Civilitas embodies the principles of social harmony, respect, and civic responsibility essential for thriving communities. Emphasizing mutual understanding and active participation, it nurtures a culture where individuals contribute positively to society. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Civilitas can transform your community engagement.
Table of Comparison
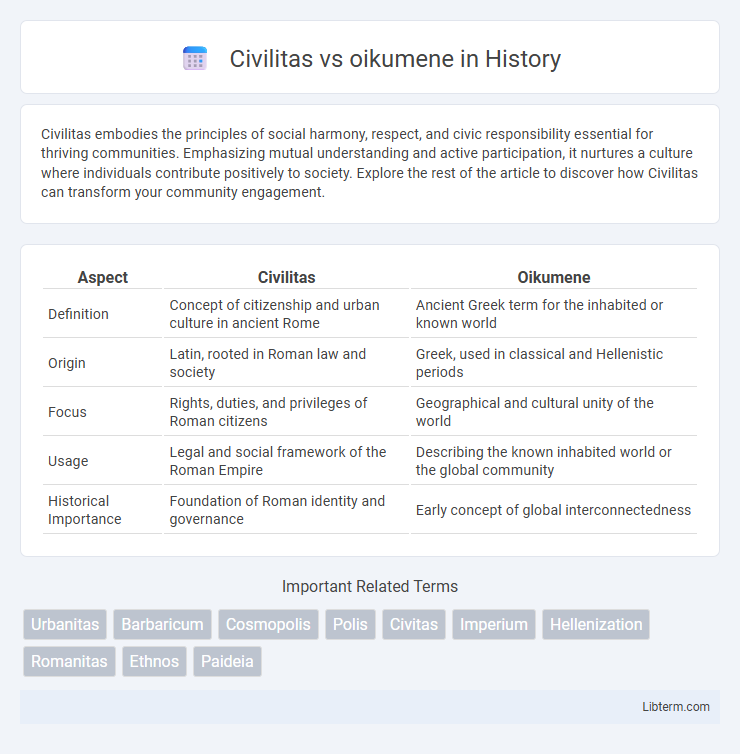
| Aspect | Civilitas | Oikumene |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concept of citizenship and urban culture in ancient Rome | Ancient Greek term for the inhabited or known world |
| Origin | Latin, rooted in Roman law and society | Greek, used in classical and Hellenistic periods |
| Focus | Rights, duties, and privileges of Roman citizens | Geographical and cultural unity of the world |
| Usage | Legal and social framework of the Roman Empire | Describing the known inhabited world or the global community |
| Historical Importance | Foundation of Roman identity and governance | Early concept of global interconnectedness |
Understanding the Concepts: Civilitas and Oikumene
Civilitas represents the ideals of civic virtue, social responsibility, and harmonious coexistence within a defined political community, emphasizing active participation and mutual respect among citizens. Oikumene refers to the inhabited or known world, historically used to denote the entire inhabited earth or the global human community, often highlighting interconnectedness beyond local or national boundaries. Understanding civilitas involves recognizing its role in fostering social cohesion in specific political entities, while oikumene expands this view to a broader, global context of human unity and shared existence.
Historical Origins of Civilitas
Civilitas originated in ancient Roman political theory, referring to the concept of citizenship and the active participation of citizens within the polis, emphasizing social order, civic virtue, and communal responsibility. It contrasted with the Greek notion of oikumene, which described the inhabited world and the unity of diverse peoples under a broader cosmopolitan ideal. The historical origins of civilitas highlight Rome's focus on structured governance, legal equality, and the integration of individual identity within the state's framework.
The Development of Oikumene in Ancient Thought
The development of Oikumene in ancient thought reflects the early conceptualization of a unified inhabited world, contrasting with Civilitas, which emphasized the organization and moral framework of urban civilization. Ancient Greek and Roman philosophers expanded Oikumene to signify the known, interconnected world governed by shared cultural and political ideals. This evolution underscores an emerging awareness of global unity and collective identity beyond local city-states or civil communities.
Civilitas: Social Order and Public Virtue
Civilitas represents the foundational concept of social order and public virtue essential for cohesive communities, emphasizing shared responsibilities and mutual respect among citizens. Rooted in Roman and classical traditions, Civilitas fosters governance structures that prioritize common good, civic engagement, and moral conduct. This contrasts with oikumene, which broadly refers to the inhabited world or global community without the intrinsic focus on individual social ethics and structured civic duties.
Oikumene: The Idea of a Universal Community
Oikumene represents the concept of a universal community encompassing all human societies and cultures, emphasizing interconnectedness and shared humanity across geographical borders. This idea originated in ancient Greek thought, evolving into a philosophical and theological framework that advocates global unity and collective responsibility. Oikumene contrasts with Civilitas, which centers more on localized civic identity and community, by promoting inclusivity and universal ethical bonds that transcend individual city-states or nations.
Comparing Civilitas and Oikumene in Political Philosophy
Civilitas and oikumene represent distinct concepts in political philosophy, where civilitas emphasizes the social order and civic duty within a political community, while oikumene refers to the inhabited world or the global political sphere. Civilitas centers on fostering communal values, justice, and hierarchical structures within a defined polity, contrasting with oikumene's broader, more inclusive notion of governance and human interconnectedness across diverse societies. The comparison highlights civilitas' localized, culturally embedded governance against oikumene's universalistic approach to political organization and global citizenship.
Influence on Roman and Greek Societies
Civilitas emphasized civic duty, legal order, and social cohesion in Roman society, shaping the foundation of Roman law and governance structures. Oikumene, rooted in Greek thought, referred to the inhabited world and informed Hellenistic cultural identity, promoting a shared worldview across city-states through philosophy and communal rituals. The interaction between Civilitas and oikumene influenced the integration of local customs with imperial administration, fostering political unity and cultural exchange across the Mediterranean.
Civilitas and Oikumene in Modern Discourse
Civilitas in modern discourse often represents social cohesion and ethical citizenship within diverse societies, emphasizing mutual respect and shared values. Oikumene, rooted in ancient cosmopolitan ideals, is increasingly invoked to discuss global interconnectedness and cultural inclusivity in international relations. Contemporary debates highlight Civilitas as foundational for local community engagement, while Oikumene frames broader dialogues on globalization and multicultural coexistence.
Contemporary Relevance of Civilitas vs Oikumene
Civilitas represents localized civic engagement and social virtues foundational to democratic societies, while oikumene reflects a broader, global interconnectedness rooted in shared cultural and ethical values. Contemporary relevance of civilitas lies in fostering inclusive communities and participatory governance, essential for addressing local challenges and sustaining social cohesion. Oikumene's significance emerges in promoting global cooperation, cross-cultural dialogue, and collective responsibility amidst globalization and transnational issues like climate change and human rights.
Implications for Global Citizenship and Governance
Civilitas, emphasizing structured civic life and shared values within political communities, contrasts with oikumene's broader concept of a unified, inhabited world encompassing diverse cultures. This distinction shapes global citizenship by balancing localized civic responsibilities with a universal sense of belonging and interconnectedness. Governance frameworks must integrate the principles of civilitas to ensure social cohesion while embracing oikumene's inclusivity to address global challenges effectively.
Civilitas Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com