Archaeology uncovers the mysteries of ancient civilizations through the careful excavation and analysis of artifacts, structures, and cultural landscapes. This scientific discipline reveals insights into human history, evolution, and cultural development over millennia. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of archaeology's role in connecting us to our past.
Table of Comparison
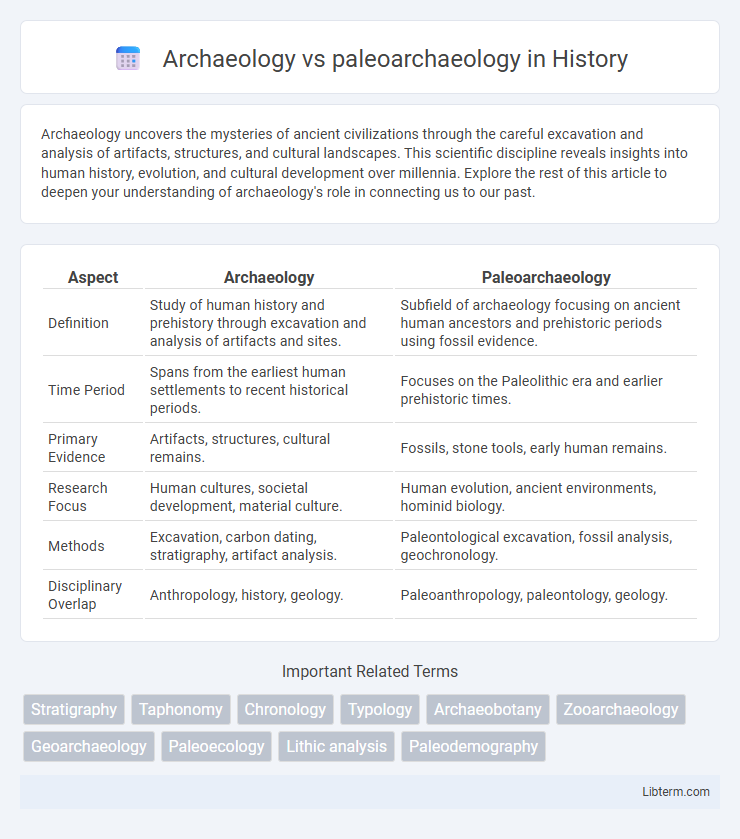
| Aspect | Archaeology | Paleoarchaeology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human history and prehistory through excavation and analysis of artifacts and sites. | Subfield of archaeology focusing on ancient human ancestors and prehistoric periods using fossil evidence. |
| Time Period | Spans from the earliest human settlements to recent historical periods. | Focuses on the Paleolithic era and earlier prehistoric times. |
| Primary Evidence | Artifacts, structures, cultural remains. | Fossils, stone tools, early human remains. |
| Research Focus | Human cultures, societal development, material culture. | Human evolution, ancient environments, hominid biology. |
| Methods | Excavation, carbon dating, stratigraphy, artifact analysis. | Paleontological excavation, fossil analysis, geochronology. |
| Disciplinary Overlap | Anthropology, history, geology. | Paleoanthropology, paleontology, geology. |
Defining Archaeology: Scope and Focus
Archaeology investigates past human societies through material remains including artifacts, structures, and cultural landscapes, aiming to reconstruct historical contexts and human behavior. Paleoarchaeology, as a specialized subfield, concentrates on the earliest periods of human history by analyzing fossilized remains and ancient tools to understand human evolution and early cultural development. This distinction highlights archaeology's broad scope across all human history, whereas paleoarchaeology narrows the focus to prehistoric origins and paleoanthropology.
What is Paleoarchaeology?
Paleoarchaeology is a specialized branch of archaeology that focuses on the study of early humans and their prehistoric environments through fossil evidence and ancient artifacts. It combines methods from archaeology, paleontology, and anthropology to reconstruct the behavior, culture, and evolution of hominins from millions of years ago. This field provides critical insights into human origins, adaptation, and technological development during the Paleolithic era.
Key Differences Between Archaeology and Paleoarchaeology
Archaeology studies human history and culture through artifacts, structures, and landscapes, focusing on a broad temporal range including historic and prehistoric periods. Paleoarchaeology narrows this scope, specializing in early human evolution by analyzing fossilized remains, stone tools, and ancient environments from millions to thousands of years ago. Key differences include the time scale, with paleoarchaeology emphasizing early hominins, and the methods, which combine archaeological techniques with paleoanthropological and geological analyses.
Historical Development of Both Disciplines
Archaeology formally emerged in the 19th century with a focus on excavating and interpreting human artifacts to understand historical civilizations, while paleoarchaeology developed later to specifically study early human ancestors and prehistoric cultures through fossil records. The historical development of paleoarchaeology integrated advances in geology, paleontology, and anthropology, enabling a multidisciplinary approach to unearthing hominin evolution. Both disciplines evolved with improved stratigraphic techniques and radiometric dating, but paleoarchaeology places greater emphasis on ancient paleoenvironmental contexts and early human origins.
Core Methods and Techniques
Archaeology employs excavation, stratigraphy, and artifact analysis to understand past human activities, focusing on historical and prehistoric contexts. Paleoarchaeology integrates these methods with paleoenvironmental reconstruction, paleontological data, and dating techniques like radiocarbon and thermoluminescence to study early human ancestors. Both disciplines utilize GIS mapping and remote sensing, but paleoarchaeology places greater emphasis on fossil analysis and geological context to trace human evolution.
Types of Evidence Studied
Archaeology primarily examines material artifacts such as pottery, tools, and structures to understand past human cultures and civilizations, often focusing on relatively recent historical periods. Paleoarchaeology, a subfield of archaeology, concentrates on much older evidence including fossilized bones, ancient stone tools, and hominin remains to study early human evolution and prehistoric life. Both fields utilize stratigraphy and dating techniques, but paleoarchaeology relies heavily on paleoanthropological data to reconstruct ancient environments and biological development.
Major Discoveries in Archaeology and Paleoarchaeology
Major discoveries in archaeology include the excavation of ancient cities like Pompeii, the unearthing of the Rosetta Stone, and the discovery of King Tutankhamun's tomb, providing critical insights into human history and culture. Paleoarchaeology, focusing on early human ancestors, has revealed important fossils like the Australopithecus afarensis ("Lucy") and the Homo habilis remains, illuminating human evolutionary origins. These findings collectively enhance understanding of both cultural development and physical evolution across prehistoric periods.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration in archaeology and paleoarchaeology integrates fields such as geology, biology, and anthropology to enhance understanding of human history and prehistory. Paleoarchaeology particularly benefits from advanced methods in paleontology and climate science to reconstruct ancient environments and human evolution. Collaborative efforts improve artifact analysis, dating techniques, and environmental reconstructions, driving comprehensive insights into past civilizations.
Career Paths and Specializations
Archaeology offers diverse career paths in cultural resource management, museum curation, and academic research, focusing on human history through artifact analysis. Paleoarchaeology specializes in studying ancient human ancestors using fossil evidence, leading to roles in paleoanthropological research and evolutionary biology. Both fields require strong skills in excavation, data analysis, and interdisciplinary collaboration, with paleoarchaeology emphasizing prehistoric time periods and evolutionary contexts.
Future Trends in Archaeology and Paleoarchaeology
Future trends in archaeology and paleoarchaeology emphasize integrating advanced technologies such as LiDAR, drone surveying, and AI-driven data analysis to enhance site discovery and artifact interpretation. The growing application of ancient DNA analysis and isotopic studies enables deeper insights into past human migrations, diet, and environmental interactions. Interdisciplinary collaboration and sustainable excavation practices are reshaping research methodologies to address both cultural heritage preservation and climate change impacts on archaeological sites.
Archaeology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com