Pencils remain essential tools for writing, drawing, and sketching with precision and ease. Their versatility allows artists, students, and professionals to express creativity and ideas effortlessly. Explore this article to discover everything you need to know about choosing and using pencils effectively.
Table of Comparison
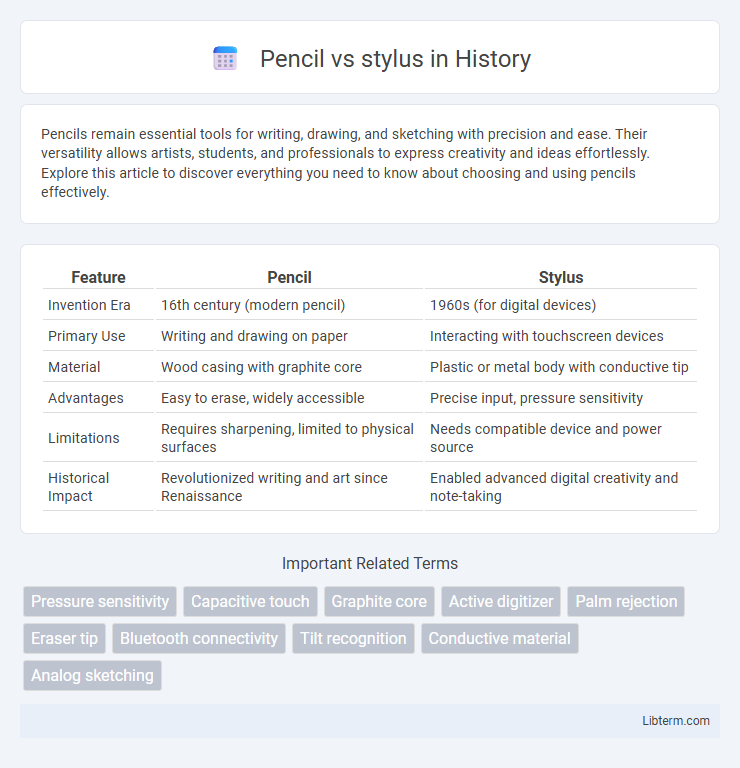
| Feature | Pencil | Stylus |
|---|---|---|
| Invention Era | 16th century (modern pencil) | 1960s (for digital devices) |
| Primary Use | Writing and drawing on paper | Interacting with touchscreen devices |
| Material | Wood casing with graphite core | Plastic or metal body with conductive tip |
| Advantages | Easy to erase, widely accessible | Precise input, pressure sensitivity |
| Limitations | Requires sharpening, limited to physical surfaces | Needs compatible device and power source |
| Historical Impact | Revolutionized writing and art since Renaissance | Enabled advanced digital creativity and note-taking |
Introduction: Pencil vs Stylus
Pencils are traditional writing tools with graphite cores ideal for sketching, shading, and precise manual drawing, offering tactile feedback on paper surfaces. Styluses function as digital input devices designed for touchscreen gadgets, enabling accurate navigation, drawing, and handwriting recognition on tablets and smartphones. The choice between a pencil and stylus depends on the medium--physical versus digital--and desired interaction with creative or writing activities.
Historical Evolution of Writing Tools
The historical evolution of writing tools traces a transformation from the traditional pencil, first introduced in the 16th century, to the modern stylus used in digital devices. Pencils, made from graphite encased in wood, revolutionized manual writing and drawing for centuries before the proliferation of touchscreens brought the stylus to prominence. The stylus, initially a simple pointed instrument for tablets, has evolved into advanced, pressure-sensitive devices compatible with smartphones and tablets, enhancing precision and creativity in digital art and note-taking.
Physical Differences: Pencil and Stylus
Pencils have a wooden or mechanical body with a graphite or colored core, providing tactile feedback and natural pressure sensitivity for traditional drawing and writing. Styluses feature a smooth plastic or rubber tip designed for touchscreen interaction, often lacking the fine tip and tactile resistance of a pencil. The physical difference lies in the rigidity and material composition, with pencils offering a firmer grip and distinct point, while styluses prioritize compatibility with digital devices and varying touch sensitivity.
Writing Experience and Precision
The writing experience with a pencil offers natural tactile feedback and subtle texture variations, enhancing control and comfort for detailed sketches or handwriting. A stylus provides digital precision with pressure sensitivity and customizable tips, ideal for smooth lines and accurate input on touchscreens. While pencils excel in organic feel and shading nuances, styluses optimize efficiency and precision in digital note-taking and design applications.
Digital Compatibility and Integration
A stylus offers superior digital compatibility, seamlessly integrating with touchscreens, tablets, and graphic design software for precise input and pressure sensitivity. Unlike traditional pencils, which are limited to analog media, styluses support advanced features like palm rejection, tilt recognition, and customizable buttons, enhancing efficiency in digital workflows. Integration with popular platforms such as iPadOS, Windows Ink, and Android further establishes the stylus as an essential tool for creative professionals and note-takers in digital environments.
Creative Applications: Art and Design
Pencils offer tactile precision and natural shading ideal for traditional sketching, allowing artists to create detailed textures and gradients easily. Styluses provide enhanced control and versatility with pressure sensitivity, customizable brushes, and layering features in digital art software, optimizing workflows for illustrators and designers. Both tools are essential for creative applications, with pencils excelling in tactile feedback while styluses enable dynamic digital manipulation and seamless integration with design platforms.
Educational Uses and Accessibility
A pencil offers tactile feedback and fine motor skill development essential for early education, enabling students to practice handwriting and drawing with physical interaction. A stylus provides seamless integration with digital devices, enhancing accessibility for students with disabilities through customizable features like pressure sensitivity and text-to-speech compatibility. Both tools support diverse learning environments, but the stylus excels in bridging traditional writing with interactive, multimedia educational content.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pencils, made primarily from wood and graphite, generally have a lower environmental impact due to their biodegradable nature and the renewable resources used in their production. Styli, often composed of plastic and electronic components, pose challenges in recycling and contribute to e-waste, raising concerns about long-term sustainability. Sustainable practices favor wooden pencils or styluses with replaceable tips and recyclable materials to minimize ecological footprints.
Cost Comparison and Maintenance
Pencils are significantly cheaper upfront, typically costing only a few cents or dollars, while styluses range from affordable models at $10 to high-end options exceeding $150. Maintenance for pencils involves simple sharpening and occasional replacement, whereas styluses require battery charging or replacement, with tips that wear out and need periodic renewal. Overall, pencils offer low-cost and low-maintenance usability, but styluses provide advanced features that may justify higher cost and upkeep for digital tasks.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Choosing between a pencil and a stylus depends on your specific needs and tasks; pencils offer precise control for traditional sketching and shading, while styluses provide versatility and seamless integration with digital devices for drawing, note-taking, and design work. Consider factors such as medium preference, compatibility with tablets or touchscreen devices, and the type of projects you undertake, whether they require tactile feedback or digital manipulation. Evaluating these elements helps select the optimal tool to enhance creativity, accuracy, and workflow efficiency.
Pencil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com