Democracy ensures that power is vested in the people, allowing citizens to participate directly or indirectly in decision-making processes. This system promotes equality, freedom, and accountability within governance structures to uphold the rights of individuals. Explore this article to understand how democracy shapes societies and impacts your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
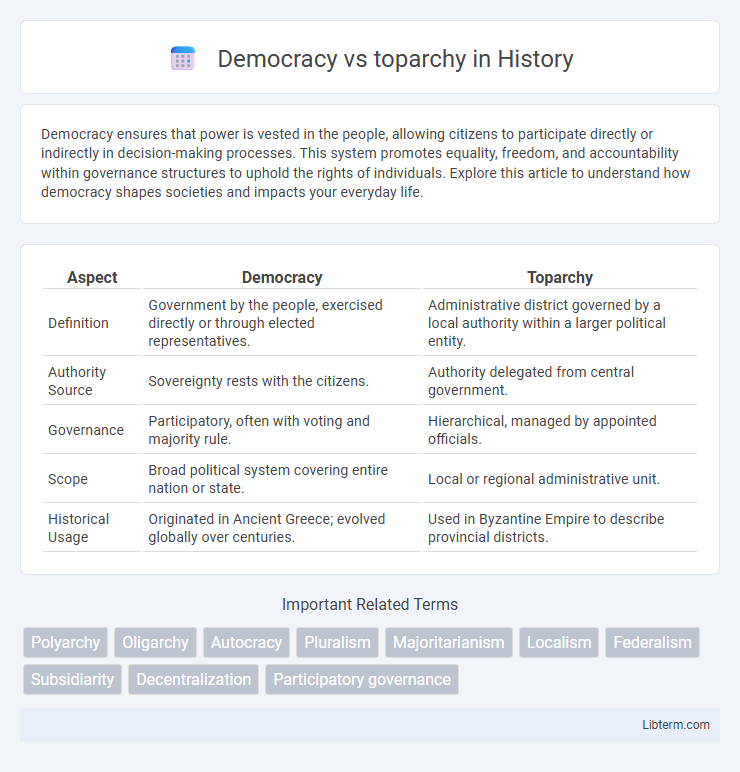
| Aspect | Democracy | Toparchy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government by the people, exercised directly or through elected representatives. | Administrative district governed by a local authority within a larger political entity. |
| Authority Source | Sovereignty rests with the citizens. | Authority delegated from central government. |
| Governance | Participatory, often with voting and majority rule. | Hierarchical, managed by appointed officials. |
| Scope | Broad political system covering entire nation or state. | Local or regional administrative unit. |
| Historical Usage | Originated in Ancient Greece; evolved globally over centuries. | Used in Byzantine Empire to describe provincial districts. |
Understanding Democracy: Core Principles and Features
Democracy is characterized by principles of popular sovereignty, political equality, and majority rule, where citizens participate directly or through elected representatives in decision-making processes. Core features include free and fair elections, protection of individual rights and freedoms, and accountability of government officials to the electorate. This system contrasts with toparchy, a localized governance model centered on small, community-based authority structures limiting broader democratic engagement.
Defining Toparchy: Origins and Key Characteristics
Toparchy originates from ancient governance concepts, referring to a localized administrative unit or district within a larger political entity. Characterized by decentralized authority, toparchy involves local leaders or councils exerting control over specific territories, contrasting with centralized power structures. This system emphasizes regional autonomy, often allowing for tailored governance based on local customs and needs, differing fundamentally from democratic models that prioritize broad citizen participation and collective decision-making.
Historical Evolution: Democracy vs. Toparchy
Democracy evolved from ancient Athens, characterized by citizen participation and collective decision-making, while toparchy originated as localized governance structures in ancient Greece where small communities or districts exercised administrative autonomy. The historical evolution of democracy centers on expanding political rights and institutions to protect individual freedoms and promote equality, whereas toparchy maintained decentralized control focused on local governance and regional influence. Over time, democracy transformed into complex national systems emphasizing representation and legal frameworks, contrasting with toparchy's persistent role in managing local affairs within broader state mechanisms.
Governance Structures Compared: Power Distribution and Decision-Making
Democracy features a decentralized power distribution where citizens participate directly or through elected representatives, ensuring collective decision-making and accountability. In contrast, toparchy centralizes authority within a select group or council, limiting broader public input and concentrating governance. The democratic model promotes transparency and inclusiveness, while toparchy emphasizes hierarchical control and swift decision enforcement.
Representation and Citizen Participation: A Comparative Analysis
Democracy emphasizes broad citizen participation and representative institutions where elected officials act on behalf of the populace, ensuring accountability through regular elections and transparent governance. In contrast, toparchy is characterized by localized governance structures that allow direct citizen involvement in decision-making within small communities or regions, often lacking formal representative layers. The comparative analysis reveals that democracy scales citizen representation through institutionalized mechanisms, while toparchy facilitates more immediate and participatory engagement at the local level.
Accountability and Transparency in Both Systems
In democracy, accountability is ensured through regular elections and transparent governance structures that allow citizens to monitor and influence decision-making processes. Toparchy, a decentralized form of government, emphasizes local autonomy which can enhance transparency by bringing power closer to the people but may face challenges in maintaining uniform accountability standards across diverse local units. Both systems require robust mechanisms for reporting, oversight, and citizen participation to uphold transparency and hold leaders accountable for their actions.
Efficiency and Stability: Which System Delivers Better?
Democracy often provides greater efficiency through inclusive decision-making that leverages diverse perspectives and decentralized authority, fostering adaptability and innovation. Toparchy, characterized by hierarchical governance and centralized control, tends to deliver stability by ensuring consistent policy enforcement and reducing dissent through clear command structures. Efficient governance depends on the complexity of society's needs, while stability is reinforced in toparchies via streamlined administrative processes and predictable leadership, making the optimal system context-dependent.
Socioeconomic Impacts of Democracy and Toparchy
Democracy often promotes socioeconomic equality by enabling broader participation in decision-making, which can lead to policies supporting public welfare, education, and healthcare improvements. Toparchy, characterized by localized, autonomous governance, may foster efficient resource management and community-specific economic initiatives but risks uneven development and limited access to broader social services. The socioeconomic impacts of democracy tend to favor inclusive growth, whereas toparchy emphasizes localized control with variable outcomes depending on regional capacities.
Global Case Studies: Democracies and Toparchies in Action
Global case studies reveal democracies like the United States and Sweden prioritize citizen participation, transparent governance, and rule of law, fostering political stability and economic growth. In contrast, toparchies such as tribal regions in Papua New Guinea rely on localized, hierarchical leadership structures emphasizing traditional authority and community consensus over formal state institutions. These differing governance models highlight how context-specific political systems adapt to cultural norms and social complexities, influencing development outcomes and conflict management.
Future Prospects: The Relevance of Democracy and Toparchy Today
Democracy remains a dominant governance model promising inclusivity, accountability, and citizen participation amid rising global interconnectedness. Toparchy, emphasizing decentralized, localized authority, responds to increasing demands for autonomy and tailored governance in diverse communities. Future prospects suggest a hybrid approach leveraging democratic values while empowering toparchic structures to address complex socio-political challenges efficiently.
Democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com