The Maratha Confederacy was a powerful and decentralized Hindu state that dominated much of India during the 17th and 18th centuries. Known for its military prowess and strategic governance, it played a crucial role in weakening Mughal dominance. Discover more about the rise, influence, and legacy of the Maratha Confederacy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
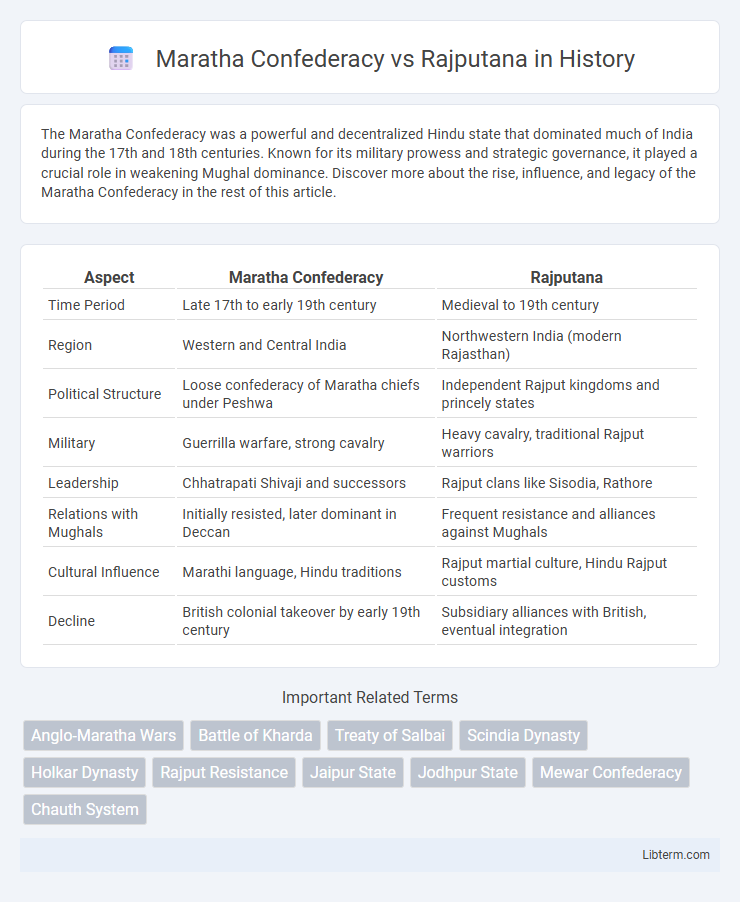
| Aspect | Maratha Confederacy | Rajputana |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Late 17th to early 19th century | Medieval to 19th century |
| Region | Western and Central India | Northwestern India (modern Rajasthan) |
| Political Structure | Loose confederacy of Maratha chiefs under Peshwa | Independent Rajput kingdoms and princely states |
| Military | Guerrilla warfare, strong cavalry | Heavy cavalry, traditional Rajput warriors |
| Leadership | Chhatrapati Shivaji and successors | Rajput clans like Sisodia, Rathore |
| Relations with Mughals | Initially resisted, later dominant in Deccan | Frequent resistance and alliances against Mughals |
| Cultural Influence | Marathi language, Hindu traditions | Rajput martial culture, Hindu Rajput customs |
| Decline | British colonial takeover by early 19th century | Subsidiary alliances with British, eventual integration |
Origins and Formation of the Maratha Confederacy
The Maratha Confederacy originated in the 17th century under the leadership of Shivaji Maharaj, who established a strong, decentralized power base in the western Deccan region by uniting various Maratha chiefs. The confederacy expanded through a network of semi-autonomous chiefs known as sardars who controlled different territories, strengthening Maratha influence across central and northern India, including incursions into Rajputana. This political and military coalition challenged Rajputana's traditional Rajput kingdoms by asserting Maratha dominance through strategic alliances and coercive campaigns.
The Rise of Rajputana States
The rise of Rajputana states during the decline of the Mughal Empire led to increased resistance against the expanding Maratha Confederacy in the 18th century. Rajputana, comprising kingdoms like Mewar, Jaipur, and Jodhpur, leveraged strategic alliances and fortified defenses to maintain autonomy and counter Maratha incursions. This period marked a crucial consolidation of Rajput power that challenged Maratha dominance in northern India.
Political Structure and Governance Comparison
The Maratha Confederacy operated under a decentralized political structure with semi-autonomous chiefs governing regions under the nominal authority of the Peshwa, emphasizing a confederation model that allowed flexible alliances and military coordination. In contrast, Rajputana was characterized by a collection of independent princely states led by Rajput rulers who maintained hereditary sovereignty and adhered to traditional feudal governance with strong emphasis on clan loyalty and warrior codes. The Maratha administration integrated revenue collection, military organization, and diplomacy under a relatively pragmatic system, while Rajputana's governance relied heavily on aristocratic traditions, local customs, and alliances maintained through marriage and warfare.
Key Leaders and Influential Figures
The Maratha Confederacy's expansion into Rajputana during the 18th century prominently involved leaders such as Peshwa Balaji Bajirao, whose military campaigns aimed to establish Maratha supremacy in the region. Rajputana's defense was spearheaded by rulers like Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II of Jaipur and Maharana Fateh Singh of Mewar, who skillfully navigated alliances and resistance against Maratha advances. These influential figures shaped the political landscape of Rajputana, balancing power dynamics through warfare, diplomacy, and strategic alliances.
Territorial Expansion and Military Strategies
The Maratha Confederacy rapidly expanded its territory in the 18th century by implementing guerrilla warfare tactics and leveraging a decentralized command structure, enabling flexible and swift military campaigns against Rajputana kingdoms. Rajputana, known for its fortified hill forts and cavalry-based warfare, employed defensive strategies and strategic alliances to resist Maratha incursions. While the Marathas sought to control key trade routes and fertile plains, Rajputana focused on preserving its regional autonomy through fortification and conventional battlefield engagements.
Maratha Confederacy–Rajputana Interactions
The Maratha Confederacy engaged in numerous military campaigns and diplomatic efforts in Rajputana during the 18th century, aiming to expand their influence in northern India. These interactions involved both confrontations with Rajput states and strategic alliances with local rulers to counter Mughal dominance. The dynamic exchanges significantly impacted the political landscape, altering power balances and facilitating Maratha penetration into Rajput territories.
Major Battles and Alliances
The Maratha Confederacy engaged in critical battles against Rajputana forces, notably the Battle of Rajgarh (1740), where the Marathas secured a decisive victory, enhancing their influence in central India. Alliances played a pivotal role as Maratha generals like Peshwa Balaji Bajirao forged strategic partnerships with Rajput rulers such as the Sisodias and Rathores to counter Mughal dominance. The oscillating alliances between these powers often shaped the political landscape, influencing subsequent conflicts including the Battle of Gangwana (1741), which marked fierce resistance from Rajputana forces against Maratha expansion.
Socio-Cultural Dynamics and Influence
The Maratha Confederacy's expansion into Rajputana introduced a complex interplay of socio-cultural dynamics marked by mutual respect for warrior traditions and strategic alliances through marriage and diplomacy. This interaction fostered a blend of Maratha militant governance with Rajputana's feudal and clan-based social structure, influencing art, architecture, and local customs. The integration of Maratha administrative practices and Rajput cultural heritage significantly shaped the regional identity and strengthened resistance against external invasions.
Impact on Regional Power Balance in India
The Maratha Confederacy's expansion into Rajputana during the 18th century significantly shifted the regional power balance by diminishing Rajput influence and consolidating Maratha dominance across central and western India. The weakening of Rajput states' autonomy facilitated the Marathas' control over key trade routes and political centers, altering the dynamics of alliance and tribute systems. This reconfiguration of power laid groundwork for subsequent British colonial advances by fragmenting traditional Rajput resistance.
Legacy and Historical Significance
The Maratha Confederacy's campaigns against Rajputana significantly altered the political landscape of 18th-century India by weakening Rajput autonomy and facilitating Maratha dominance in the region. This conflict underscored the military prowess of the Marathas while highlighting the resilience of Rajput forts and warrior traditions, shaping subsequent regional alliances. Their legacy endures in Indian history as a pivotal example of shifting power dynamics between emerging confederacies and established kingdoms.
Maratha Confederacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com