Corregidor, a historic island fortress located at the entrance of Manila Bay in the Philippines, played a crucial role during World War II as a key defense point against invading forces. The island's well-preserved ruins, underground tunnels, and war memorials offer visitors a profound glimpse into the country's wartime history. Discover more about Corregidor's strategic importance and how you can explore its rich heritage in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
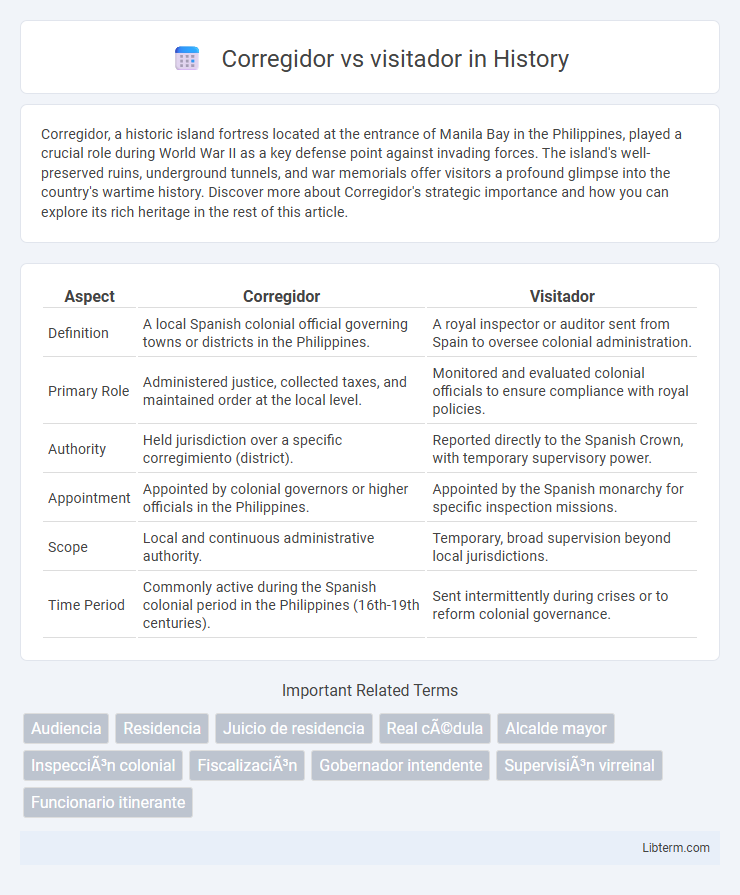
| Aspect | Corregidor | Visitador |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A local Spanish colonial official governing towns or districts in the Philippines. | A royal inspector or auditor sent from Spain to oversee colonial administration. |
| Primary Role | Administered justice, collected taxes, and maintained order at the local level. | Monitored and evaluated colonial officials to ensure compliance with royal policies. |
| Authority | Held jurisdiction over a specific corregimiento (district). | Reported directly to the Spanish Crown, with temporary supervisory power. |
| Appointment | Appointed by colonial governors or higher officials in the Philippines. | Appointed by the Spanish monarchy for specific inspection missions. |
| Scope | Local and continuous administrative authority. | Temporary, broad supervision beyond local jurisdictions. |
| Time Period | Commonly active during the Spanish colonial period in the Philippines (16th-19th centuries). | Sent intermittently during crises or to reform colonial governance. |
Understanding Corregidor and Visitador: Definitions
Corregidor was a Spanish colonial official responsible for governing a town or district, overseeing administrative and judicial functions to maintain order and enforce laws. Visitador refers to an inspector or royal auditor sent by the Spanish crown to supervise and investigate the actions of colonial officials, ensuring compliance with royal policies. Both roles were crucial in the colonial administration system, with the Corregidor managing local governance while the Visitador provided oversight and accountability.
Historical Origins of Corregidor and Visitador
The historical origins of the Corregidor trace back to the Spanish colonial period in the Philippines, serving as a fortified island crucial for defense against naval attacks. The Visitador, a royal inspector appointed by the Spanish Crown, emerged as a tool for oversight and reform within colonial administration to curb abuses and ensure compliance with the law. Both institutions reflect the centralized control mechanisms established by Spain to maintain authority and regulate governance in its overseas territories.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Corregidors acted as local administrators and judges in Spanish colonial towns, responsible for maintaining law and order, collecting taxes, and overseeing municipal governance. Visitadors held supervisory authority, conducting audits and inspections to ensure compliance with royal policies and investigating misconduct among officials. The Corregidor's role was more localized and operational, while the Visitador functioned as an external enforcer of accountability and reform.
Appointment Process: Corregidor vs Visitador
The appointment process for a Corregidor involved royal or central authorities directly selecting candidates based on loyalty and administrative skills to govern a town or district during the Spanish colonial period. In contrast, a Visitador was typically appointed by higher-ranking officials or the crown specifically to conduct investigations and audits, ensuring governance standards and legality were maintained. Corregidores exercised ongoing administrative and judicial powers, while Visitadores held temporary mandates focused on oversight and reform.
Jurisdiction and Areas of Influence
Corregidors exercised administrative and judicial authority over towns or districts, primarily in rural or provincial areas, focusing on local governance and law enforcement. Visitadors held broader oversight roles, often appointed by higher colonial authorities to inspect and investigate the conduct of officials across multiple regions, ensuring compliance with royal policies. Jurisdiction of corregidors was localized with direct influence on community affairs, while visitadors operated with expansive, sometimes temporary authority to enforce accountability within various colonial territories.
Administrative Functions Compared
Corregidors held executive, judicial, and military authority in Spanish colonial towns, managing local governance, tax collection, and law enforcement. Visitadors operated as royal inspectors tasked with auditing and supervising government officials to ensure compliance with colonial regulations. Their administrative functions differed as corregidors performed direct governance and day-to-day administration, while visitadors had oversight roles meant to check corruption and inefficiency.
Legal Authority and Powers
Corregidores in Spanish colonial administration held judicial, administrative, and military authority within a town or district, including power to enforce laws, collect taxes, and preside over local courts. Visitadores were royal inspectors appointed to audit and investigate colonial officials, possessing temporary authority to review governance, correct abuses, and recommend reforms directly to the Crown. While corregidores exercised ongoing local power, visitadores operated as external oversight agents with broad investigatory and supervisory powers but without permanent jurisdiction.
Challenges and Controversies
The Corregidor system faced significant challenges due to its overlapping authority with the Visitador, leading to frequent jurisdictional disputes and administrative inefficiencies. Controversies arose from conflicting reports and accusations of corruption, undermining the effectiveness of colonial governance and sparking conflicts between local officials and Spanish crown representatives. These challenges highlighted the complexities in balancing centralized control with regional oversight during the Spanish colonial period.
Impact on Colonial Governance
Corregidors, as royal officials, directly managed local governance, judicial matters, and tax collection, reinforcing Spanish control over colonial territories. Visitadors wielded broader authority by investigating and auditing colonial administration, identifying corruption, and recommending reforms to the Crown. The dynamic between corregidors' localized power and visitadors' oversight significantly shaped colonial governance, promoting accountability yet sometimes provoking administrative tensions.
Legacy and Historical Significance
Corregidor Island stands as a symbol of Filipino resilience and heroism during World War II, notably for its strategic role in resisting Japanese occupation and serving as the last bastion of defense. The legacy of Corregidor is preserved through its numerous war memorials, bunkers, and museums, highlighting its importance in Philippine military history and national identity. In contrast, the legacy of the Visitador, a Spanish colonial inspector, reflects administrative control and reform efforts in the Philippines, shaping colonial governance and contributing to the evolving relationship between the Spanish authorities and local populations during the colonial period.
Corregidor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com