Tribune plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion through its influential articles and editorials. It covers a wide range of topics, offering in-depth analysis and up-to-date news that keeps readers well-informed. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Tribune can enhance Your understanding of current events.
Table of Comparison
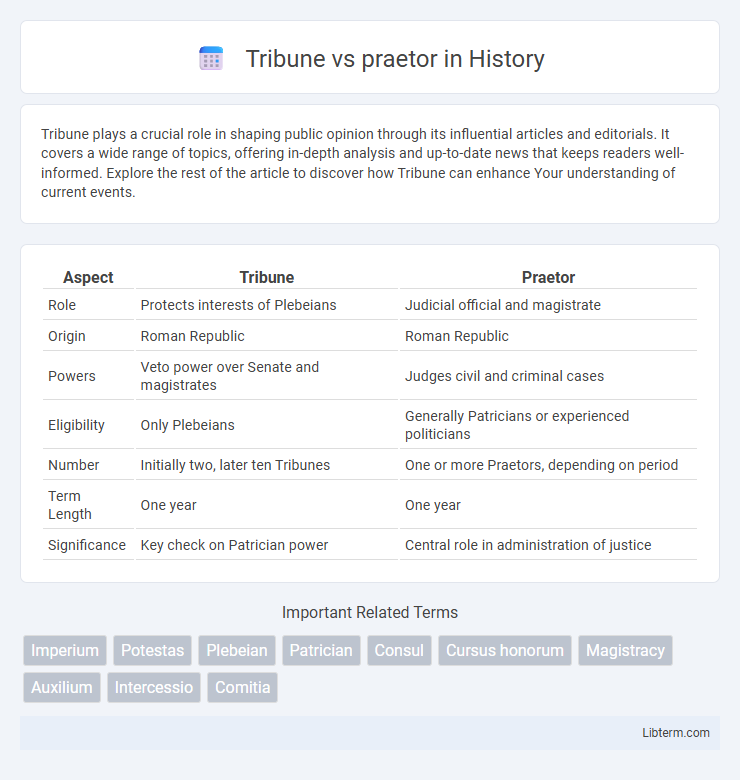
| Aspect | Tribune | Praetor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Protects interests of Plebeians | Judicial official and magistrate |
| Origin | Roman Republic | Roman Republic |
| Powers | Veto power over Senate and magistrates | Judges civil and criminal cases |
| Eligibility | Only Plebeians | Generally Patricians or experienced politicians |
| Number | Initially two, later ten Tribunes | One or more Praetors, depending on period |
| Term Length | One year | One year |
| Significance | Key check on Patrician power | Central role in administration of justice |
Introduction to Tribune and Praetor
Tribunes were elected officials in ancient Rome who primarily represented the interests of the plebeians, wielding the power to veto decisions by magistrates to protect common citizens. Praetors served as judicial magistrates responsible for administering justice and overseeing legal proceedings, often acting as judges or governors in Roman provinces. Both roles were crucial in balancing power within the Roman Republic, with tribunes championing popular rights and praetors ensuring legal order.
Historical Origins of Tribune and Praetor
The tribunes of the plebs originated in early Rome around 494 BCE as officials elected to protect the interests of the common people against patrician magistrates, playing a key role in the struggle of the orders. Praetors emerged later, circa 367 BCE, initially established through the Licinian-Sextian laws to serve as judicial magistrates with imperium, complementing consuls by overseeing civil law and presiding over courts. Both offices reflect early Roman efforts to balance political power and provide specialized governance, with tribunes defending plebeian rights and praetors administering justice.
Roles and Responsibilities: Tribune vs Praetor
Tribunes served as the representatives of the plebeians, wielding veto power over magistrates' decisions to protect common citizens' rights and convene the Plebeian Council. Praetors functioned as judicial magistrates responsible for overseeing civil and criminal courts, issuing edicts that guided legal procedures throughout the Roman Republic. While tribunes primarily safeguarded popular interests and political rights, praetors administered justice and facilitated legal order within Roman governance.
Election and Appointment Processes
Tribunes were elected annually by the Plebeian Council, emphasizing the representation of plebeian interests in Roman government. Praetors were appointed through election by the Centuriate Assembly, reflecting their role as senior magistrates with judicial powers. The election of tribunes ensured a direct plebeian voice, whereas praetors underwent a competitive electoral process among Rome's higher classes to secure legal authority.
Powers and Authority in Roman Government
Tribunes of the Plebs wielded sacrosanct authority, granting veto power over Senate decisions and protection for plebeians against magistrates' actions, while praetors primarily exercised judicial powers, overseeing civil law and acting as judges in legal disputes. Tribune powers were rooted in their role as protectors of the common people with political influence, whereas praetors held imperium, enabling them to command armies and govern provinces. Both offices were integral to the balance of power in Roman government, with tribunician veto shaping legislation and praetorian imperium enforcing legal and military authority.
Social Class and Eligibility
Tribunes were exclusively plebeians, representing the interests of the common people in the Roman Republic, while praetors were primarily from the patrician or wealthy plebeian classes, serving as senior magistrates. Eligibility for tribunes required plebeian status and was often linked to political activism within the plebeian assembly. In contrast, praetors had to possess prior experience in lower magistracies and were elected by the Centuriate Assembly, reflecting a higher social standing and political influence.
Legal Functions: Tribune vs Praetor
Tribunes wielded significant legal power by protecting the rights of plebeians through their veto authority over magistrates' decisions and the ability to convene the Plebeian Council to pass laws. Praetors primarily administered justice, presiding over civil and criminal courts, issuing edicts that shaped Roman law, and overseeing the execution of legal procedures. While tribunes served as defenders of the common people with political and legal influence, praetors functioned as judicial officials ensuring legal order and interpretation within Rome's evolving legal system.
Influence on Roman Politics
Tribunes wielded significant influence in Roman politics through their power to veto Senate decisions and protect the interests of the plebeians, serving as a critical check on patrician authority. Praetors primarily focused on judicial functions and held imperium, enabling them to govern provinces and command armies, thereby shaping legal precedents and provincial administration. The balance between tribunes' political advocacy and praetors' administrative authority underpinned the complex governance structure of the Roman Republic.
Key Differences and Similarities
The Tribune and Praetor were both important magistrates in ancient Rome, with Tribunes representing the plebeians and possessing veto power to protect their interests, while Praetors primarily administered justice and commanded armies. Both held significant political and legal authority, but Tribunes were sacrosanct and could not be harmed, emphasizing their protective role, whereas Praetors operated within the judicial and military domains. Despite these differences, both offices contributed to Rome's complex system of checks and balances by balancing popular representation with administrative and military responsibilities.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Governance
Tribunes, as protectors of the plebeian class in Roman Republic, established early principles of political representation and veto power that influence modern concepts of checks and balances. Praetors contributed significantly to the development of Roman law, with their judicial powers laying the groundwork for contemporary legal systems and procedural law. The legacy of tribunes and praetors is evident in modern governance through institutional safeguards for minority rights and structured judicial authorities.
Tribune Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com