for legal professionals, while Kodex provides a more specialized database emphasizing regional legal codes and statutes. Digest's integration of AI-driven analytics enhances case law interpretation, whereas Kodex excels in delivering updated regulatory information with a focus on compliance. Cost-effectiveness and subscription flexibility further distinguish Digest, making it suitable for larger firms, whereas Kodex appeals to niche practitioners requiring detailed statutory references.
Notable Contributors and Compilers
The Digest, compiled under Emperor Justinian I in the 6th century, featured notable contributors such as Tribonian, a key legal scholar who led the commission, and Pomponius, Ulpian, and Paulus, whose juristic writings were extensively excerpted. In contrast, the Kodex (Code) also part of Justinian's Corpus Juris Civilis, synthesized imperial enactments but relied more on existing imperial constitutions, lacking the juristic diversity found in the Digest. The Digest's rich blend of jurist opinions shaped Roman law profoundly, while the Kodex served primarily as a streamlined compilation of enacted statutes.
Legacy and Long-term Impact
Digest systems streamline data processing by summarizing large information sets, facilitating quicker decision-making and preserving essential knowledge efficiently over time. Kodex solutions offer a robust framework for codifying and standardizing complex data, ensuring consistency and reliability in legacy system integration and long-term archival. Both approaches significantly influence enterprise data management strategies, with Digest optimizing information retrieval and Kodex enhancing structural integrity and compliance for enduring data legacy.
Relevance in Contemporary Legal Studies
Digest and kodex represent distinct methodologies in contemporary legal studies, with digest serving as a comprehensive compilation of case law organized by topics, facilitating efficient legal research and precedent analysis. Kodex, typically a systematic code of laws, emphasizes statutory regulations and serves as a foundational tool for legal interpretation and application in jurisdictions following civil law traditions. The relevance of these tools today lies in their complementary roles: digests enhance judicial reasoning through case references, while kodex provides structured legal frameworks essential for legislative clarity and consistency.
Digest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com