Vestal Virgins were priestesses of Vesta, goddess of the hearth, in ancient Rome, entrusted with maintaining the sacred fire that symbolized the city's eternal life. Their unique role required a vow of chastity for thirty years, during which they received privileges and protections uncommon for Roman women. Discover how the Vestal Virgins shaped Roman religion, law, and society throughout history in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
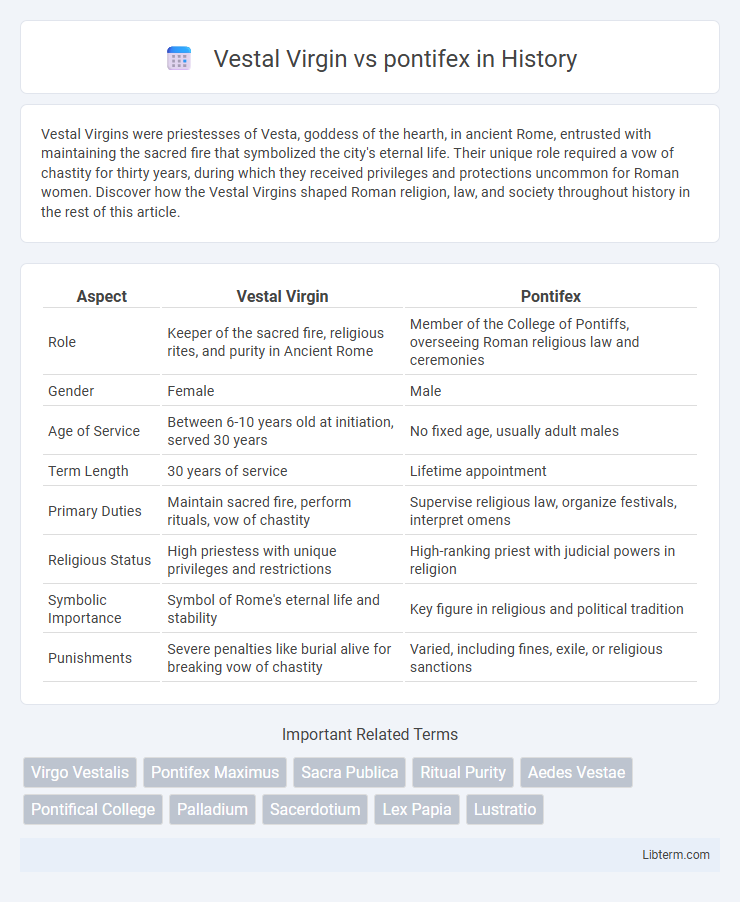
| Aspect | Vestal Virgin | Pontifex |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Keeper of the sacred fire, religious rites, and purity in Ancient Rome | Member of the College of Pontiffs, overseeing Roman religious law and ceremonies |
| Gender | Female | Male |
| Age of Service | Between 6-10 years old at initiation, served 30 years | No fixed age, usually adult males |
| Term Length | 30 years of service | Lifetime appointment |
| Primary Duties | Maintain sacred fire, perform rituals, vow of chastity | Supervise religious law, organize festivals, interpret omens |
| Religious Status | High priestess with unique privileges and restrictions | High-ranking priest with judicial powers in religion |
| Symbolic Importance | Symbol of Rome's eternal life and stability | Key figure in religious and political tradition |
| Punishments | Severe penalties like burial alive for breaking vow of chastity | Varied, including fines, exile, or religious sanctions |
Introduction to the Vestal Virgin and Pontifex Roles
Vestal Virgins were priestesses of Vesta, goddess of the hearth, entrusted with maintaining the sacred fire in ancient Rome, symbolizing the city's eternal life and security. Pontifices, including the chief pontifex, were members of the College of Pontiffs responsible for overseeing Roman religious rituals, laws, and calendar, ensuring harmony between the state and the gods. Both roles were central to Roman religion, with Vestal Virgins dedicated to purity and ritual service, and pontifices managing broader religious authority and practices.
Historical Origins and Development
The Vestal Virgins, established around 7th century BCE in ancient Rome, served as priestesses dedicated to Vesta, the goddess of the hearth, symbolizing the city's security and eternal flame, while the Pontifex, originating during the Roman Kingdom period, was a high-ranking male priest responsible for overseeing religious ceremonies and maintaining the pax deorum (peace with the gods). The Vestal Virgins' unique role involved strict vows of chastity and lifelong service, reflecting their ritual importance and societal status, whereas the Pontifex, especially the Pontifex Maximus, evolved into a politically influential figure managing the Roman religious hierarchy. Both institutions developed alongside Rome's religious and political structures, highlighting the intertwining of spirituality, law, and governance in ancient Roman civilization.
Selection and Initiation Processes
Vestal Virgins were chosen between the ages of 6 and 10 from patrician families through a highly selective process overseen by the Pontifex Maximus, emphasizing purity and social status. Their initiation involved a secretive ritual conferring lifelong chastity and sacred duties guarding the sacred fire of Vesta. In contrast, pontifices were adult males, often from elite Roman families, appointed by co-optation within the college and initiated through formal ceremonies signifying their authority in religious law and ritual administration.
Religious Duties and Ritual Responsibilities
Vestal Virgins were priestesses in ancient Rome entrusted with maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta, symbolizing the city's eternal life, and performing essential rites like preparing mola salsa for sacrifices. Pontifices, led by the Pontifex Maximus, were senior priests responsible for overseeing the Roman state's religious calendar, supervising public rituals, and interpreting sacred law. While Vestal Virgins focused on preserving purity and domestic religious rites, pontifices managed broader religious administration and legal frameworks within Roman religion.
Social Status and Legal Privileges
Vestal Virgins held a unique and elevated social status in ancient Rome, distinguished by their lifelong vow of chastity and exclusive role in maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta, granting them privileges such as immunity from certain legal penalties and the ability to own property independently. Pontifices, as male members of the College of Pontiffs, wielded significant religious and political influence, overseeing public rites and laws but lacked the personal legal immunities reserved for Vestals. While both held esteemed religious roles, Vestal Virgins enjoyed exceptional legal protections and social reverence due to their sacred duties and symbolic purity.
Gender Roles within Roman Religion
Vestal Virgins, exclusively female priestesses, were responsible for maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta and symbolized purity and domestic stability within Roman religion. Pontifices, predominantly male priests, oversaw broader religious duties including public rituals and legal matters related to religion, reflecting the gendered division of religious authority. This distinction highlights the gender-specific roles where Vestal Virgins embodied a unique, revered spiritual purity, while pontifices exercised institutional religious power.
Vestal Virgin vs Pontifex: Power and Influence
Vestal Virgins held a unique religious authority in ancient Rome, serving as priestesses dedicated to Vesta, goddess of the hearth, and were entrusted with maintaining the sacred fire, symbolizing the security of the state. Pontifices formed the principal college of Roman priests, wielding extensive power over legal and religious policy, including calendar regulation and public morality enforcement, directly influencing Rome's political and religious spheres. While Vestal Virgins exercised spiritual influence predominantly through ritual purity and state protection, Pontifices commanded broader institutional power that shaped Rome's religious governance and societal norms.
Symbols, Attire, and Public Perception
Vestal Virgins symbolized purity and chastity, wearing the distinctive suffibulum and tunica alba, a simple white dress denoting their sacred vow, while their role included tending the sacred fire and performing rituals central to Rome's spiritual well-being. Pontifices, as chief priests, donned the toga praetexta with a purple border and carried a lituus, signifying their authority in religious law and state ceremonies, often overseeing public rites and temple functions. Public perception revered Vestal Virgins as paragons of virtue and guardians of Rome's eternal flame, whereas Pontifices commanded respect as powerful intermediaries between the gods and the Roman people, wielding substantial religious and political influence.
End of Service and Career Aftermath
Vestal Virgins concluded their 30-year service with full freedom to marry, often receiving pensions and respect in Roman society due to their sacred role in maintaining the eternal flame of Vesta. Pontifices, including the chief Pontifex Maximus, served lifelong, with no formal retirement, and their careers often culminated in influential political or religious authority, shaping Roman law and state religion. Upon the end of their tenure or death, pontifices left significant legacies within religious institutions, while Vestal Virgins transitioned into civilian life with social benefits reflecting their unique status.
Lasting Legacy in Roman History
The Vestal Virgins maintained Rome's sacred fire and symbolized purity, influencing religious practices for over a millennium until the late 4th century AD. The Pontifex, particularly the Pontifex Maximus, wielded significant political and religious power as chief priest, shaping Roman law and state religion extensively throughout the Republic and Empire. Both institutions left enduring legacies by embedding religious authority into Rome's cultural identity and governance structures.
Vestal Virgin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com