Civitas represents the concept of active citizenship and community engagement rooted in shared values and responsibilities. Understanding Civitas can empower Your role in fostering social cohesion and democratic participation. Dive deeper into this article to explore how Civitas shapes society and impacts Your community involvement.
Table of Comparison
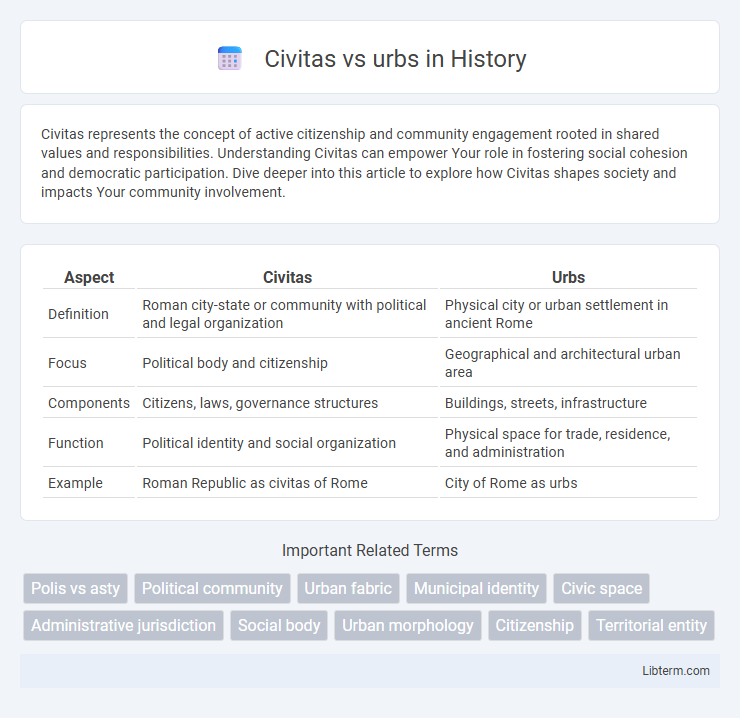
| Aspect | Civitas | Urbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Roman city-state or community with political and legal organization | Physical city or urban settlement in ancient Rome |
| Focus | Political body and citizenship | Geographical and architectural urban area |
| Components | Citizens, laws, governance structures | Buildings, streets, infrastructure |
| Function | Political identity and social organization | Physical space for trade, residence, and administration |
| Example | Roman Republic as civitas of Rome | City of Rome as urbs |
Defining Civitas and Urbs: Semantic Differences
Civitas refers to the body of citizens who hold legal and political rights within a community, emphasizing social organization and civic identity. Urbs denotes the physical city or urban area, highlighting architectural structures and geographic boundaries. The semantic distinction centers on civitas as a collective of people bound by law and citizenship, while urbs signifies the tangible cityscape.
Historical Origins of Civitas and Urbs
The terms Civitas and Urbs originate from ancient Roman civilization, where Civitas referred to the body of citizens and their collective legal and political rights within a community, emphasizing social organization and citizenship. Urbs specifically denoted the physical city or urban center, particularly Rome as the archetypal urban entity, highlighting its architectural and infrastructural aspects. The historical distinction reflects the dual nature of Roman society: Civitas encompassed the legal-political framework of the populace, while Urbs represented the tangible city landscape and urban environment.
Civitas: The Concept of Community and Citizenship
Civitas embodies the concept of community and citizenship in ancient Roman society, representing more than just a physical city (urbs) but the collective body of citizens with shared rights and responsibilities. It signifies legal status, political participation, and a sense of belonging integral to civic identity and governance. The idea of civitas laid the foundation for modern notions of citizenship as an active, communal engagement within a defined political body.
Urbs: The Physical Structure of the City
Urbs refers to the tangible physical structure of the city characterized by its buildings, streets, walls, and public spaces that define the urban environment. This encompasses architectural design, urban planning, and infrastructure which form the city's spatial organization and functional layout. The concept of Urbs emphasizes the material and spatial dimension of the city, distinguishing it from the sociopolitical community embodied by Civitas.
Roman Urban Planning: Integration of Civitas and Urbs
Roman urban planning masterfully integrated the civitas, the administrative and political community, with the urbs, the physical cityscape, creating a functional and symbolic unity. The civitas embodied the collective identity, legal structures, and governance, while the urbs represented the engineered environment including forums, roads, and public buildings designed for social and economic activities. This synthesis ensured efficient administration, facilitated civic participation, and projected Roman authority through monumental architecture and organized spatial planning.
Civic Identity vs. Urban Infrastructure
Civitas represents the collective civic identity centered on citizenship rights, political participation, and social belonging, emphasizing the active engagement of individuals within the community. Urbs refers to the physical urban infrastructure, including buildings, streets, and public spaces, which supports the functioning and growth of the city. The interplay between civitas and urbs highlights how civic identity shapes public spaces, while urban infrastructure facilitates social interaction and community development.
Social Functions: Civitas in Daily Roman Life
Civitas in daily Roman life functioned as a structured community encompassing legal rights, political participation, and social identity, distinguishing citizens from non-citizens within the empire. Unlike the urbs, which referred primarily to the physical city and its urban infrastructure, civitas emphasized collective social responsibilities, civic duties, and access to public services such as baths, forums, and courts. This social framework fostered a sense of belonging and legal protection critical to maintaining order and governance across diverse Roman populations.
Architectural Features of the Urbs
The architectural features of the Urbs highlight its status as a densely built urban center with monumental structures such as forums, basilicas, temples, and amphitheaters that symbolize political power and social life. Unlike the Civitas, which spread across rural and suburban areas with dispersed settlements and agricultural land, the Urbs showcases advanced engineering feats like aqueducts, sewers, and paved roads reflecting sophisticated urban planning. The concentration of civic buildings, monumental arches, and public spaces in the Urbs served as focal points for administrative, religious, and commercial activities distinct from the more decentralized nature of the Civitas.
Legacy of Civitas and Urbs in Modern Cities
The legacy of civitas and urbs shapes modern cities by blending political organization with urban development; civitas emphasizes citizenship, governance, and legal frameworks that inform contemporary civic institutions and public administration. Urbs contributes the spatial and infrastructural blueprint, including roads, public spaces, and architectural planning, foundational to modern urban design and city functioning. Together, these Roman concepts underpin the integration of social order and physical space in today's metropolitan environments, influencing urban policy, community identity, and sustainable city planning.
Civitas vs. Urbs: Ongoing Relevance in Urban Studies
Civitas and Urbs represent distinct concepts in urban studies, where Civitas refers to the social and political community of citizens, emphasizing collective identity and civic engagement. Urbs denotes the physical city, including infrastructure, architecture, and spatial organization, highlighting urban form and development. Understanding the dynamic interplay between Civitas and Urbs remains crucial for addressing contemporary challenges in urban planning, governance, and social cohesion.
Civitas Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com