Matriarchalism refers to a social system where women, particularly mothers, hold primary power in political leadership, moral authority, social privilege, and control of property. This structure contrasts with patriarchal systems and often emphasizes the importance of maternal influence in societal organization. Explore the rest of the article to understand how matriarchalism shapes communities and its relevance in modern discussions on gender and power.
Table of Comparison
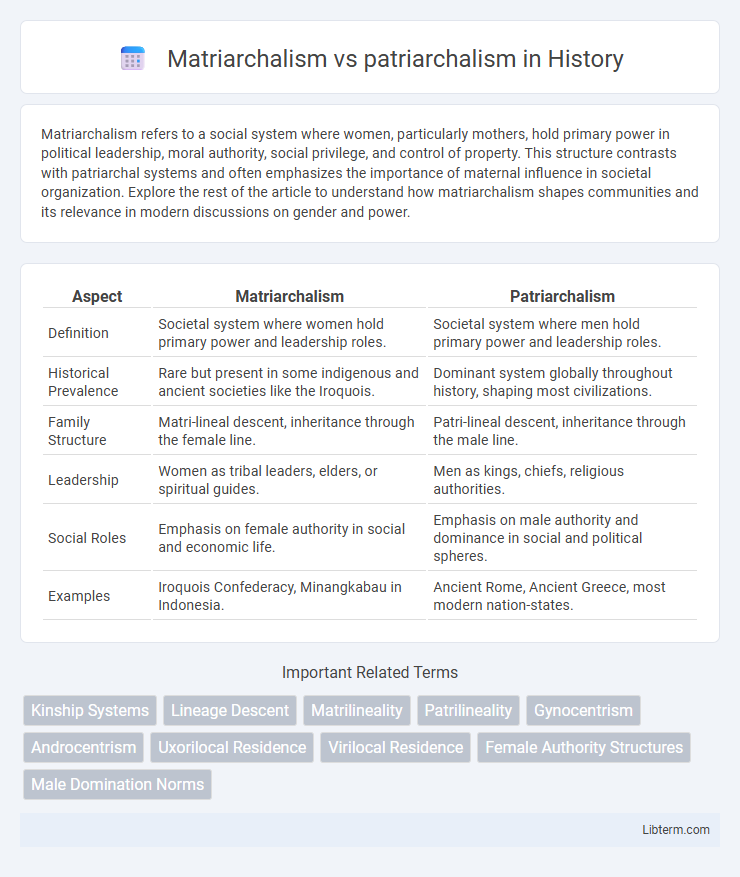
| Aspect | Matriarchalism | Patriarchalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Societal system where women hold primary power and leadership roles. | Societal system where men hold primary power and leadership roles. |
| Historical Prevalence | Rare but present in some indigenous and ancient societies like the Iroquois. | Dominant system globally throughout history, shaping most civilizations. |
| Family Structure | Matri-lineal descent, inheritance through the female line. | Patri-lineal descent, inheritance through the male line. |
| Leadership | Women as tribal leaders, elders, or spiritual guides. | Men as kings, chiefs, religious authorities. |
| Social Roles | Emphasis on female authority in social and economic life. | Emphasis on male authority and dominance in social and political spheres. |
| Examples | Iroquois Confederacy, Minangkabau in Indonesia. | Ancient Rome, Ancient Greece, most modern nation-states. |
Defining Matriarchalism and Patriarchalism
Matriarchalism is a social system in which women, particularly mothers, hold primary power in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property. Patriarchalism, in contrast, is characterized by male dominance in governance, inheritance, and societal norms defining authority and family structure. The distinction hinges on gender-based power distribution, influencing cultural practices and legal frameworks globally.
Historical Roots of Matriarchal and Patriarchal Societies
Matriarchal societies trace their historical roots to early human civilizations where women often held central roles in social, economic, and religious life, particularly in agrarian and tribal communities such as the Iroquois and the Mosuo. Patriarchal systems emerged prominently with the development of hereditary states and organized religions, as witnessed in ancient Mesopotamia and classical Greece, where male dominance structured family, property ownership, and governance. These divergent social frameworks reflect evolving power dynamics influenced by environmental conditions, economic needs, and cultural practices across human history.
Power Structures: Matriarchal vs Patriarchal Systems
Matriarchal systems centralize power within women, emphasizing maternal lineage, communal decision-making, and cooperation, while patriarchal systems concentrate authority in men, often through hierarchical governance and control over resources. Power in matriarchal societies typically aligns with kinship ties and social harmony, contrasting with patriarchal structures that prioritize dominance, inheritance, and political control. These divergent frameworks shape cultural norms, family roles, and leadership models across different civilizations and historical periods.
Gender Roles and Expectations in Each System
Matriarchalism assigns leadership and property inheritance predominantly to women, emphasizing communal decision-making and nurturing roles, while patriarchalism centers authority and lineage through men, enforcing traditional male dominance in political, economic, and familial spheres. Gender roles in matriarchal systems often celebrate female autonomy and caregiving responsibilities, contrasting with patriarchal expectations that prioritize male authority, protection, and provision. These divergent frameworks shape societal norms, influencing individual behavior, power dynamics, and the distribution of resources based on gender.
Family Dynamics and Lineage Transmission
Matriarchalism centers family dynamics around female authority, with lineage and inheritance typically traced through the maternal line, fostering strong female bonds and communal child-rearing. Patriarchalism emphasizes male dominance in familial roles, where lineage transmission follows the paternal line, reinforcing male authority and inheritance rights. These contrasting systems shape social roles, familial responsibilities, and cultural values regarding descent and kinship.
Impact on Social Organization and Governance
Matriarchalism often centers social organization around maternal lineage and communal decision-making, promoting egalitarian governance and shared leadership roles among women. Patriarchalism structures society with male dominance in leadership and inheritance, concentrating power within patriarchal family units and hierarchical institutions. These differing frameworks shape gender roles, authority distribution, and influence political and legal systems in diverse cultural contexts.
Influence on Religion and Cultural Narratives
Matriarchalism often shapes religions and cultural narratives by emphasizing feminine divine figures, maternal authority, and communal harmony, influencing myths and rituals centered around fertility and earth goddesses. Patriarchalism typically reinforces male dominance in religious hierarchies and stories, promoting patriarchal gods and heroes while legitimizing male authority in social and spiritual domains. These contrasting frameworks deeply affect gender roles, power structures, and value systems within societies worldwide.
Economic Consequences of Matriarchal and Patriarchal Models
Matriarchal economic systems often emphasize communal resource management and equitable distribution, fostering social welfare and sustainability through cooperative labor and shared property ownership. Patriarchal economic models typically prioritize individual wealth accumulation, hierarchical control, and inheritance patterns that reinforce male-dominated leadership and economic inequality. These contrasting frameworks influence labor division, property rights, and access to economic opportunities, shaping societal development and gender-based economic disparities.
Psychological Effects and Identity Formation
Matriarchalism often fosters a nurturing environment that enhances emotional intelligence and promotes identity formation through communal support and egalitarian values. Patriarchalism typically emphasizes hierarchical structures, which can influence psychological development by reinforcing gender roles and authority-based identity constructs. Both systems deeply impact self-concept, mental health, and social behavior by shaping individual and collective identity frameworks.
Contemporary Debates and Future Perspectives
Contemporary debates on matriarchalism versus patriarchalism examine power dynamics, gender roles, and social structures, emphasizing the impact of patriarchy on systemic inequality and exploring matriarchal societies as models for egalitarian governance. Feminist theorists and anthropologists analyze historical evidence and cultural narratives to challenge patriarchal dominance and highlight matriarchal values such as cooperation and communal decision-making. Future perspectives envision hybrid social frameworks integrating matriarchal principles to promote gender equity, social justice, and sustainable community development in global policy discourses.
Matriarchalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com