Accurate translation bridges language barriers by conveying meaning precisely and maintaining cultural nuances. Your message reaches a wider audience when translated skillfully, ensuring clarity and engagement across markets. Discover effective strategies to enhance your translation quality by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
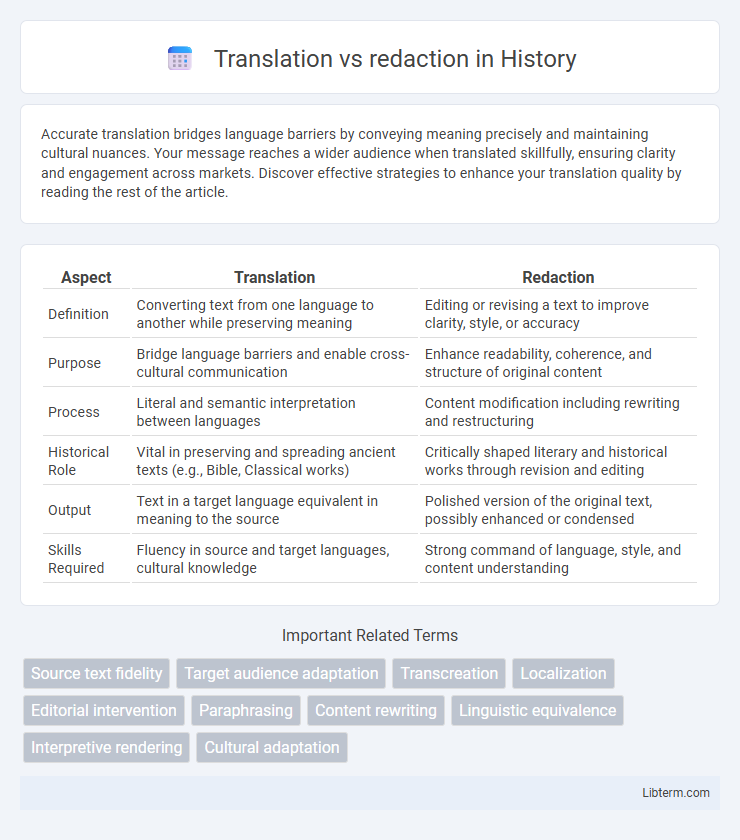
| Aspect | Translation | Redaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting text from one language to another while preserving meaning | Editing or revising a text to improve clarity, style, or accuracy |
| Purpose | Bridge language barriers and enable cross-cultural communication | Enhance readability, coherence, and structure of original content |
| Process | Literal and semantic interpretation between languages | Content modification including rewriting and restructuring |
| Historical Role | Vital in preserving and spreading ancient texts (e.g., Bible, Classical works) | Critically shaped literary and historical works through revision and editing |
| Output | Text in a target language equivalent in meaning to the source | Polished version of the original text, possibly enhanced or condensed |
| Skills Required | Fluency in source and target languages, cultural knowledge | Strong command of language, style, and content understanding |
Understanding Translation and Redaction
Understanding translation involves accurately converting text from one language to another while preserving meaning, tone, and context. Redaction refers to the process of editing or censoring parts of a text to protect sensitive information or improve clarity. Both practices require deep linguistic knowledge and attention to detail, but translation prioritizes linguistic equivalence whereas redaction emphasizes content security and readability.
Key Differences Between Translation and Redaction
Translation involves converting text from one language to another while preserving its original meaning and cultural nuances, ensuring accuracy and clarity across languages. Redaction refers to the selective editing or censoring of sensitive information within a text to protect privacy or comply with legal requirements. The key differences lie in translation's emphasis on linguistic equivalence versus redaction's focus on content modification for confidentiality and security purposes.
The Goals of Translation
Translation aims to accurately convey the original message's meaning, tone, and context across languages, preserving cultural nuances and intent. It seeks to ensure fidelity to the source text while making the content accessible and natural to the target audience. Effective translation balances linguistic precision with cultural adaptation to facilitate clear communication and understanding.
The Purpose of Redaction
Redaction serves the critical purpose of protecting sensitive information by selectively obscuring or removing confidential content from documents to ensure privacy, legal compliance, and security. Unlike translation, which aims to convert text from one language to another for clarity and understanding, redaction focuses on controlling information access to prevent unauthorized disclosure. Effective redaction techniques are essential in legal, governmental, and corporate contexts to maintain confidentiality while preserving the overall integrity of the document.
Skills Required for Translators vs Redactors
Translators require strong linguistic proficiency, cultural awareness, and the ability to accurately interpret meaning between source and target languages, ensuring context and nuance are preserved. Redactors need exceptional editing skills, attention to detail, and expertise in content organization and clarity, often focusing on refining and restructuring text for coherence and readability. Both roles demand a deep understanding of language mechanics, but translators emphasize bilingual fluency while redactors prioritize editorial precision and stylistic consistency.
Processes Involved in Translation and Redaction
Translation involves the process of converting text from one language to another, ensuring linguistic accuracy, cultural relevance, and preservation of original meaning through techniques such as localization and transcreation. Redaction focuses on editing, revising, and structuring content to enhance clarity, coherence, and style, often including fact-checking, rephrasing, and content organization. Both processes require specialized skills, but translation prioritizes language conversion, while redaction emphasizes content refinement and readability.
Common Challenges in Translation
Common challenges in translation include maintaining cultural nuances, preserving original meaning, and accurately conveying idiomatic expressions. Translators often face difficulties with context, tone, and specialized terminology, which require deep subject knowledge and linguistic expertise. These obstacles can lead to mistranslations that affect the quality and effectiveness of the final text.
Common Challenges in Redaction
Redaction involves the strategic removal or obscuring of sensitive information to protect confidentiality, often facing challenges like maintaining document coherence, ensuring accuracy without context loss, and adhering to legal or regulatory standards. Unlike translation, which focuses on converting text between languages while preserving meaning, redaction demands a delicate balance between transparency and privacy, requiring advanced techniques to prevent accidental data exposure. Common obstacles include identifying all sensitive data, avoiding over-redaction that renders documents useless, and managing varied formats across digital or physical documents.
Choosing Between Translation and Redaction
Choosing between translation and redaction depends on the purpose of content adaptation and target audience. Translation aims to convert text from one language to another accurately, preserving meaning and tone, ideal for multilingual communication. Redaction focuses on editing or summarizing content to suit specific contexts, emphasizing clarity, confidentiality, or brevity without necessarily changing the language.
Impact on Confidentiality and Accuracy
Translation ensures accurate conversion of text from one language to another, preserving meaning and technical details, which is critical for maintaining document confidentiality and preventing misinterpretation. Redaction involves selectively obscuring sensitive information within a document to protect confidentiality while potentially altering the completeness and context, which may affect the overall accuracy of the content. Both processes require strict adherence to security protocols and linguistic precision to uphold data integrity and safeguard sensitive information.
Translation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com