A Welsh prince symbolizes a rich heritage of leadership and bravery rooted in the mountainous landscapes and historic castles of Wales. These princes historically defended their lands against invaders and fostered a unique cultural identity that continues to inspire pride today. Discover how the legacy of Welsh princes shapes modern Wales and what it means for your appreciation of history in the full article.
Table of Comparison
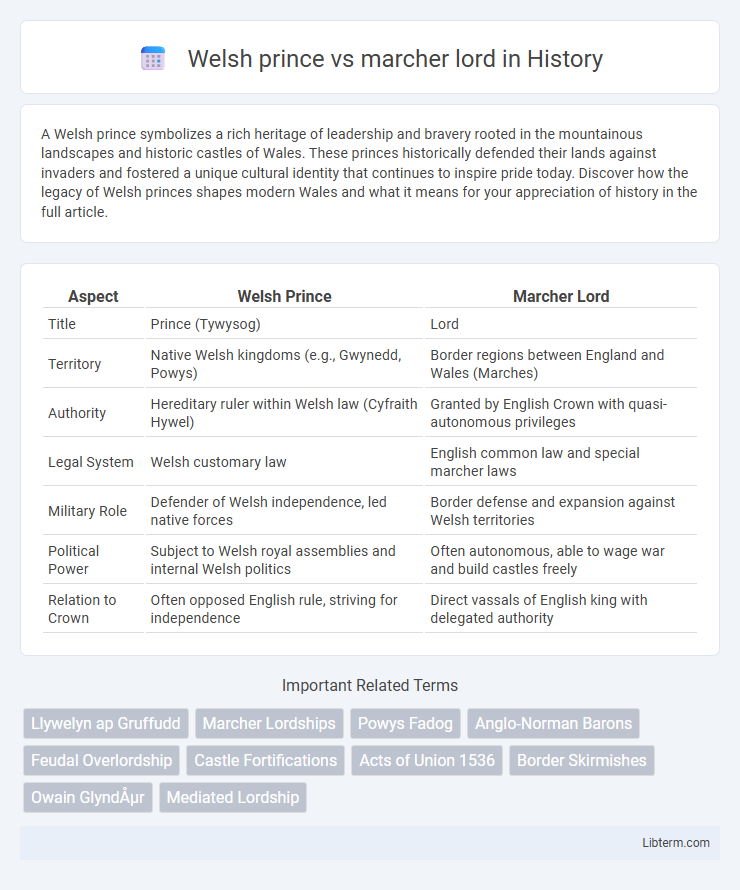
| Aspect | Welsh Prince | Marcher Lord |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Prince (Tywysog) | Lord |
| Territory | Native Welsh kingdoms (e.g., Gwynedd, Powys) | Border regions between England and Wales (Marches) |
| Authority | Hereditary ruler within Welsh law (Cyfraith Hywel) | Granted by English Crown with quasi-autonomous privileges |
| Legal System | Welsh customary law | English common law and special marcher laws |
| Military Role | Defender of Welsh independence, led native forces | Border defense and expansion against Welsh territories |
| Political Power | Subject to Welsh royal assemblies and internal Welsh politics | Often autonomous, able to wage war and build castles freely |
| Relation to Crown | Often opposed English rule, striving for independence | Direct vassals of English king with delegated authority |
Historical Background: Wales and the Marches
The Welsh princes governed native kingdoms in Wales, maintaining Celtic traditions and resisting Norman and English incursions, while the Marcher Lords were Norman nobles granted extensive autonomous powers by the English crown to secure and manage the volatile borderlands known as the Welsh Marches. These border territories, established after the Norman Conquest of England in the 11th century, functioned as militarized zones with their own legal systems, blending Norman feudal authority and local customs. The continuous conflict and shifting alliances between Welsh princes and Marcher Lords shaped the political and cultural landscape of medieval Wales and the English border region.
The Rise of Welsh Princes
The rise of Welsh princes during the 11th and 12th centuries reshaped power dynamics along the Welsh-English border, as native rulers asserted control over fragmented territories formerly dominated by marcher lords. Welsh princes like Gruffudd ap Cynan and Owain Gwynedd capitalized on internal instability within the marcher lordships to consolidate power, promote Welsh law, and fortify their principalities. This resurgence weakened marcher lord influence, setting the stage for ongoing conflicts and creating a distinct political identity in medieval Wales.
The Role of the Marcher Lords
Marcher Lords held significant military and administrative power along the borderlands between England and Wales, serving as the king's representatives tasked with defending against Welsh incursions. Their authority included the rights to build castles, administer justice, and wage private wars, enabling them to maintain control over contested territories. This autonomy often brought them into direct conflict with Welsh princes striving to reclaim land and assert sovereignty over the Marches.
Key Conflicts and Battles
The key conflicts between Welsh princes and marcher lords centered on territorial control and political dominance during the medieval period. Notable battles include the Battle of Bryn Derwin (1255), where Llywelyn ap Gruffudd secured power among Welsh rulers, and the Battle of Orewin Bridge (1282), which marked Edward I's decisive victory over Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, leading to the fall of Welsh independence. These conflicts were pivotal in the struggle between native Welsh principalities and the Anglo-Norman marcher lordships encroaching from the English border.
Political Alliances and Rivalries
Welsh princes and marcher lords often engaged in complex political alliances and rivalries shaped by territorial control and power dynamics along the Welsh-English border. Marcher lords, with their semi-autonomous lordships granted by the English crown, negotiated alliances through marriage, military support, and treaties to counterbalance Welsh princely influence. Welsh princes, such as those of Gwynedd and Powys, formed strategic coalitions both within Wales and with foreign powers to resist marcher lord encroachment and assert sovereignty.
Castles and Strongholds: Symbols of Power
Welsh princes and marcher lords constructed castles and strongholds as vital symbols of power and territorial control during the medieval period. Welsh castles often emphasized native architectural styles and strategic locations within mountainous terrain to assert sovereignty, while marcher lords built imposing stone fortifications featuring concentric designs to dominate border regions and impose Norman authority. These castles not only served military purposes but also reinforced political authority, projecting influence over contested lands in the Welsh Marches.
Legal Systems: Welsh Laws vs Marcher Customs
The legal systems of Welsh princes were governed by the native Welsh Laws, which emphasized communal landholding, kinship obligations, and restitution over punishment. In contrast, Marcher lords operated under a blend of English common law and local customs, granting them considerable judicial autonomy to enforce feudal and martial authority in border territories. This legal divergence created a complex landscape where Welsh customary law coexisted uneasily with Marcher lordship's evolving feudal judiciary.
Cultural Clashes and Influences
Welsh princes and marcher lords symbolized contrasting cultural identities shaped by divergent legal, linguistic, and social traditions along the Welsh-English border. Welsh princes upheld native customs and the Welsh language, emphasizing kinship and tribal loyalty, while marcher lords introduced Norman feudal law, castles, and the English language, creating a frontier of cultural negotiation and conflict. The resulting blend influenced border governance, architecture, and cross-cultural alliances, laying foundational elements for modern Welsh identity and Anglo-Welsh relations.
Notable Figures: Famous Princes and Lords
Welsh princes like Llywelyn the Great and Owain Glyndwr are renowned for their leadership in resisting English domination and striving to unify Wales. In contrast, marcher lords such as Roger Mortimer and the de Clare family wielded significant military and political power along the volatile Welsh-English border, establishing fortified castles to consolidate their authority. These notable figures embody the persistent struggle for control over the Welsh Marches during the medieval period.
Legacy and Impact on Welsh-English Relations
The Welsh princes symbolized native sovereignty and cultural resilience, while marcher lords represented English authority and feudal expansion along the volatile borderlands. This dynamic fueled centuries of conflict and negotiation, shaping a complex legacy of contested governance and cultural exchange. The enduring impact on Welsh-English relations includes a deeply ingrained sense of Welsh identity alongside legal and political structures influenced by Anglo-Norman institutions.
Welsh prince Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com