Roman roads were engineering marvels, designed to connect the vast Roman Empire efficiently, enabling rapid movement of armies, trade, and information across continents. Their durable construction, using layers of stone, gravel, and sand, allowed many roads to survive for millennia, influencing modern infrastructure. Discover how these ancient routes shaped history and why they remain integral to understanding Roman engineering by exploring the rest of this article.
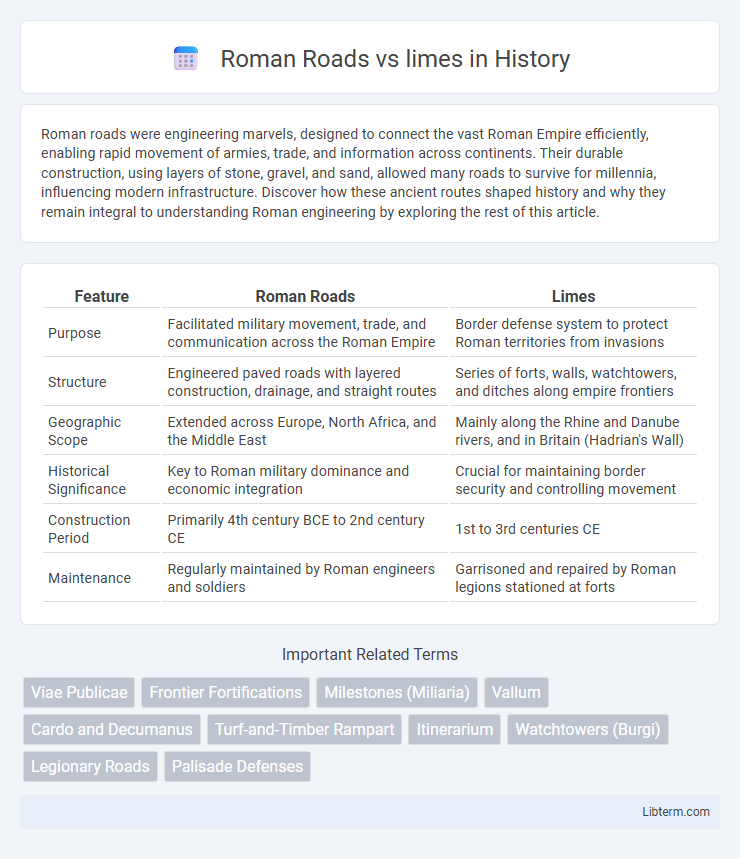
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Roman Roads | Limes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitated military movement, trade, and communication across the Roman Empire | Border defense system to protect Roman territories from invasions |
| Structure | Engineered paved roads with layered construction, drainage, and straight routes | Series of forts, walls, watchtowers, and ditches along empire frontiers |
| Geographic Scope | Extended across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East | Mainly along the Rhine and Danube rivers, and in Britain (Hadrian's Wall) |
| Historical Significance | Key to Roman military dominance and economic integration | Crucial for maintaining border security and controlling movement |
| Construction Period | Primarily 4th century BCE to 2nd century CE | 1st to 3rd centuries CE |
| Maintenance | Regularly maintained by Roman engineers and soldiers | Garrisoned and repaired by Roman legions stationed at forts |
Introduction to Roman Roads and Limes
Roman roads were engineered networks of durable stone and gravel highways designed to facilitate military operations, trade, and communication across the expansive Roman Empire, spanning over 400,000 kilometers at their peak. The limes, on the other hand, were fortified borders and defensive systems, including walls, forts, and watchtowers, constructed to protect Roman territories from external invasions and control movement. While Roman roads enhanced internal connectivity and economic integration, the limes served as physical barriers reinforcing the empire's geopolitical frontiers.
Historical Context: Expansion of the Roman Empire
Roman roads played a crucial role in the expansion and administration of the Roman Empire by facilitating the rapid movement of troops, trade, and communication across vast territories. The limes, a system of fortified boundaries, marked the empire's frontiers and defended against external invasions, often integrating natural and man-made barriers. Together, these infrastructures exemplify Rome's strategic approach to territorial control and military logistics during its height.
Design and Construction Techniques
Roman roads employed layered construction with a compacted foundation of sand, gravel, and paving stones to ensure durability and efficient drainage, featuring a convex surface to prevent water accumulation. In contrast, the limes, comprising fortifications like walls and watchtowers, focused on defensive architecture using stone and turf, designed for surveillance and military control rather than transportation. The engineering of Roman roads emphasized rapid troop movement and trade, while limes prioritized strategic border security through robust fortifications and observation posts.
Strategic Purposes: Transportation vs. Defense
Roman roads facilitated rapid movement of troops, trade, and communication across the empire, ensuring logistical efficiency and administrative control. The limes functioned primarily as fortified frontiers, designed to prevent invasions and monitor border activities with military posts and watchtowers. Together, these infrastructures created a complementary system enhancing both strategic mobility and territorial security.
Geographic Distribution Across the Empire
Roman roads extended across the entire empire, connecting major cities from Britannia in the northwest to Mesopotamia in the east, facilitating military movements, trade, and communication. In contrast, limes represented fortified border zones primarily along the Rhine and Danube rivers, marking the empire's northern and eastern frontiers to control invasions and monitor interactions with Germania and other neighboring tribes. The geographic distribution of Roman roads underscored internal integration, while the limes delineated defensive perimeters, highlighting differing strategic functions across imperial territories.
Engineering Marvels: Materials and Methods
Roman roads utilized layered construction techniques combining sand, gravel, and large stone slabs to ensure durability and efficient drainage, while the limes frontier fortifications employed stone, brick, and wood reinforced with mortar to create formidable defensive walls and watchtowers. Advanced engineering methods such as precise surveying tools and concrete technology enabled the Romans to build roads spanning thousands of miles and limes structures capable of withstanding environmental and military pressures. These infrastructures epitomize Roman innovation in materials science and civil engineering, reflecting their strategic importance in controlling and integrating the empire.
Economic and Military Impacts
Roman roads facilitated efficient trade routes, boosting economic integration across the empire by enabling faster movement of goods, merchants, and tax revenues. The limes, serving as fortified frontiers, provided military defense against invasions but also regulated trade and controlled migration, impacting economic stability in border provinces. Together, these infrastructures supported Rome's military logistics and economic expansion, ensuring sustained control and prosperity throughout diverse regions.
Notable Examples of Roman Roads and Limes
Notable Roman roads such as the Via Appia, also known as the "Queen of Roads," and the Via Augusta illustrate the engineering prowess of ancient Rome, facilitating military and commercial movement across vast territories. The Roman limes, serving as fortified frontiers like the Upper German-Raetian Limes and Hadrian's Wall, define the empire's boundaries and demonstrate advanced defensive infrastructure. These roads and limes collectively underscore Rome's strategic combination of mobility and protection throughout its empire.
Legacy and Preservation Today
Roman Roads remain foundational to modern European infrastructure, with many contemporary highways tracing their ancient routes, showcasing remarkable engineering durability and influencing urban development patterns. The limes, as fortified frontiers, have left a critical archaeological legacy, providing insights into Roman military strategy and border control, with sites like the Upper German-Raetian Limes designated as UNESCO World Heritage. Preservation efforts for both prioritize conservation and public education, employing advanced technology to maintain structural integrity and facilitate immersive historical experiences.
Comparative Analysis: Influence on Modern Infrastructure
Roman roads established the foundation for modern highways by demonstrating advanced engineering techniques such as layered construction and durable materials, which enhanced connectivity and trade across vast territories. In contrast, the limes, as fortified boundaries, influenced contemporary border security infrastructure by integrating natural and man-made barriers to control movement and protect regions. Together, these infrastructures exemplify early dual strategies of mobility and defense that continue to inform modern urban planning and national security frameworks.
Roman Roads Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com