Pirates are notorious seafarers known for their daring raids and treasure hunting during the Golden Age of Piracy. Their legacy lives on in popular culture as symbols of adventure, rebellion, and freedom on the open seas. Dive into the rest of this article to uncover the fascinating history and legends surrounding pirates.
Table of Comparison
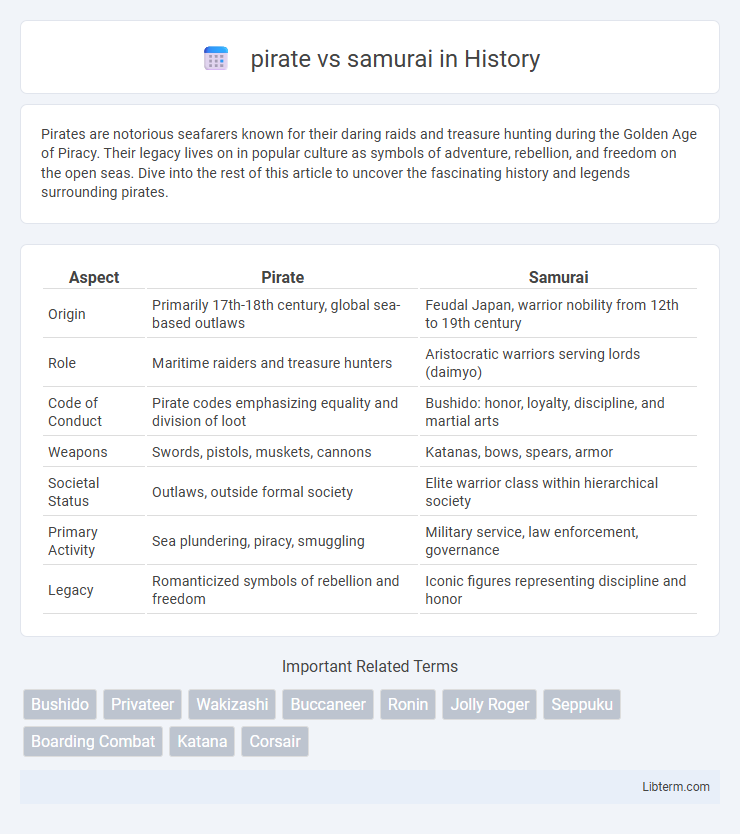
| Aspect | Pirate | Samurai |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Primarily 17th-18th century, global sea-based outlaws | Feudal Japan, warrior nobility from 12th to 19th century |
| Role | Maritime raiders and treasure hunters | Aristocratic warriors serving lords (daimyo) |
| Code of Conduct | Pirate codes emphasizing equality and division of loot | Bushido: honor, loyalty, discipline, and martial arts |
| Weapons | Swords, pistols, muskets, cannons | Katanas, bows, spears, armor |
| Societal Status | Outlaws, outside formal society | Elite warrior class within hierarchical society |
| Primary Activity | Sea plundering, piracy, smuggling | Military service, law enforcement, governance |
| Legacy | Romanticized symbols of rebellion and freedom | Iconic figures representing discipline and honor |
Introduction: Unveiling the Legend of Pirates and Samurai
Pirates and samurai represent two iconic warrior cultures defined by distinct codes of honor and combat styles. Pirates, driven by freedom and wealth, thrived on the high seas with ruthless tactics and naval expertise. Samurai, bound by Bushido, exemplified disciplined swordsmanship and loyalty in feudal Japan's rigid social hierarchy.
Historical Background: Origins of Pirates and Samurai
Pirates originated primarily during the late Middle Ages and the early modern period, thriving in regions such as the Caribbean, the Mediterranean, and Southeast Asia, where maritime trade routes provided lucrative opportunities for raiding and plundering. Samurai emerged in 12th-century Japan as a distinct warrior class serving feudal lords, known as daimyo, with origins tracing back to the Heian period's provincial military forces. The historical context of pirates is rooted in opportunistic seafaring banditry, while samurai were bound by a strict code of honor, Bushido, reflecting their role in Japan's hierarchical feudal system.
Code of Conduct: Pirate Law vs Bushido
Pirate Law emphasized freedom, loyalty to the crew, and division of loot, often codified in articles that governed behavior and dispute resolution to maintain order among diverse and unruly crews. Bushido, the samurai code of conduct, prioritized honor, loyalty to one's lord, discipline, and martial prowess, guiding samurai through strict ethical principles and a deep sense of duty. While Pirate Law fostered egalitarianism and pragmatism within a rebellious framework, Bushido upheld hierarchical loyalty and moral rectitude rooted in centuries of Japanese feudal tradition.
Weaponry and Combat Tactics
Pirates wielded cutlasses, flintlock pistols, and boarding axes, favoring close-quarters combat and surprise attacks on ships to overwhelm opponents quickly. Samurai utilized katanas, yumi bows, and yari spears, emphasizing precision, discipline, and strategic formations in battle. The pirate's aggressive, chaotic fighting style contrasts with the samurai's ritualized, skillful approach centered on honor and technique.
Life at Sea vs Life in Feudal Japan
Pirates thrived in the unpredictable and harsh conditions of the high seas, relying on agility, teamwork, and resourcefulness for survival and plundering. Samurai lived under a strict code of honor called Bushido, navigating the rigid social hierarchy and political complexities of feudal Japan. Life at sea demanded constant adaptation to weather, navigation, and combat, while feudal Japan required discipline, ritual, and allegiance to one's lord in both warfare and daily existence.
Notable Figures: Infamous Pirates and Renowned Samurai
Notable pirates such as Blackbeard and Anne Bonny are infamous for their ruthless tactics and legendary sea dominance, while renowned samurai like Miyamoto Musashi and Oda Nobunaga are celebrated for their strategic brilliance and unmatched swordsmanship. Blackbeard's fearsome reputation and Anne Bonny's fearless defiance made them icons of piracy lore. Miyamoto Musashi's undefeated record in duels and Nobunaga's role in unifying Japan highlight the samurai's disciplined prowess and historical significance.
Appearance and Attire: Symbolism and Function
Pirates are often depicted wearing loose, weather-worn clothing with bandanas and eye patches, symbolizing freedom and a life of rebellion on the high seas, while their attire served practical functions like quick movement and protection from harsh marine elements. Samurai attire, consisting of the intricate kimono, armor, and kabuto helmet, symbolized honor, discipline, and social status within feudal Japan, with each piece designed for both protection in battle and ceremonial significance. The contrasting appearances reflect the cultural values and environmental demands faced by these historical warriors, reinforcing their distinct identities through clothing symbolism and functionality.
Impact on Culture and Mythology
Pirates shaped global culture through romanticized tales of freedom, rebellion, and adventure, influencing literature, film, and fashion worldwide. Samurai embedded principles of honor, discipline, and loyalty deeply into Japanese culture, inspiring martial arts, ethical philosophy, and traditional ceremonies. Both archetypes evolved into powerful mythological symbols representing contrasting values of lawlessness versus structured honor.
Pirate vs Samurai: Who Would Win?
Pirates and samurai each possess distinct combat skills and strategies that influence their battle outcomes. Samurai excel in disciplined swordsmanship, armor defense, and strategic battlefield tactics, while pirates rely on agility, improvisation, and ranged weapons such as pistols and cutlasses. In a direct confrontation, samurai's rigorous training and armored protection typically offer an advantage over pirates' unarmored, guerrilla-style fighting methods.
Legacy: Influence on Modern Media and Pop Culture
Pirates and samurai have left enduring legacies that shape modern media and pop culture, with pirates symbolizing freedom and rebellion in countless films, video games, and literature. Samurai embody honor, discipline, and martial skill, influencing genres like anime, manga, and action cinema, often depicted as noble warriors or tragic heroes. Their contrasting archetypes continue to inspire character development, storytelling tropes, and aesthetic styles in contemporary entertainment worldwide.
pirate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com