The Grand Vizier was the highest-ranking official in the Ottoman Empire, acting as the sultan's chief minister and overseeing state administration, military affairs, and judicial matters. This powerful role required exceptional political acumen, as the Grand Vizier often held significant influence over the empire's governance and policies. Discover more about the impact and responsibilities of the Grand Vizier in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
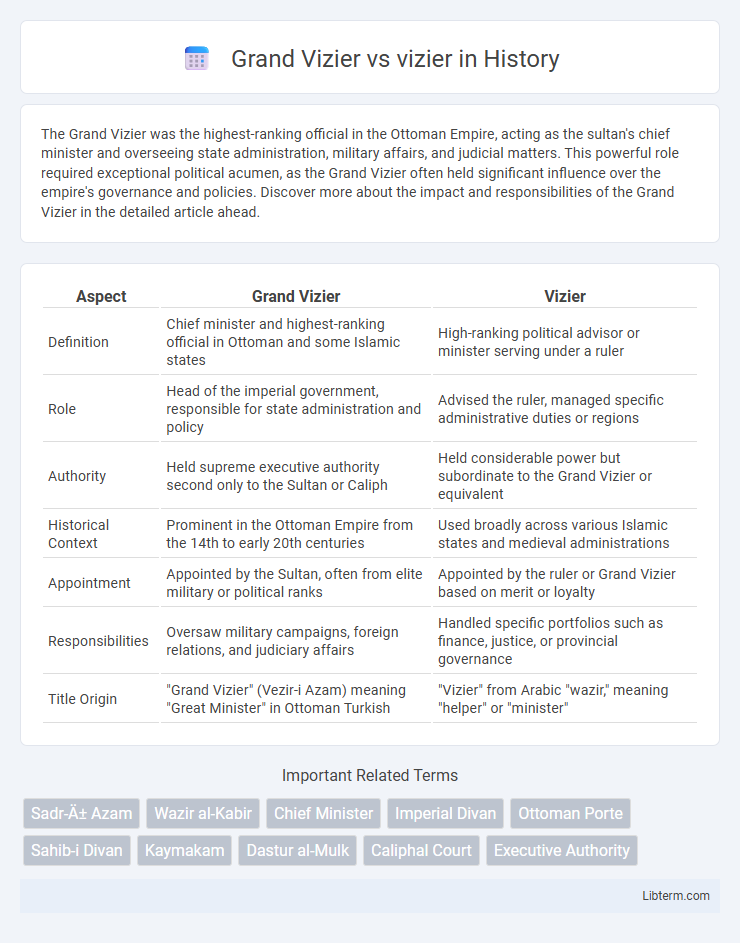
| Aspect | Grand Vizier | Vizier |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chief minister and highest-ranking official in Ottoman and some Islamic states | High-ranking political advisor or minister serving under a ruler |
| Role | Head of the imperial government, responsible for state administration and policy | Advised the ruler, managed specific administrative duties or regions |
| Authority | Held supreme executive authority second only to the Sultan or Caliph | Held considerable power but subordinate to the Grand Vizier or equivalent |
| Historical Context | Prominent in the Ottoman Empire from the 14th to early 20th centuries | Used broadly across various Islamic states and medieval administrations |
| Appointment | Appointed by the Sultan, often from elite military or political ranks | Appointed by the ruler or Grand Vizier based on merit or loyalty |
| Responsibilities | Oversaw military campaigns, foreign relations, and judiciary affairs | Handled specific portfolios such as finance, justice, or provincial governance |
| Title Origin | "Grand Vizier" (Vezir-i Azam) meaning "Great Minister" in Ottoman Turkish | "Vizier" from Arabic "wazir," meaning "helper" or "minister" |
Introduction to Viziers and Grand Viziers
Viziers were high-ranking political advisors and ministers in Islamic empires, responsible for administering state affairs, justice, and military oversight. The Grand Vizier held the highest office among viziers, acting as the sultan's chief minister and wielding supreme executive authority, often directing the entire government bureaucracy. Their roles evolved in empires like the Ottoman, where the Grand Vizier had powers comparable to a prime minister, while other viziers managed specific provinces or sectors.
Historical Origins of the Vizier Role
The title of Grand Vizier originated in the Ottoman Empire as the chief minister and head of the imperial government, wielding considerable executive power and acting as the Sultan's primary advisor. The role of vizier, with roots tracing back to the Abbasid Caliphate, was a high-ranking political advisor responsible for administration, justice, and military matters within Islamic governance structures. Historical records show that the vizier position evolved from early Persian and Islamic bureaucratic traditions, gradually becoming formalized in various Muslim empires, with the Grand Vizier embodying the pinnacle of this role in Ottoman political hierarchy.
The Definition and Duties of a Vizier
A vizier is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in Muslim governments, responsible for administrative duties, implementing royal decrees, and overseeing various state affairs. The Grand Vizier holds the highest vizier rank, acting as the Sultan's chief executive, managing the overall government, and coordinating between different ministries. Both roles involve key decision-making, but the Grand Vizier wields broader authority and often commands the empire's military and judicial systems.
The Emergence of the Grand Vizier Title
The title of Grand Vizier emerged in the Ottoman Empire as a distinct rank above the standard vizier, signifying the chief minister with supreme authority in the imperial administration. Unlike regular viziers who served as advisors or provincial governors, the Grand Vizier held the sultan's delegated powers, commanding the imperial council and military expeditions. This evolution was driven by the increasing complexity of governance, necessitating a central figure to coordinate state affairs and enforce the sultan's policies.
Key Differences: Grand Vizier vs. Vizier
The Grand Vizier served as the highest-ranking minister in the Ottoman Empire, often acting as the Sultan's chief advisor and head of government, whereas a vizier was a lower-ranking official responsible for specific administrative duties or regions. The Grand Vizier possessed extensive executive authority, including commanding the imperial council (Divan) and making significant policy decisions, while viziers operated under the Grand Vizier's supervision. Key differences lie in hierarchical status, scope of power, and responsibilities within the Ottoman political structure.
Power Dynamics Within Islamic Empires
The Grand Vizier held supreme authority as the chief minister in Islamic empires, often acting as the sultan's right hand and overseeing all administrative, military, and political affairs. In contrast, a vizier typically served under the Grand Vizier, managing specific governmental departments or regions with limited autonomy. The power dynamics centered on the Grand Vizier's ability to consolidate influence and act as a pivotal intermediary between the ruler and the bureaucracy, shaping empire-wide policy and decision-making.
Notable Grand Viziers in History
Grand Viziers served as the highest-ranking officials in the Ottoman Empire, wielding supreme administrative authority, unlike ordinary viziers who held more limited advisory roles. Notable Grand Viziers such as Sokollu Mehmed Pasha, who served under Suleiman the Magnificent and initiated significant reforms, and Koprulu Mehmed Pasha, founder of the influential Koprulu dynasty, left lasting impacts on Ottoman governance. These figures exemplify the distinction in power and influence between Grand Viziers and other viziers throughout Ottoman history.
Influence of Viziers in Government Administration
The Grand Vizier held the highest-ranking position among viziers, serving as the Sultan's chief advisor and often wielding significant executive authority over government administration. While viziers generally managed specific state affairs or provinces, the Grand Vizier coordinated the entire imperial bureaucracy, influencing policy decisions and overseeing military and financial matters. This hierarchical distinction amplified the Grand Vizier's role as the central figure in Ottoman governance, effectively acting as the prime minister.
Decline and Transformation of the Vizier System
The Grand Vizier, as the chief adviser and highest-ranking official, oversaw the decline and transformation of the vizier system during the late Ottoman period, reflecting the empire's administrative centralization and modernization efforts. The traditional vizier roles diminished in power as the Grand Vizier assumed more direct control, mirroring shifts toward bureaucratic governance and reducing decentralized authority. This transformation marked the gradual obsolescence of the classical vizier system, adapting it into a more structured and hierarchical state administration.
Lasting Legacy of Grand Viziers and Viziers
Grand Viziers, as the highest-ranking officials in Ottoman and Mughal empires, wielded substantial political power, often acting as the sultan's chief advisor and head of government, which cemented their lasting legacy in shaping administrative reforms and imperial policies. Viziers, serving as ministers or officials within various Islamic empires, contributed significantly to governance, diplomacy, and judicial matters, establishing institutional foundations that endured beyond their tenures. Both Grand Viziers and Viziers left enduring historical impacts through their roles in consolidating centralized authority and influencing cultural and political frameworks in Middle Eastern and South Asian history.
Grand Vizier Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com