Preservation safeguards valuable cultural, historical, and natural resources, ensuring they remain intact for future generations. Effective preservation techniques protect your heritage from decay, destruction, or neglect, promoting sustainability and education. Explore the rest of the article to discover essential strategies for successful preservation.
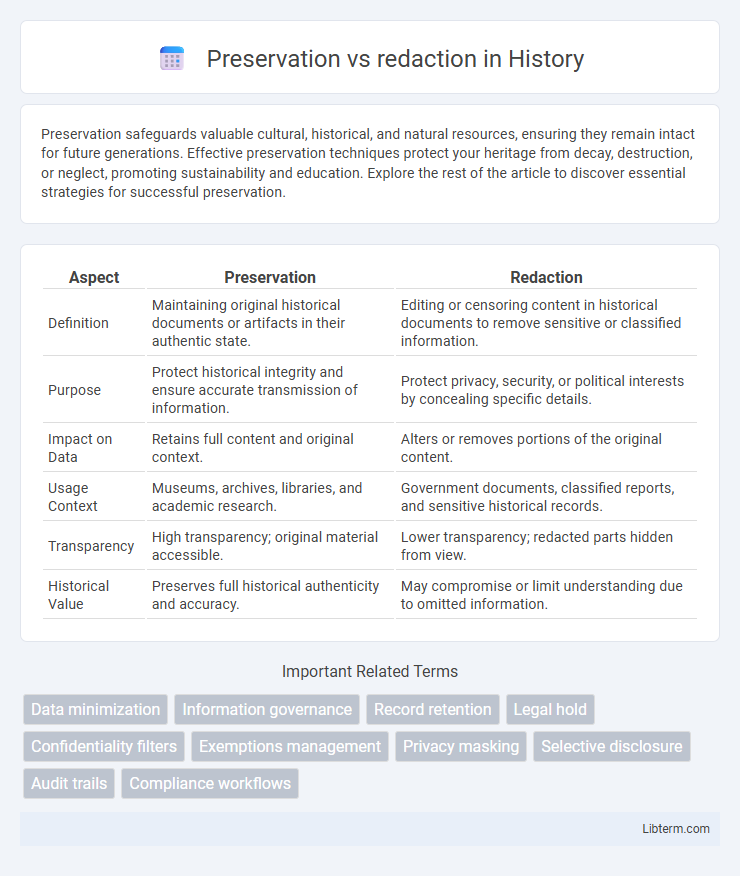
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Preservation | Redaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining original historical documents or artifacts in their authentic state. | Editing or censoring content in historical documents to remove sensitive or classified information. |
| Purpose | Protect historical integrity and ensure accurate transmission of information. | Protect privacy, security, or political interests by concealing specific details. |
| Impact on Data | Retains full content and original context. | Alters or removes portions of the original content. |
| Usage Context | Museums, archives, libraries, and academic research. | Government documents, classified reports, and sensitive historical records. |
| Transparency | High transparency; original material accessible. | Lower transparency; redacted parts hidden from view. |
| Historical Value | Preserves full historical authenticity and accuracy. | May compromise or limit understanding due to omitted information. |
Understanding Preservation and Redaction
Preservation ensures that digital or physical records remain intact and unaltered for legal, compliance, or historical purposes, maintaining their original state for future access and review. Redaction involves selectively concealing or blacking out sensitive or confidential information within documents to protect privacy and comply with data protection regulations while still preserving the overall content. Understanding the distinct roles of preservation and redaction is critical for effective records management, legal discovery, and information security strategies.
Key Differences Between Preservation and Redaction
Preservation involves maintaining the original form and content of data to ensure its integrity for future use, often in legal or compliance contexts. Redaction is the process of selectively obscuring or removing sensitive or confidential information from documents to protect privacy or comply with regulations. Key differences include preservation retaining full data accuracy, whereas redaction permanently alters the document by masking or deleting specific content.
Legal Requirements for Data Preservation
Legal requirements for data preservation mandate retaining electronic records and communications intact to ensure evidence integrity for litigation or regulatory compliance. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SEC Rule 17a-4 specify mandatory retention periods and data accessibility standards to prevent spoliation or unauthorized alteration. Failure to adhere to legal preservation obligations can result in significant penalties, sanctions, and adverse judgments in legal proceedings.
The Role of Redaction in Data Privacy
Redaction plays a critical role in data privacy by selectively removing or obscuring sensitive information from documents before sharing or publication, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Unlike preservation, which maintains the integrity and completeness of data for legal or archival purposes, redaction minimizes the risk of unauthorized disclosure by masking identifiers such as names, social security numbers, or financial details. Effective redaction techniques combine automated tools with manual review to balance transparency and confidentiality in data management workflows.
Preservation Techniques in Digital Evidence
Preservation techniques in digital evidence involve creating exact, bit-for-bit copies of original data to maintain integrity and prevent tampering during investigations. Methods such as cryptographic hashing, write blockers, and forensic imaging tools ensure the authenticity and chain of custody of digital evidence. Employing these techniques is crucial to uphold the evidentiary value in legal proceedings and digital forensic analysis.
Redaction Best Practices for Sensitive Information
Redaction best practices for sensitive information involve carefully identifying and masking confidential data such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial details, and proprietary content to prevent unauthorized access. Use automated tools with pattern recognition capabilities to ensure consistent and thorough redaction while maintaining document integrity. Verify redacted documents through manual review to confirm that all sensitive information is irreversibly removed without compromising the usability of the remaining content.
Challenges in Balancing Preservation and Redaction
Balancing preservation and redaction presents challenges in maintaining data integrity while protecting sensitive information. Ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements demands precise identification of confidential content without compromising the overall dataset. Effective strategies must address the risk of data loss or distortion alongside privacy concerns to support accurate analysis and secure document management.
Compliance Standards Influencing Preservation and Redaction
Compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX critically influence preservation and redaction processes by mandating strict data handling and privacy protections. Preservation requires maintaining data integrity and accessibility for audits and legal reviews, while redaction focuses on concealing sensitive information to meet privacy regulations. Organizations must balance these standards to ensure legally compliant retention policies without compromising personal or confidential data security.
Tools and Technologies Supporting Both Processes
Advanced tools like Adobe Acrobat Pro and ABBYY FineReader support both preservation and redaction by offering precise document editing, text recognition, and secure layer management. Technologies such as AI-powered content discovery and automated classification enable efficient identification of sensitive data, facilitating accurate redaction while preserving the original document integrity. Cloud-based platforms like Microsoft Purview provide integrated solutions for maintaining compliance by combining encryption, audit trails, and granular access controls for both preservation and redaction workflows.
Future Trends in Preservation and Redaction
Future trends in preservation and redaction emphasize advanced AI-driven techniques that enhance data security while ensuring regulatory compliance. Emerging technologies enable automated identification and contextual masking of sensitive information, reducing human error and operational costs. Integration of blockchain for immutable audit trails improves transparency and trust in data handling processes.
Preservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com