The Bundestag serves as Germany's federal parliament, playing a crucial role in legislative processes and government oversight. It represents the will of the people, shaping national policies and ensuring democratic governance within the country. Discover how the Bundestag influences your daily life and the intricacies of its functions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
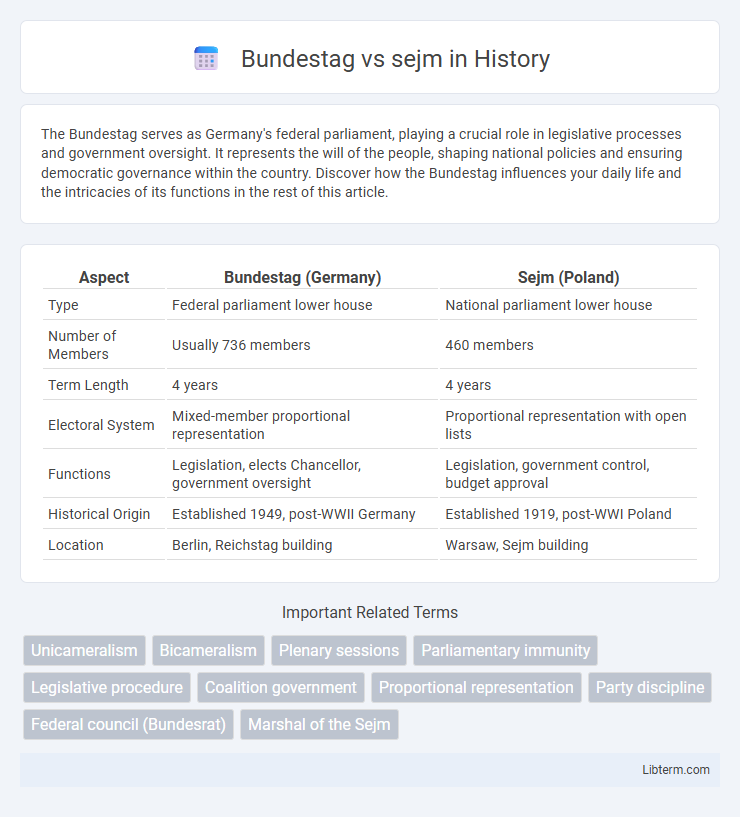
| Aspect | Bundestag (Germany) | Sejm (Poland) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Federal parliament lower house | National parliament lower house |
| Number of Members | Usually 736 members | 460 members |
| Term Length | 4 years | 4 years |
| Electoral System | Mixed-member proportional representation | Proportional representation with open lists |
| Functions | Legislation, elects Chancellor, government oversight | Legislation, government control, budget approval |
| Historical Origin | Established 1949, post-WWII Germany | Established 1919, post-WWI Poland |
| Location | Berlin, Reichstag building | Warsaw, Sejm building |
Overview: Bundestag and Sejm Defined
The Bundestag is the federal parliament of Germany, serving as the primary legislative body responsible for enacting national laws and overseeing the federal government. The Sejm is the lower house of the Polish parliament and plays a central role in Poland's legislative process, including drafting, debating, and approving laws. Both institutions represent the core of parliamentary democracy in their respective countries, with distinct structures and responsibilities tailored to Germany's federal system and Poland's unitary system.
Historical Backgrounds
The Bundestag, established in 1949, serves as the primary legislative body in Germany, rooted in the post-World War II Federal Republic framework aimed at ensuring democratic governance. The Sejm, with origins tracing back to the 15th century, is Poland's historic parliament that evolved through various political transformations, solidifying its role in Polish sovereignty after the 1989 fall of communism. Both institutions reflect distinct national histories shaped by periods of authoritarian rule and democratization efforts in Central Europe.
Structure and Composition
The Bundestag, Germany's federal parliament, comprises 736 members elected through a mixed-member proportional representation system, ensuring a balance between direct constituency representatives and party list candidates. In contrast, the Sejm, Poland's lower house, consists of 460 deputies elected via an open-list proportional representation system across multi-member constituencies. Both bodies operate unicamerally within their national legislative frameworks, with the Bundestag serving alongside the Bundesrat in Germany's bicameral system, while the Sejm functions alongside the Senate in Poland.
Electoral Systems
The Bundestag employs a mixed-member proportional representation system, combining direct constituency seats with party list votes to ensure proportionality and local representation. The Sejm uses an open-list proportional representation system based on multi-member constituencies, allowing voters to influence the order of candidates on party lists. Both systems aim to balance proportional representation with individual candidate accountability, but the Bundestag's two-vote system offers a more distinct separation between candidate and party preferences.
Main Functions and Powers
The Bundestag serves as Germany's federal parliament, responsible for legislation, electing the Chancellor, and overseeing the federal government, while the Sejm is the lower house of Poland's parliament with powers to enact laws, approve the budget, and control the executive branch. Both bodies debate and pass legal statutes, but the Bundestag has exclusive authority to vote on the federal budget and ratify international treaties. The Sejm also holds the unique power to initiate investigations into government actions and can pass votes of no confidence to trigger the government's resignation.
Legislative Procedures
The Bundestag employs a multi-stage legislative procedure that includes readings, committee reviews, and debate before voting, emphasizing transparency and public participation. The Sejm uses a similar process, consisting of three readings, committee analyses, and plenary sessions, allowing for multiple amendments and government oversight. Both parliaments engage specialized committees to scrutinize bills, but the Bundestag incorporates the Bundesrat's role for federal states' input, enhancing federal balance.
Role of Political Parties
The Bundestag serves as Germany's federal parliament where political parties play a crucial role in forming coalitions and influencing legislative processes through proportional representation. In Poland's Sejm, political parties dominate parliamentary structure, with a mixed-member proportional system ensuring party influence over policy-making and government formation. Both institutions emphasize party discipline, yet the Bundestag's multiparty coalitions often shape more consensus-driven politics compared to the Sejm's party-centric majority rule.
Leadership and Key Figures
The Bundestag, Germany's federal parliament, is led by the President of the Bundestag, a position currently held by Barbel Bas, who oversees legislative sessions and ensures parliamentary order. The Sejm, Poland's lower house of parliament, is chaired by the Marshal of the Sejm, presently Elzbieta Witek, responsible for managing debates and representing the chamber externally. Both institutions feature prominent political leaders who play critical roles in steering legislative agendas and maintaining procedural discipline within their respective parliamentary frameworks.
Public Participation and Transparency
The Bundestag facilitates public participation through open plenary sessions, live broadcasts, and accessible parliamentary documents, enhancing transparency in legislative processes. The Sejm also promotes transparency by providing live-streamed sessions and detailed legislative tracking online, but its public engagement tools are less extensive compared to the Bundestag. Both institutions aim to involve citizens in governance, yet the Bundestag's digital platforms and information openness offer a more robust framework for public scrutiny and participation.
Comparing Legislative Impact
The Bundestag, Germany's federal parliament, exercises significant legislative power by passing laws that affect all 16 federal states, shaping national policies on economics, defense, and social issues, with a strong emphasis on coalition consensus. The Sejm, Poland's lower house of parliament, holds substantial influence over domestic and foreign legislation but operates in a political environment with a dominant ruling party, often enabling swifter enactment of government proposals. Both bodies have the authority to approve budgets and oversee the executive branch, yet the Bundestag's federal structure leads to more complex, negotiated legislation compared to the Sejm's relatively centralized policy impact.
Bundestag Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com