Annotation provides concise explanations or summaries that clarify the meaning of texts, images, or data, enhancing comprehension and analysis. It is essential for academic research, digital content, and data processing, enabling users to quickly grasp key points and underlying concepts. Explore the full article to discover how effective annotation techniques can elevate your understanding and productivity.
Table of Comparison
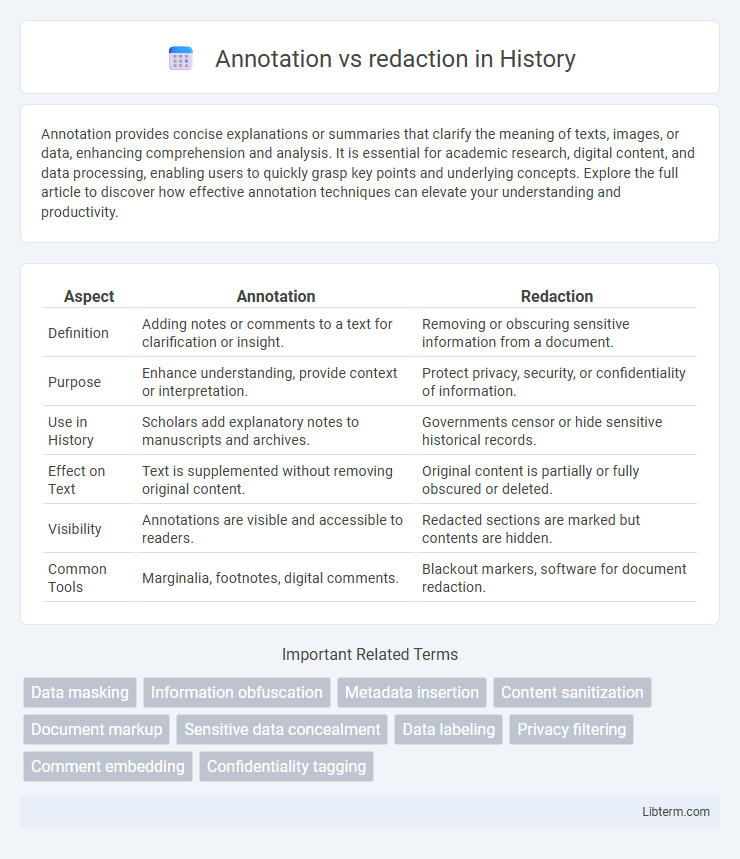
| Aspect | Annotation | Redaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding notes or comments to a text for clarification or insight. | Removing or obscuring sensitive information from a document. |
| Purpose | Enhance understanding, provide context or interpretation. | Protect privacy, security, or confidentiality of information. |
| Use in History | Scholars add explanatory notes to manuscripts and archives. | Governments censor or hide sensitive historical records. |
| Effect on Text | Text is supplemented without removing original content. | Original content is partially or fully obscured or deleted. |
| Visibility | Annotations are visible and accessible to readers. | Redacted sections are marked but contents are hidden. |
| Common Tools | Marginalia, footnotes, digital comments. | Blackout markers, software for document redaction. |
Understanding Annotation and Redaction
Annotation involves adding explanatory notes, comments, or highlights to a document for clarity and context, enhancing comprehension without altering the original content. Redaction is the process of obscuring or removing sensitive or confidential information from a document to protect privacy and comply with legal standards. Understanding annotation and redaction is crucial for effective document management, ensuring accurate communication while safeguarding sensitive data.
Key Differences Between Annotation and Redaction
Annotation involves adding explanatory notes or comments to a document, enhancing clarity and understanding without altering the original content. Redaction refers to the process of permanently obscuring or removing sensitive information from a document to protect privacy or confidentiality. Key differences include annotation being additive and visible, while redaction is subtractive and concealed, affecting data accessibility and document transparency.
Common Use Cases for Annotation
Annotation is commonly used in education and research to highlight key concepts, add explanations, and facilitate collaborative learning or review. In software development, annotations help document code, making it easier to understand and debug. Legal professionals use annotations to comment on contracts and case law, enhancing clarity without altering the original document.
Typical Scenarios Requiring Redaction
Typical scenarios requiring redaction include legal documents, medical records, and government filings where sensitive information such as personal identifiers, social security numbers, or confidential business data must be obscured to protect privacy and comply with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. Redaction is crucial in litigation processes to prevent exposure of privileged information while preserving the integrity of disclosed content. In intelligence and security sectors, redaction prevents unauthorized access to classified information and maintains operational confidentiality.
Benefits of Annotating Documents
Annotating documents enhances clarity by allowing users to add comments, highlights, and explanations directly on the text, improving comprehension and collaboration. It facilitates efficient information retrieval through keyword tagging, which streamlines research and review processes. Annotation preserves original content while enabling detailed analysis, unlike redaction that removes sensitive information and limits context.
Importance of Redaction for Data Privacy
Redaction plays a crucial role in data privacy by permanently removing sensitive information, such as personal identifiers, financial details, and confidential records, to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Unlike annotation, which involves adding explanatory notes or metadata without altering the original content, redaction ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by securely masking or deleting private data. Effective redaction safeguards individuals' privacy, reduces legal risks, and maintains organizational trust in handling confidential information.
Tools for Annotation and Redaction
Annotation tools such as Adobe Acrobat, Hypothesis, and Microsoft OneNote enable users to highlight, comment, and add notes directly on documents for collaborative review and analysis. Redaction tools like Adobe Acrobat Pro, PDF Studio, and Nitro Pro specialize in permanently removing sensitive information by blacking out or erasing text and images from digital files. Choosing the appropriate tool depends on whether the goal is to enhance document understanding through annotations or to ensure confidentiality via secure redaction.
Best Practices for Effective Annotation
Effective annotation involves clear, concise notes directly linked to specific content, enhancing comprehension without obscuring original data. Best practices include using consistent terminology, applying standardized symbols or color codes, and ensuring annotations are easily accessible and relevant to the context. Prioritizing clarity and relevance in annotations supports better information retrieval and collaboration across teams.
Ensuring Accuracy in Document Redaction
Ensuring accuracy in document redaction requires precise identification of sensitive information to prevent accidental exposure or excessive removal of content. Annotation involves marking up documents with metadata or comments for clarity or review but does not remove information, whereas redaction permanently obscures or deletes confidential data such as personal identifiers, legal details, or proprietary information. Employing advanced tools with AI-driven pattern recognition enhances the accuracy and reliability of redaction processes, minimizing human error and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Choosing Between Annotation and Redaction
Choosing between annotation and redaction depends on the need for information visibility versus confidentiality. Annotation allows adding comments or explanations while preserving the original content, ideal for collaborative analysis or document review. Redaction permanently obscures sensitive information to protect privacy and comply with legal standards, making it essential for security and compliance in legal, medical, and corporate documents.
Annotation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com