A guild is an organization of artisans or merchants who oversee the practice of their craft or trade in a particular area, often established during the medieval period to maintain standards and protect members' interests. Guilds played a crucial role in regulating competition, setting quality benchmarks, and providing training through apprenticeships, influencing today's professional associations and trade unions. Discover how the legacy of guilds continues to shape modern industries and what this means for your business practices.
Table of Comparison
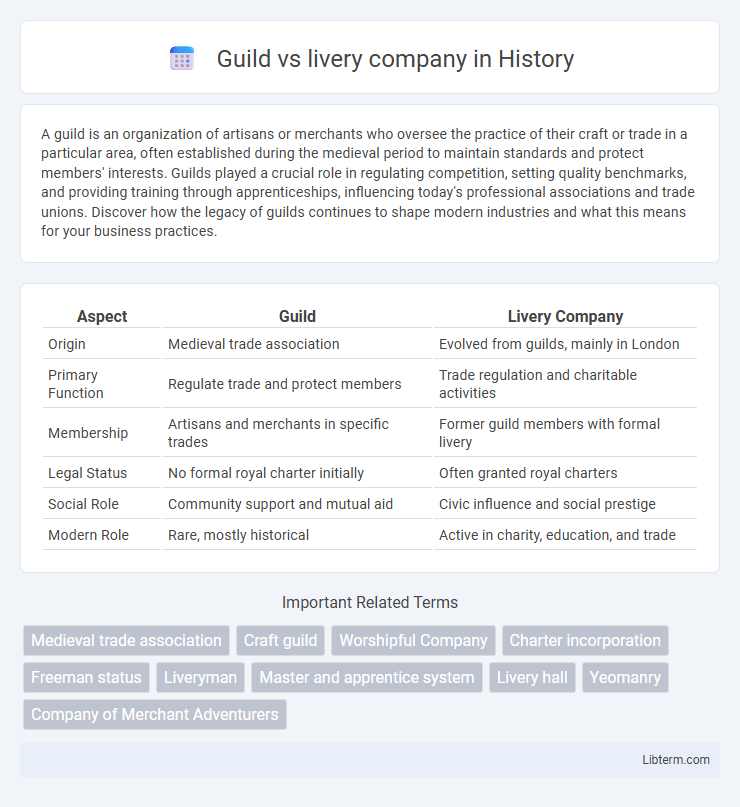
| Aspect | Guild | Livery Company |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Medieval trade association | Evolved from guilds, mainly in London |
| Primary Function | Regulate trade and protect members | Trade regulation and charitable activities |
| Membership | Artisans and merchants in specific trades | Former guild members with formal livery |
| Legal Status | No formal royal charter initially | Often granted royal charters |
| Social Role | Community support and mutual aid | Civic influence and social prestige |
| Modern Role | Rare, mostly historical | Active in charity, education, and trade |
Introduction to Guilds and Livery Companies
Guilds originated as medieval associations of craftsmen or merchants controlling trade standards and protecting members' interests within specific trades. Livery Companies evolved from these guilds, becoming more formalized organizations in the City of London with ceremonial roles and charitable activities alongside trade regulation. Both entities played crucial roles in shaping economic governance and social networks during the Middle Ages.
Historical Origins of Guilds
Guilds originated in medieval Europe as organized associations of craftsmen and merchants, established to regulate trade, maintain quality standards, and protect members' economic interests. These early guilds also played significant social and religious roles within urban communities, often linked to specific trades or crafts. Livery companies, emerging in the City of London during the late Middle Ages, evolved from these guilds, gaining royal charters and formal governance structures that distinguished them as influential civic institutions.
Emergence of Livery Companies
Livery companies emerged in medieval London as evolved guilds, originally formed to regulate trades and maintain quality standards among craftsmen. These organizations gained royal charters, granting them privileges and transforming guilds into influential economic and social entities within the City of London. Over time, livery companies expanded their roles to include charitable activities, education, and civic governance, distinguishing them from their earlier guild counterparts.
Key Differences Between Guilds and Livery Companies
Guilds originated as medieval associations of craftsmen or merchants focused on regulating trade quality and protecting members' economic interests, while livery companies evolved from guilds in London with formal charters and civic responsibilities. Livery companies hold significant political influence in the City of London through the right to elect the Lord Mayor and sheriffs, whereas guilds primarily centered on trade regulation and mutual support. The hierarchical structure of livery companies includes tiers such as freemen and liverymen, reflecting a broader social and ceremonial role beyond the trade-specific focus of traditional guilds.
Roles and Functions in Medieval Society
Guilds in medieval society primarily served as associations of artisans and merchants who regulated trade, maintained quality standards, and protected economic interests within specific crafts or trades. Livery companies, often evolving from guilds, played more formal roles in municipal governance, social welfare, and ceremonial functions, often holding charters granted by the crown. Both institutions were crucial in shaping urban economies, enforcing discipline among members, and influencing local political structures.
Evolution Over Time
Guilds originated in medieval Europe as associations of artisans and merchants regulating trade, quality, and training within towns, evolving into livery companies in London with formal charters granted by the Crown. Over time, livery companies transformed from trade guilds into influential civic institutions, focusing on charitable activities, education, and social networking while preserving historic traditions. This evolution reflects the shift from economic regulation to social and philanthropic roles in modern British society.
Influence on Trade and Commerce
Guilds historically regulated quality standards, controlled apprenticeships, and managed trade monopolies within specific crafts, significantly shaping urban trade dynamics. Livery companies evolved from guilds, expanding their influence by obtaining royal charters that granted legal and economic privileges, enabling them to regulate markets and influence commercial policy in cities like London. Both institutions fostered trust and cooperation among merchants, which facilitated trade growth and the establishment of early trade networks.
Social and Political Significance
Guilds historically served as early trade associations that regulated commerce and protected members' economic interests within medieval cities, fostering strong social bonds and collective identity. Livery companies evolved from guilds, holding significant political influence by controlling civic offices in London, such as electing the Lord Mayor and members of the City of London Corporation. Both institutions reinforced social hierarchies and civic governance, intertwining economic power with political authority in urban centers.
Modern-Day Guilds and Livery Companies
Modern-day guilds and livery companies continue to play significant roles in professional development and charitable activities within the UK. Livery companies often uphold centuries-old traditions while engaging in education, networking, and supporting trade standards in industries such as finance, construction, and crafts. Contemporary guilds emphasize community collaboration and skill preservation, adapting to modern economic demands while fostering industry-specific expertise.
Lasting Impact on Contemporary Organizations
Guilds laid the foundational structures for modern professional associations through their regulation of trade practices, quality standards, and mutual support among members. Livery companies evolved these principles by incorporating charitable activities and civic responsibilities, influencing the governance models of contemporary nonprofit and trade organizations. The enduring legacy of both entities is evident in today's corporate social responsibility initiatives and professional certification systems.
Guild Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com