The King's Council served as a vital advisory body, shaping the decisions and policies of medieval monarchs through strategic counsel and governance. Understanding the intricate roles and influences within this council reveals how royal power was exercised and balanced in historical monarchies. Explore the detailed dynamics and significance of the King's Council in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
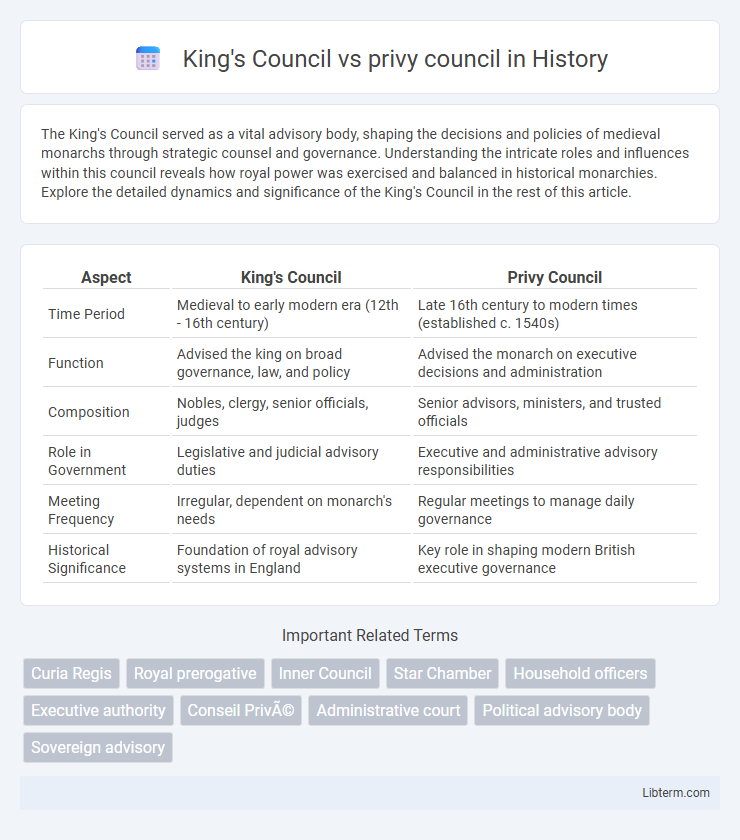
| Aspect | King's Council | Privy Council |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Medieval to early modern era (12th - 16th century) | Late 16th century to modern times (established c. 1540s) |
| Function | Advised the king on broad governance, law, and policy | Advised the monarch on executive decisions and administration |
| Composition | Nobles, clergy, senior officials, judges | Senior advisors, ministers, and trusted officials |
| Role in Government | Legislative and judicial advisory duties | Executive and administrative advisory responsibilities |
| Meeting Frequency | Irregular, dependent on monarch's needs | Regular meetings to manage daily governance |
| Historical Significance | Foundation of royal advisory systems in England | Key role in shaping modern British executive governance |
Introduction to Royal Councils
The King's Council, established during medieval England, served as the monarch's advisory body, integrating nobles, clergy, and officials to guide royal decisions on governance and justice. The Privy Council, emerging in the Tudor period, evolved as a smaller, more efficient group providing confidential counsel directly to the sovereign on state affairs and administration. Both councils shaped the development of the English government by influencing policy, law, and royal prerogative throughout history.
Historical Origins of the King’s Council
The King's Council, originating in medieval England, served as a royal advisory body composed of nobles and clergy who counseled the monarch on matters of governance and justice. This early council evolved from the king's household court and was instrumental in shaping the formation of the Privy Council by the Tudor period. The Privy Council inherited the King's Council's functions but became a more formalized executive body handling day-to-day administrative and political decisions.
Evolution and Structure of the Privy Council
The King's Council evolved from a medieval advisory body of nobles and clergy into the Privy Council, a more formalized and institutionalized group entrusted with executive authority and confidential state matters. The Privy Council's structure became complex, consisting of senior politicians, judges, and officials who guided the monarch on policy, administration, and legal issues. Over centuries, it transitioned from a broad royal council into a streamlined executive council, reflecting shifts toward centralized governmental control.
Key Differences Between King’s Council and Privy Council
The King's Council primarily functioned as an advisory body to medieval English monarchs, composed of nobles, clergy, and royal officials, whereas the Privy Council emerged later as a more centralized and formalized institution focused on executing royal decisions and governance. The King's Council lacked a fixed membership or regular meetings, emphasizing broader counsel, while the Privy Council operated with a defined group of trusted advisors with ongoing administrative responsibilities. The Privy Council also played a crucial role in judicial and executive matters, shaping the development of modern governmental systems.
Roles and Functions of the King’s Council
The King's Council primarily served as an advisory body to the monarch, offering counsel on matters of governance, law, and military strategy, while overseeing the administration of royal justice. It played a critical role in the formulation of policy, management of local officials, and enforcement of the king's authority throughout the realm. Unlike the Privy Council, which evolved into a more formal cabinet handling daily executive decisions and privacy of state matters, the King's Council functioned as a broader, less specialized advisory assembly rooted in medieval governance.
Powers and Responsibilities of the Privy Council
The Privy Council holds significant executive powers, including advising the monarch on the issuance of royal proclamations, exercising judicial functions as the final court of appeal, and overseeing the implementation of government policies. Unlike the King's Council, which historically focused on broad governance and military counsel, the Privy Council specifically manages matters related to state security, the administration of colonial affairs, and acts as a formal advisory body to the Crown. Responsibilities also encompass issuing Orders in Council, supervising government departments, and authorizing urgent legislative actions without the immediate approval of Parliament.
Notable Members and Influencers
The King's Council historically included notable figures such as Archbishop Thomas Cranmer and Sir Thomas More, whose roles shaped early English governance and religious reform. The Privy Council features influential members like Sir Francis Walsingham and Edward Coke, who played crucial roles in Elizabethan politics and the development of common law. These councils influenced royal decisions with the expertise and political power of their distinguished members across different periods.
Impact on Monarchical Governance
The King's Council served as an early advisory body composed mainly of nobles and clergy, providing direct influence on royal decisions and reinforcing centralized monarchical authority in medieval England. The Privy Council evolved into a smaller, more specialized group of trusted advisors, enhancing efficient governance and enabling quicker responses to political and administrative matters. This transition from the King's Council to the Privy Council marked a significant shift towards modern executive decision-making, strengthening the monarch's control over government affairs.
Transition from King’s Council to Privy Council
The transition from the King's Council to the Privy Council marked a significant evolution in English governance during the Tudor period, shifting from a broad advisory group to a smaller, more specialized body directly serving the monarch. The Privy Council centralized decision-making, enhancing administrative efficiency and royal control over legal, financial, and political matters. This transformation reflected the increasing complexity of government and the need for a more streamlined, confidential advisory system by the 16th century.
Legacy and Modern Relevance
The King's Council, a medieval advisory body composed of nobles and clergy, laid the foundation for modern governance by centralizing royal authority and shaping early administrative law. Its legacy endures in the Privy Council, which evolved into a formal institution advising the British monarch on constitutional and executive matters, reflecting centuries of legal and political continuity. Today, the Privy Council retains ceremonial importance and judicial functions, underscoring its enduring relevance in the United Kingdom's constitutional framework.
King's Council Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com