The Crusades were a series of religious and military campaigns between the 11th and 13th centuries, primarily aimed at reclaiming the Holy Land from Muslim rule. These conflicts significantly shaped medieval European and Middle Eastern history, influencing culture, politics, and religion. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these events impacted Your world and their lasting legacy.
Table of Comparison
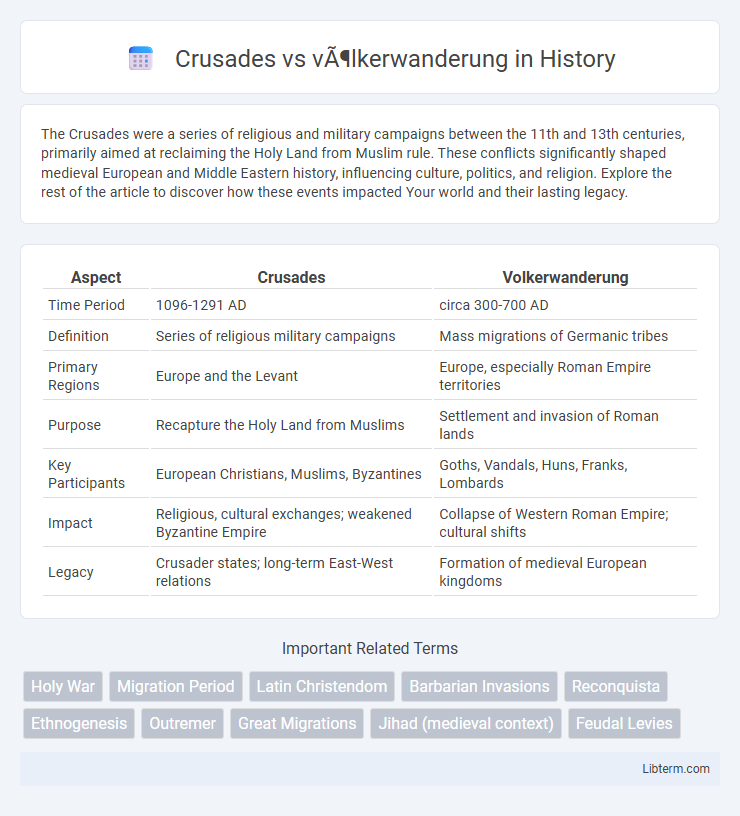
| Aspect | Crusades | Volkerwanderung |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 1096-1291 AD | circa 300-700 AD |
| Definition | Series of religious military campaigns | Mass migrations of Germanic tribes |
| Primary Regions | Europe and the Levant | Europe, especially Roman Empire territories |
| Purpose | Recapture the Holy Land from Muslims | Settlement and invasion of Roman lands |
| Key Participants | European Christians, Muslims, Byzantines | Goths, Vandals, Huns, Franks, Lombards |
| Impact | Religious, cultural exchanges; weakened Byzantine Empire | Collapse of Western Roman Empire; cultural shifts |
| Legacy | Crusader states; long-term East-West relations | Formation of medieval European kingdoms |
Origins: Understanding the Crusades and Völkerwanderung
The Crusades originated in the late 11th century as religious military campaigns initiated by the Latin Church to reclaim Jerusalem and the Holy Land from Muslim rule, fueled by papal calls and knightly zeal. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period, occurred between the 4th and 6th centuries, characterized by mass migrations of Germanic, Hunnic, and other tribes across Europe, driven by pressures from the Huns and internal social dynamics. Both events profoundly reshaped Europe's political and cultural landscape, but stemmed from distinct triggers: religious crusading fervor versus widespread tribal displacement and settlement.
Key Players and Peoples Involved
The Crusades featured key players such as European Christian knights, notably the French and English nobility, alongside Muslim leaders like Saladin, who defended the Holy Land. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung (Migration Period) involved diverse groups including the Goths, Vandals, Huns, and Franks, which reshaped the Roman Empire's borders through mass migrations and invasions. Both events significantly influenced the political and cultural landscapes of medieval Europe, but while the Crusades centered around religious conflict, the Volkerwanderung was characterized by large-scale population movements and tribal alliances.
Motivations Behind the Movements
The Crusades were primarily motivated by religious zeal to reclaim the Holy Land and defend Christendom, fueled by papal calls and promises of spiritual rewards. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period, was driven largely by socio-political pressures such as climate change, population shifts, and the collapse of Roman authority, prompting Germanic tribes to seek new territories. Both movements reflect complex interactions of faith, survival, and power during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages.
Geographical Scope and Trajectories
The Crusades primarily unfolded across the Eastern Mediterranean, targeting the Levant, Anatolia, and parts of the Byzantine Empire, while the Volkerwanderung spanned across Central and Western Europe, involving mass migrations from Scandinavia, Eastern Europe, and Central Asia into the Roman Empire territories. The Crusades followed more linear, military expedition routes from Western Europe to the Holy Land, often via Mediterranean sea passages. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung consisted of diverse migratory waves with complex, multi-directional trajectories across Europe, reshaping demographic and political landscapes throughout the Late Antiquity period.
Religious Influences and Ideological Drivers
The Crusades were motivated by a blend of religious zeal and papal calls to reclaim the Holy Land, emphasizing Christian pilgrimage and the defense against Muslim expansion. The Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period, was driven more by socio-political pressures and tribal movements with less theological impetus, often fueled by the decline of the Roman Empire and internal power struggles. While the Crusades embodied a codified religious ideology centered on salvation and holy warfare, the Volkerwanderung reflected fluid power dynamics and cultural transformations with comparatively minimal religious doctrinal impetus.
Military Strategies and Tactics
The Crusades employed fortified castles, heavy cavalry charges, and coordinated siege warfare emphasizing logistics across long-distance campaigns, while the Volkerwanderung utilized rapid, decentralized movements with light infantry and guerrilla tactics, exploiting mobility and surprise. Crusader forces relied on disciplined hierarchical command structures and supply lines, contrasting with the more fluid and adaptive tribal coalitions of the Volkerwanderung. The Crusades showcased evolving siege technologies and strategic territorial control, whereas the Volkerwanderung exemplified large-scale migrations impacting Roman military responses through persistent raids and territorial incursions.
Sociopolitical Impacts on Europe
The Crusades reshaped European sociopolitical structures by intensifying the power of monarchies and the Catholic Church while catalyzing economic growth through increased trade with the East. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period, triggered widespread political fragmentation and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, leading to the emergence of early medieval kingdoms and shifting tribal alliances. Both events profoundly influenced the evolution of European identities and territorial boundaries, laying foundations for the medieval sociopolitical landscape.
Cultural Exchanges and Consequences
The Crusades facilitated extensive cultural exchanges between Europe and the Middle East, introducing Europeans to advanced knowledge in science, medicine, and philosophy, while promoting trade and the transfer of technologies like navigation and architecture. In contrast, the Volkerwanderung (Migration Period) primarily caused widespread demographic shifts and cultural assimilation among Germanic tribes and the Roman Empire, leading to the foundation of medieval European kingdoms but limited long-distance cultural interaction. Both events shaped European history profoundly: the Crusades expanded intellectual horizons and economic networks, whereas the Volkerwanderung reshaped the continent's political and ethnic landscape.
Legacy and Historical Interpretations
The Crusades left a legacy marked by religious fervor, cultural exchanges, and enduring conflicts between Christianity and Islam, shaping medieval geopolitics and European identity. The Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period, profoundly influenced the demographic and political transformations of Europe, contributing to the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the formation of early medieval kingdoms. Historical interpretations of the Crusades emphasize their role in cross-cultural contact and military-religious expeditions, while the Volkerwanderung is viewed as a complex migration phenomenon that redefined ethnic boundaries and power structures in late antiquity.
Contrasts and Comparisons: Crusades vs Völkerwanderung
The Crusades were religious military campaigns from the 11th to 13th centuries aimed at reclaiming the Holy Land, involving organized armies under papal authority, while the Volkerwanderung, or Migration Period (4th-6th centuries), involved large-scale movements of Germanic tribes driven by climate change, economic pressures, and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. The Crusades centralized European power through feudal states and the Church, contrasting with the Volkerwanderung's decentralized tribal displacements that reshaped Europe's ethnic map and contributed to the formation of medieval kingdoms. Both events significantly impacted European societal structures but differed in motivations--religious fervor versus survival and territorial resettlement--and in their long-term cultural and political outcomes.
Crusades Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com