Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities for all individuals, challenging social disparities and advocating fairness in wealth, status, and power distribution. This philosophy emphasizes the importance of reducing inequality to create a just and inclusive society where everyone can thrive. Explore the rest of the article to understand how egalitarianism can impact your life and society as a whole.
Table of Comparison
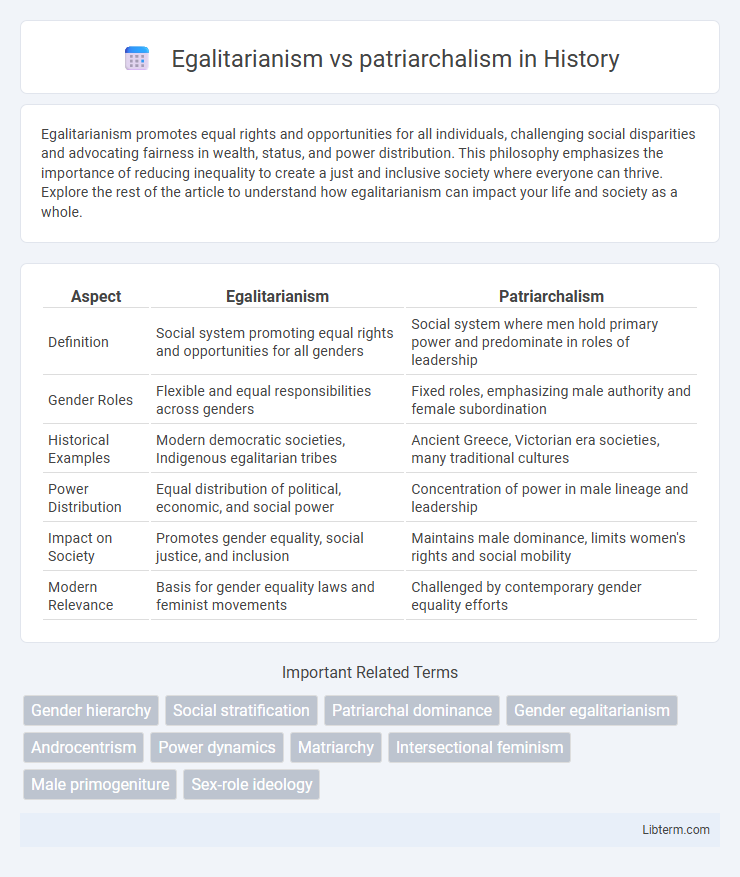
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Patriarchalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system promoting equal rights and opportunities for all genders | Social system where men hold primary power and predominate in roles of leadership |
| Gender Roles | Flexible and equal responsibilities across genders | Fixed roles, emphasizing male authority and female subordination |
| Historical Examples | Modern democratic societies, Indigenous egalitarian tribes | Ancient Greece, Victorian era societies, many traditional cultures |
| Power Distribution | Equal distribution of political, economic, and social power | Concentration of power in male lineage and leadership |
| Impact on Society | Promotes gender equality, social justice, and inclusion | Maintains male dominance, limits women's rights and social mobility |
| Modern Relevance | Basis for gender equality laws and feminist movements | Challenged by contemporary gender equality efforts |
Defining Egalitarianism and Patriarchalism
Egalitarianism defines a social framework where equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities are accessible to all individuals regardless of gender, promoting fairness and non-discrimination. Patriarchalism embodies a system dominated by male authority, often characterized by gender-based power imbalances and systemic privileges favoring men in political, social, and economic domains. These contrasting ideologies shape societal structures and influence gender roles, rights, and social interactions within diverse cultures.
Historical Roots of Patriarchal Societies
Patriarchal societies trace their roots to ancient agricultural communities where male dominance emerged due to roles in warfare, property control, and lineage inheritance. These historical structures enforced hierarchical gender roles that privileged men in governance, social status, and economic power. In contrast, egalitarianism challenges these norms by advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender.
Evolution of Egalitarian Ideals
Egalitarianism has evolved through philosophical, social, and political movements advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, race, or class, challenging the longstanding dominance of patriarchal systems that prioritize male authority and hierarchical structures. The rise of feminist theory, civil rights activism, and international human rights frameworks has significantly contributed to the diffusion of egalitarian ideals, promoting policies that aim to dismantle institutionalized inequality. This evolution reflects a growing recognition of diverse identities and the need for inclusive governance, reshaping societal norms toward fairness and equity.
Gender Roles in Patriarchal Systems
Patriarchal systems rigidly define gender roles by positioning men as dominant figures in familial and societal hierarchies, often assigning women to domestic and subordinate roles. These prescribed roles perpetuate gender inequality by limiting women's access to leadership, economic opportunities, and decision-making power. Research shows that gender role socialization in patriarchal cultures reinforces stereotypes, negatively impacting women's empowerment and societal participation.
Social Impact of Egalitarian Principles
Egalitarian principles promote social equity by ensuring equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, race, or socioeconomic status, leading to decreased discrimination and enhanced social cohesion. Societies embracing egalitarianism often experience improved educational outcomes, higher workforce participation rates among marginalized groups, and reduced income inequality. These social impacts contribute to sustainable development and foster a culture of mutual respect and inclusivity.
Power Dynamics and Authority Structures
Egalitarianism promotes equal distribution of power and authority, emphasizing shared decision-making and dismantling hierarchical structures that concentrate control in the hands of a few. In contrast, patriarchalism operates through centralized power dynamics, where authority is predominantly held by men, reinforcing gender-based hierarchies and limiting equitable participation. These contrasting frameworks shape societal organization by either fostering inclusive governance or perpetuating dominance through rigid authority channels.
Economic Implications: Equality vs. Hierarchy
Egalitarianism promotes equal economic opportunities and income distribution, fostering social mobility and reducing poverty through inclusive policies and fair wages. Patriarchalism enforces economic hierarchies that concentrate wealth and resources among dominant groups, often marginalizing women and lower social classes, resulting in persistent income inequality and limited access to economic power. The contrasting economic implications highlight that egalitarian systems tend to enhance overall economic growth and stability by maximizing human capital, whereas patriarchal structures often hinder broad-based economic development due to systemic exclusion.
Legal Frameworks: Rights and Representation
Egalitarian legal frameworks promote equal rights and representation regardless of gender, implementing policies that eliminate discrimination and ensure equitable participation in governance and public life. Patriarchal legal systems often enshrine male dominance by limiting women's rights to property, voting, and political representation, reinforcing systemic gender inequality. International conventions like CEDAW actively challenge patriarchal laws by advocating gender equality and legal reforms to secure women's full legal rights and representation.
Cultural Narratives and Identity Formation
Cultural narratives shape identity formation by reinforcing egalitarianism through stories of equality, shared power, and mutual respect, contrasting with patriarchalism that perpetuates male dominance, hierarchical roles, and gender-based norms. These narratives influence individual self-concept and community values, where egalitarian frameworks promote inclusivity and diverse representation, whereas patriarchal narratives often marginalize women and non-binary identities. The tension between these competing cultural scripts impacts socialization processes, affecting gender roles, expectations, and the distribution of power within societies.
Future Prospects: Shifting from Patriarchy to Egalitarianism
The future prospects of shifting from patriarchalism to egalitarianism depend heavily on ongoing social reforms, educational initiatives, and legal frameworks promoting gender equality. Technological advancements and global interconnectedness are accelerating awareness and activism, empowering marginalized groups and challenging traditional power structures. Sustained efforts in policy-making and cultural transformation are crucial to dismantling patriarchal systems and establishing inclusive societies based on equal rights and opportunities.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com