Crafting a compelling draft is essential for organizing your ideas clearly and effectively. It sets the foundation for refining your message and ensuring your content resonates with your target audience. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for perfecting your draft and enhancing your writing process.
Table of Comparison
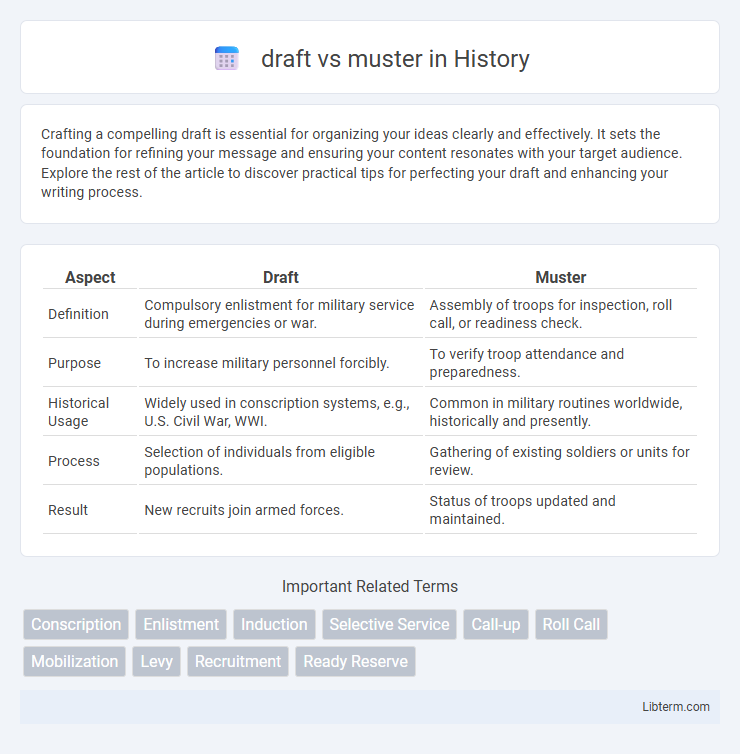
| Aspect | Draft | Muster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compulsory enlistment for military service during emergencies or war. | Assembly of troops for inspection, roll call, or readiness check. |
| Purpose | To increase military personnel forcibly. | To verify troop attendance and preparedness. |
| Historical Usage | Widely used in conscription systems, e.g., U.S. Civil War, WWI. | Common in military routines worldwide, historically and presently. |
| Process | Selection of individuals from eligible populations. | Gathering of existing soldiers or units for review. |
| Result | New recruits join armed forces. | Status of troops updated and maintained. |
Understanding the Concepts: Draft vs Muster
Draft refers to the process of selecting individuals, often for military service, through a formal call or lottery system based on eligibility criteria. Muster involves the assembling and inspection of personnel to ensure readiness and accountability, typically in military or organizational settings. Understanding the distinction between draft as a selection mechanism and muster as an organizational procedure is crucial for interpreting military operations and historical recruitment practices.
Historical Origins of Draft and Muster
The historical origins of the draft trace back to ancient civilizations like Greece and Rome, where compulsory military service was enforced to assemble armies quickly during wartime. Musters originated in medieval Europe as formal assemblies of troops for inspection, training, and readiness assessment before deployment. Both draft and muster were essential methods for mobilizing and organizing soldiers, reflecting evolving military practices over time.
Definitions: What is a Draft?
A draft is a written order issued by one party instructing another to pay a specified sum of money to a third party at a predetermined date or on demand. It functions as a negotiable instrument commonly used in trade and finance for transferring funds securely and efficiently. Drafts are often categorized into sight drafts, payable immediately upon presentation, and time drafts, payable at a future date.
Definitions: What is a Muster?
A muster is a formal assembly of personnel, often military or naval, conducted to account for individuals, perform inspections, or deliver instructions. It serves as an organized roll call ensuring all members are present and operationally ready. Distinguished from a draft, which typically refers to the selection or conscription of individuals, a muster emphasizes gathering and organizing existing personnel for specific purposes.
Key Differences Between Draft and Muster
The key differences between draft and muster lie in their purpose and usage: a draft refers to a preliminary version of a written document or plan, often created to outline ideas and allow for revisions, while muster involves assembling personnel or troops for inspection, roll call, or combat readiness. Draft emphasizes the creation and refinement process in writing or design, whereas muster focuses on organization and accountability in a military or group setting. Understanding these distinctions highlights that draft is associated with document preparation, while muster is linked to personnel management.
Legal Implications and Requirements
Drafting a contract involves preparing a detailed document outlining terms and obligations that must comply with legal standards to ensure enforceability. Muster refers to the formal review or assembly of individuals or documents, often required by law for verification or accountability purposes. Failure to properly draft or muster relevant documents can lead to legal disputes, non-compliance penalties, or invalidation of agreements.
Draft vs Muster in Military Contexts
In military contexts, a draft refers to the compulsory selection and conscription of individuals into armed forces during times of war or national emergency, often based on age and physical fitness criteria. Muster, on the other hand, involves assembling troops for inspection, roll call, or service readiness, serving as a routine organizational procedure rather than involuntary recruitment. Understanding the distinction between draft as enforced enlistment and muster as troop gathering is crucial for accurate military operational planning and personnel management.
Modern Usage in Organizations and Governments
Draft systems in modern organizations primarily refer to selective recruitment methods, often used by governments for conscription or talent pooling, involving a structured, legally bound process to fulfill manpower needs. Muster, on the other hand, is a routine administrative procedure for assembling personnel, typically employed by military units and emergency response teams to account for presence and readiness. Contemporary use of drafting emphasizes strategic resource allocation and compliance with regulatory frameworks, while mustering focuses on operational efficiency and real-time personnel management.
Common Misconceptions and Confusions
Many confuse "draft" with "muster" due to their military contexts, but a draft specifically refers to the compulsory enlistment of individuals into armed forces, while a muster involves gathering troops for inspection or roll call without mandatory induction. Another common misconception is assuming drafting is voluntary like a muster assembly; however, drafting enforces obligatory service, often during wartime, whereas mustering is a routine organizational procedure. Clarity about these distinctions is crucial for understanding military protocols and recruitment processes.
Choosing the Right Process: Draft or Muster?
Choosing the right process between draft and muster depends on the project's requirements and team preferences. Drafting involves creating preliminary designs or written content that outline ideas, while mustering focuses on gathering resources or personnel efficiently for execution. Evaluating factors such as timeline, resource availability, and clarity of objectives ensures optimal decision-making in selecting draft or muster approaches.
draft Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com