Enlist your skills and experiences clearly to highlight your strengths in any application. Focus on relevant achievements that demonstrate your capabilities and dedication. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively present your qualifications for maximum impact.
Table of Comparison
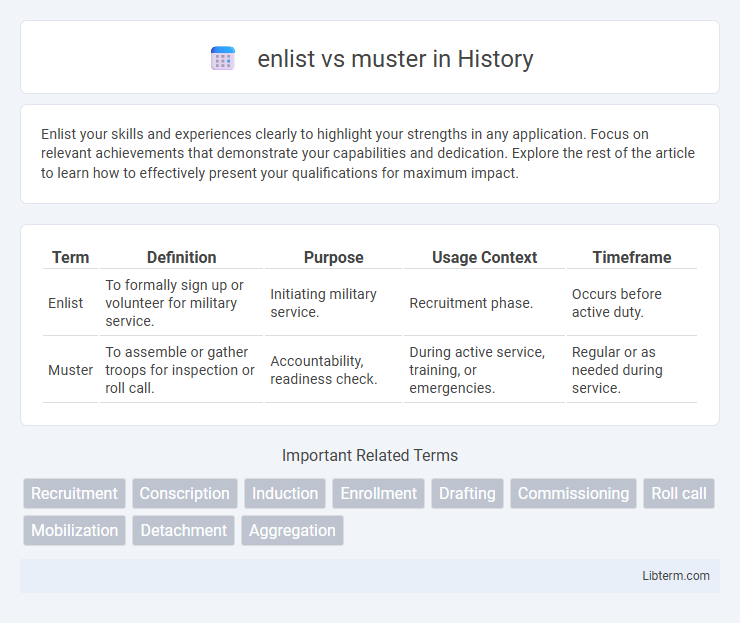
| Term | Definition | Purpose | Usage Context | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enlist | To formally sign up or volunteer for military service. | Initiating military service. | Recruitment phase. | Occurs before active duty. |
| Muster | To assemble or gather troops for inspection or roll call. | Accountability, readiness check. | During active service, training, or emergencies. | Regular or as needed during service. |
Understanding "Enlist" and "Muster": Key Definitions
Enlist" refers to the formal process of voluntarily joining the military or armed forces, typically involving a commitment through recruitment and signing up as a soldier or service member. "Muster" denotes the act of assembling troops or personnel for inspection, roll call, or readiness assessment, often used in military contexts to verify attendance or organize forces. Understanding these terms highlights enlistment as the entry point into service and mustering as the organizational step to account for and deploy enlisted members.
Historical Origins of Enlistment and Mustering
Enlistment originates from medieval military practices where individuals voluntarily signed contracts to serve in armed forces, often formalized through legal agreements or oaths, reflecting a personal commitment to military duty. Mustering, derived from the Old French "mostrer," historically referred to the gathering and inspection of troops to assess readiness and strength, ensuring proper organization and discipline within a military unit. Both terms highlight different facets of historical military administration: enlistment emphasizing recruitment and personal obligation, and mustering focusing on assembly and verification of forces.
Enlist vs Muster: Core Differences
Enlist refers to the formal process of voluntarily joining the military, often involving a commitment and oath, whereas muster denotes the act of assembling troops for inspection, roll call, or readiness verification. Enlistment establishes an individual's status as an active military member, while mustering is a routine or situational procedure conducted within an already enlisted force. Understanding these core differences is essential for distinguishing between recruitment and organizational accountability in military operations.
Usage in Military Contexts
Enlist refers to the act of voluntarily joining the military service, typically involving signing a contract to serve for a specified period. Muster, on the other hand, denotes the assembling or gathering of military personnel for inspection, roll call, or deployment orders. While enlistment marks the beginning of a service member's commitment, mustering is an organizational procedure used regularly to account for troops.
Enlist and Muster in Modern Organizations
Enlist refers to formally recruiting individuals into an organization, often emphasizing voluntary commitment and initial enrollment processes. Muster involves assembling or gathering personnel, typically to account for members or prepare them for collective action or duties. In modern organizations, enlistment is crucial for building a skilled workforce, while muster ensures coordinated operational readiness and effective resource management.
Legal Implications: Enlisting vs Mustering
Enlisting in the military involves a formal contract, creating binding legal obligations including oath-taking and commitment to service duration, while mustering primarily refers to the administrative process of assembling troops for duty or inspection without contractual implications. Enlistment typically triggers legal rights and responsibilities under military law, such as eligibility for benefits and adherence to codes of conduct, whereas mustering is procedural, ensuring troop accountability and readiness. Understanding these distinctions is critical for service members regarding their legal status and obligations within the armed forces.
Step-by-Step Process: Enlistment Procedures
Enlistment procedures involve prospective recruits completing an application, undergoing medical examinations, and attending initial orientation sessions tailored to their branch of service. The process requires verification of personal information, eligibility assessments based on age, education, and physical fitness, followed by signing a contract to formalize the commitment. This step-by-step procedure ensures structured entry into military service before proceeding to the muster phase, which focuses on assembling and accounting for personnel.
Mustering: Purpose and Protocols
Mustering serves as a systematic process for accounting and assembling personnel, ensuring all members are present and prepared for duty or emergency situations. This protocol involves precise roll calls, attendance verification, and readiness assessments to maintain operational efficiency and safety standards. Military units and organizations rely on mustering to confirm personnel status, coordinate deployments, and uphold discipline during inspections or emergencies.
Real-World Examples: Enlist vs Muster
Enlist refers to the formal process of joining the military, often involving signing contracts and taking an oath, such as a recruit enlisting in the U.S. Army during basic training. Muster describes the act of assembling troops for inspection, roll call, or drills, commonly seen in naval vessels where sailors muster daily on deck to confirm attendance. Real-world examples include soldiers enlisting before deployment, while commanders use muster to ensure operational readiness and personnel accountability.
Choosing the Right Term: Practical Guidelines
Enlist refers specifically to the act of voluntarily signing up for military service, emphasizing individual commitment and contractual obligation. Muster denotes the process of assembling troops for inspection, roll call, or deployment, focusing on organizational readiness and accountability. Choosing the right term depends on context: use enlist when discussing recruitment or joining, and muster when referring to gathering personnel for duty or inspection.
enlist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com