The British East India Company played a crucial role in establishing British trade dominance in India from the early 17th century to the mid-19th century. Its extensive network of trading posts and political influence paved the way for British colonial rule, deeply affecting India's economy and society. Discover how the company's legacy shaped modern India in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
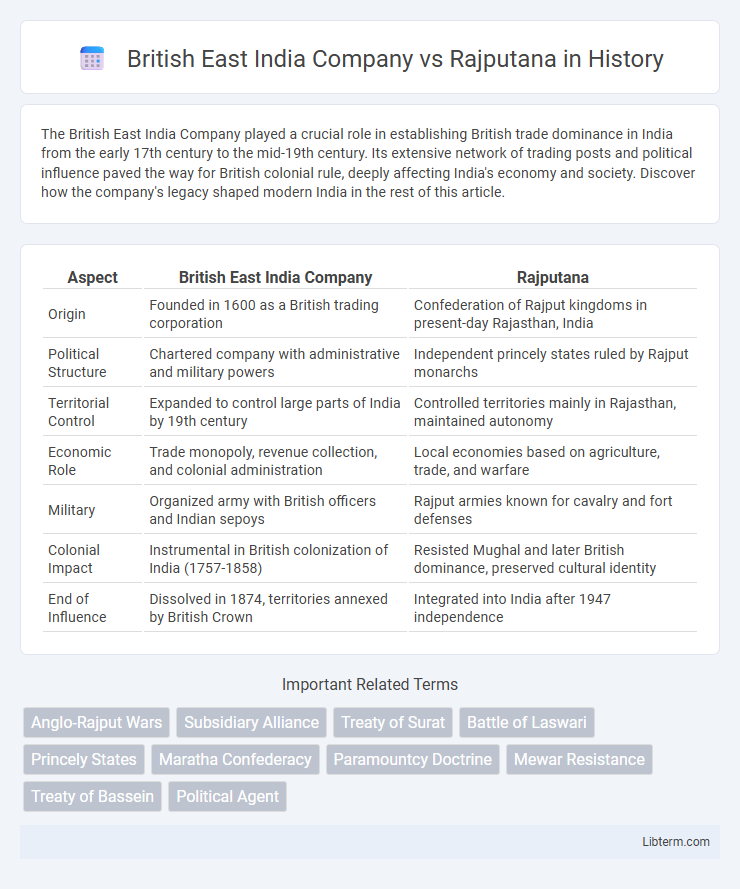
| Aspect | British East India Company | Rajputana |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Founded in 1600 as a British trading corporation | Confederation of Rajput kingdoms in present-day Rajasthan, India |
| Political Structure | Chartered company with administrative and military powers | Independent princely states ruled by Rajput monarchs |
| Territorial Control | Expanded to control large parts of India by 19th century | Controlled territories mainly in Rajasthan, maintained autonomy |
| Economic Role | Trade monopoly, revenue collection, and colonial administration | Local economies based on agriculture, trade, and warfare |
| Military | Organized army with British officers and Indian sepoys | Rajput armies known for cavalry and fort defenses |
| Colonial Impact | Instrumental in British colonization of India (1757-1858) | Resisted Mughal and later British dominance, preserved cultural identity |
| End of Influence | Dissolved in 1874, territories annexed by British Crown | Integrated into India after 1947 independence |
Origins and Rise of the British East India Company
The British East India Company was founded in 1600 as a trading corporation seeking profits from India's rich resources, establishing fortified trading posts along the subcontinent's coastline. Rajputana, a region in northwest India dominated by Rajput warrior clans, maintained a complex network of forts and kingdoms with a strong martial tradition. The Company's rise in Rajputana began through strategic alliances, military engagements, and treaties that gradually expanded British influence, supplanting traditional Rajput sovereignty.
Historical Overview of Rajputana Kingdoms
The Rajputana Kingdoms, a cluster of warrior states in northwest India, emerged prominently from the 7th century and were known for their martial culture and fierce resistance against invasions. During the 17th and 18th centuries, these kingdoms maintained relative autonomy despite increasing pressure from Mughal dominance and later, the British East India Company's expansion. The Rajputs formed strategic alliances and occasional conflicts with the British, balancing between cooperation and resistance to protect their sovereignty during the colonial period.
Initial Encounters: British and Rajputana Relations
The initial encounters between the British East India Company and Rajputana in the early 18th century were marked by strategic alliances and cautious diplomacy, as the Company sought to expand its influence in the region. British officials engaged with Rajput rulers to negotiate trade rights and military support, leveraging the fragmented political landscape of Rajputana's princely states. These early interactions laid the groundwork for eventual British political dominance through subsidiary alliances and treaties with Rajput leaders.
Political Motivations and Strategic Importance
The British East India Company sought to expand its control over Rajputana due to its strategic location on key trade routes linking northern India to the Deccan plateau. Political motivations included dismantling the fragmented Rajput alliances to prevent any unified resistance against Company expansion and to secure puppet rulers loyal to British interests. Establishing dominance in Rajputana also provided the Company with valuable access to regional resources and military recruitment opportunities essential for consolidating power in India.
Military Engagements and Key Battles
The British East India Company engaged in several pivotal military campaigns against Rajputana's princely states during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, including the Battle of Laswari (1803), which marked a significant British victory against the Rajput forces allied with the Marathas. The Siege of Bharatpur (1825-1826) was another crucial conflict where the Company's artillery and superior siege tactics overcame the strong Rajput fortifications, solidifying British dominance in the region. These battles exemplified the Company's strategic military approach, combining disciplined infantry, advanced artillery, and alliances to subdue the Rajputana kingdoms and integrate them into the British Indian Empire.
Diplomacy, Treaties, and Alliances
The British East India Company employed strategic diplomacy to establish influence over Rajputana by negotiating treaties that often involved subsidiary alliances and territorial exchanges, ensuring political and military cooperation. Various Rajput states, such as Jaipur and Udaipur, signed agreements that recognized British suzerainty while retaining nominal autonomy, facilitating the Company's indirect rule. These alliances bolstered British dominance in Northern India while maintaining relative stability in the region through a network of loyal princely states.
Economic Impacts on Rajputana under Company Rule
The British East India Company's control over Rajputana drastically altered traditional trade networks, integrating the region into the colonial economy through monopolized markets and imposed revenue systems. Local industries, particularly textiles and handicrafts, suffered due to British import policies favoring manufactured goods from Britain, leading to economic decline and unemployment among artisans. Company-imposed land revenue demands and exploitation disrupted agrarian stability, exacerbating poverty and undermining Rajputana's pre-existing feudal economy.
Social and Cultural Consequences of British Influence
The British East India Company's expansion into Rajputana disrupted traditional Rajput social hierarchies, leading to shifts in land ownership and altered caste dynamics as British policies favored cooperative princes. British educational reforms introduced Western ideas, undermining indigenous cultural practices and promoting English language and legal systems that reshaped Rajputana's social fabric. These influences marginalized local customs and accelerated the integration of Rajputana into the colonial economy, significantly transforming Rajput identity and cultural expressions.
Resistance, Collaboration, and Local Responses
The British East India Company faced fierce resistance from Rajputana's warrior clans, who utilized guerrilla tactics and fortified hill forts to challenge colonial expansion. Some Rajput rulers engaged in strategic collaboration, signing treaties that preserved local autonomy while facilitating British trade interests. Local responses varied widely, with segments of the population supporting the British for economic benefits, while others remained staunchly loyal to Rajput sovereignty and cultural traditions.
Legacy of British East India Company in Rajputana
The British East India Company established a network of political alliances and trade relations in Rajputana during the 18th and 19th centuries, significantly shaping the region's administrative and economic structures. The Company's legacy includes the introduction of centralized governance, modernization of revenue systems, and the integration of Rajputana princely states into the British colonial framework. This influence laid the groundwork for Rajputana's eventual incorporation into British India, impacting its sociopolitical landscape well into the colonial period.
British East India Company Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com