Feminism advocates for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging societal norms that perpetuate inequality. It intersects with various social, political, and economic issues to promote justice and inclusivity. Discover how feminism shapes your world and impacts ongoing movements by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
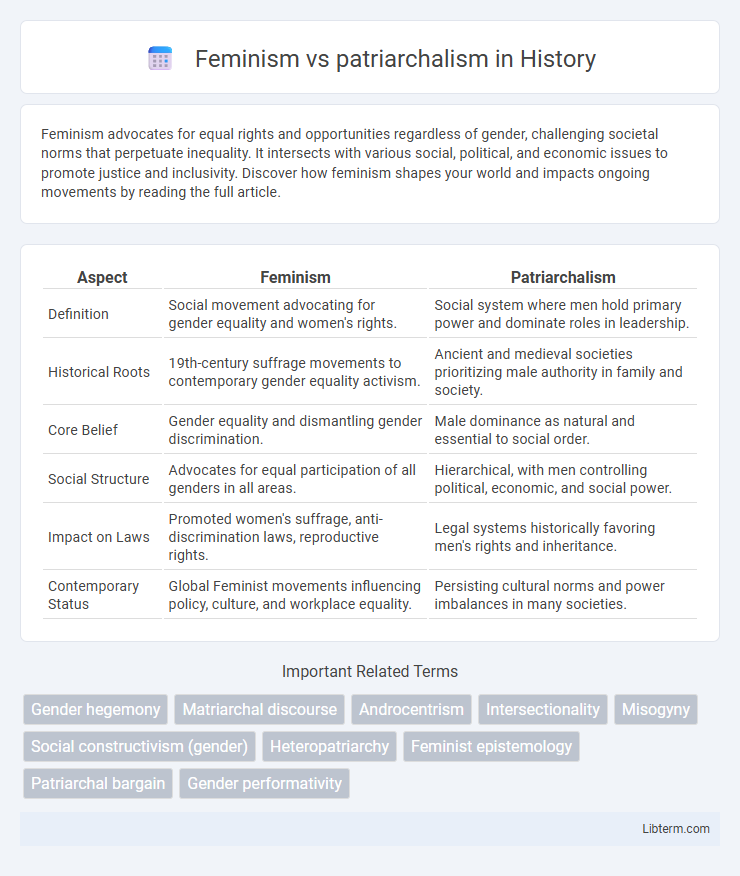
| Aspect | Feminism | Patriarchalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social movement advocating for gender equality and women's rights. | Social system where men hold primary power and dominate roles in leadership. |
| Historical Roots | 19th-century suffrage movements to contemporary gender equality activism. | Ancient and medieval societies prioritizing male authority in family and society. |
| Core Belief | Gender equality and dismantling gender discrimination. | Male dominance as natural and essential to social order. |
| Social Structure | Advocates for equal participation of all genders in all areas. | Hierarchical, with men controlling political, economic, and social power. |
| Impact on Laws | Promoted women's suffrage, anti-discrimination laws, reproductive rights. | Legal systems historically favoring men's rights and inheritance. |
| Contemporary Status | Global Feminist movements influencing policy, culture, and workplace equality. | Persisting cultural norms and power imbalances in many societies. |
Understanding Feminism: Principles and Goals
Feminism advocates for gender equality by challenging systemic discrimination and cultural norms rooted in patriarchalism, which upholds male dominance and power structures. Core principles include promoting women's rights, dismantling gender stereotypes, and fostering social, economic, and political equity across all genders. The goal of feminism is to create an inclusive society where individuals have equal opportunities regardless of gender identity or expression.
Defining Patriarchalism: Historical Roots and Impact
Patriarchalism is a social system rooted in historical structures where male dominance dictates political, economic, and cultural life, often marginalizing women and non-binary individuals. This system originated in ancient civilizations, evolving through legal codes and religious doctrines that reinforced male authority and inheritance rights. The impact of patriarchalism is evident in persistent gender inequalities, influencing contemporary issues such as wage gaps, limited leadership opportunities for women, and societal norms that uphold male privilege.
Key Differences Between Feminism and Patriarchalism
Feminism advocates for gender equality by challenging and dismantling patriarchal systems that maintain male dominance in social, political, and economic spheres. Patriarchalism reinforces traditional male authority and power structures, often marginalizing women and limiting their rights and opportunities. Key differences include feminism's emphasis on equal rights and social justice, contrasted with patriarchalism's focus on preserving established gender hierarchies and male privilege.
Societal Structures: How Patriarchalism Shapes Norms
Patriarchalism entrenches male dominance in societal structures by establishing norms that prioritize masculine authority and control over social, political, and economic spheres. These norms manifest in unequal power distribution, reinforcing gender roles that limit opportunities for women and marginalize non-conforming identities. The perpetuation of patriarchal values institutionalizes gender disparities, shaping laws, cultural practices, and organizational hierarchies that sustain systemic inequality.
Feminism’s Challenge to Traditional Gender Roles
Feminism challenges traditional gender roles by advocating for equality and dismantling patriarchal structures that limit opportunities based on sex. It questions the socially constructed norms that confine women to domestic spaces and men to public power, promoting inclusivity and diversity in gender expression. Key feminist theories emphasize autonomy, empowerment, and the deconstruction of binaries to foster equitable social, political, and economic participation.
Power Dynamics: Control, Authority, and Equality
Feminism challenges the entrenched power dynamics of patriarchalism by advocating for the redistribution of control and authority to achieve gender equality. Patriarchal systems prioritize male dominance and institutional control, often marginalizing women's voices and limiting their access to power. By promoting egalitarian principles, feminism seeks to dismantle hierarchical structures, ensuring equitable participation and authority across genders in social, political, and economic spheres.
Media Representation: Feminism vs Patriarchal Narratives
Media representation plays a crucial role in shaping public perception by either challenging or reinforcing patriarchal narratives. Feminist perspectives emphasize diverse, empowering portrayals of women that counter traditional stereotypes and promote gender equality. Patriarchal media often perpetuates limiting tropes, marginalizing women's voices and maintaining dominant power structures.
Global Perspectives: Feminism and Patriarchalism Across Cultures
Feminism challenges patriarchalism by advocating for gender equality and dismantling systems of male dominance prevalent in diverse cultural contexts worldwide. While patriarchal structures manifest uniquely across societies, common patterns include control over women's bodies, limited access to education, and unequal political representation. Global perspectives on feminism emphasize intersectionality, recognizing how race, class, and ethnicity intersect with gender to shape varied experiences of oppression and resistance.
The Role of Legislation in Shaping Gender Equality
Legislation plays a crucial role in shaping gender equality by dismantling patriarchal norms and establishing legal protections for women's rights. Anti-discrimination laws, equal pay acts, and policies addressing gender-based violence create frameworks that challenge systemic inequalities and promote feminist principles. Legal reforms not only empower marginalized genders but also foster cultural shifts towards inclusivity and fairness in society.
Future Outlook: Navigating the Path Toward Gender Justice
Feminism's future outlook emphasizes dismantling patriarchal structures through inclusive policies and intersectional advocacy, aiming to achieve gender justice globally. Advancements in technology and education are pivotal in empowering marginalized voices, fostering equality across social, economic, and political spheres. Ongoing challenges include resisting entrenched patriarchal norms and ensuring diverse representation in leadership to create sustainable systemic change.
Feminism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com