Monumental inscriptions provide valuable historical and cultural insights by preserving messages carved on statues, tombs, and buildings. These texts offer clues about ancient civilizations, commemorating significant events, individuals, and beliefs that shaped societies over time. Explore the rest of this article to discover how monumental inscriptions reveal hidden stories and enrich your understanding of history.
Table of Comparison
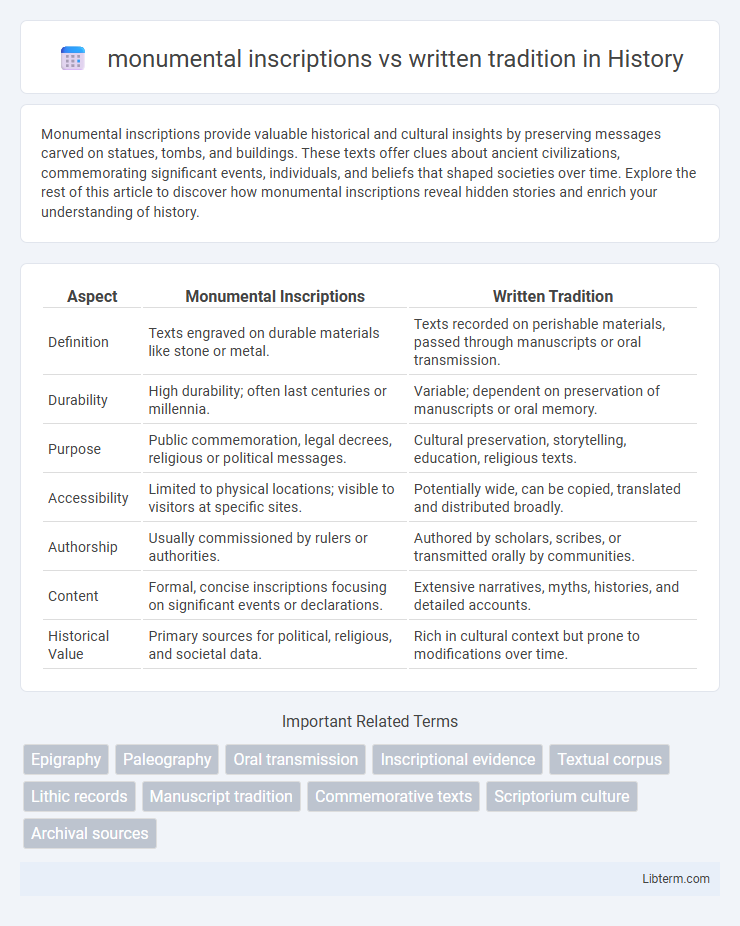
| Aspect | Monumental Inscriptions | Written Tradition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Texts engraved on durable materials like stone or metal. | Texts recorded on perishable materials, passed through manuscripts or oral transmission. |
| Durability | High durability; often last centuries or millennia. | Variable; dependent on preservation of manuscripts or oral memory. |
| Purpose | Public commemoration, legal decrees, religious or political messages. | Cultural preservation, storytelling, education, religious texts. |
| Accessibility | Limited to physical locations; visible to visitors at specific sites. | Potentially wide, can be copied, translated and distributed broadly. |
| Authorship | Usually commissioned by rulers or authorities. | Authored by scholars, scribes, or transmitted orally by communities. |
| Content | Formal, concise inscriptions focusing on significant events or declarations. | Extensive narratives, myths, histories, and detailed accounts. |
| Historical Value | Primary sources for political, religious, and societal data. | Rich in cultural context but prone to modifications over time. |
Understanding Monumental Inscriptions: An Overview
Monumental inscriptions provide direct, material evidence of historical events, social hierarchies, and cultural values engraved on durable materials like stone or metal, allowing for precise dating and contextual interpretation. Unlike written traditions often transmitted orally or through manuscripts, monumental inscriptions offer fixed texts that minimize alterations over time, enhancing their reliability for reconstructing past societies. The study of these inscriptions reveals insights into ancient governance, religious practices, and language evolution, serving as a critical complement to literary sources in historical research.
Defining Written Tradition in Historical Context
Written tradition in historical context refers to the systematic transmission of cultural, religious, or legal knowledge through written texts, often preserved in manuscripts, scrolls, or codices. Unlike monumental inscriptions, which are typically concise, public records engraved on stone or metal for durability and visibility, written traditions allow for more extensive, interpretative, and narrative content to be passed down generations. These texts form the foundation for historical scholarship by providing detailed accounts, laws, rituals, and stories that define societies beyond the symbolic or commemorative functions of inscriptions.
Origins and Purposes: Monumental Inscriptions vs Written Records
Monumental inscriptions originated as public displays engraved on materials like stone or metal, serving to commemorate events, legitimize authority, or immortalize achievements in a durable form. Written tradition, contrastingly, developed primarily for recording narratives, laws, and knowledge within portable media such as papyrus, parchment, or paper, facilitating communication across time and space. The purpose of monumental inscriptions centers on permanence and public visibility, whereas written records prioritize preservation, transmission, and detailed documentation of cultural and societal information.
Material and Medium: Stone, Parchment, and Beyond
Monumental inscriptions primarily utilize durable materials like stone and metal, ensuring longevity and public visibility, while written tradition relies on more fragile media such as parchment, papyrus, and paper, which allow for portability and widespread dissemination. Stone inscriptions serve as permanent records etched into monuments, often commemorating events or decrees, contrasting with the flexibility of parchment manuscripts that facilitate detailed narratives, religious texts, and administrative records. The physical medium shapes the transmission of information--stone anchors authority in space and time, whereas parchment supports textual complexity and historical continuity across generations.
Public Display vs Private Documentation
Monumental inscriptions serve as public displays designed to convey authoritative messages, commemorate events, or legitimize power and are often carved in durable materials like stone or metal for visibility and permanence. Written traditions, in contrast, function as private documentation, preserved in manuscripts or scrolls meant for selective readership, enabling detailed record-keeping, transmission of knowledge, and cultural continuity within specific communities. The public nature of monumental inscriptions emphasizes collective memory and official narratives, while written traditions prioritize individualized interpretation and the preservation of nuanced information over time.
Transmission and Preservation of Knowledge
Monumental inscriptions serve as durable, publicly accessible records that ensure the long-term preservation of historical events, laws, and religious texts, often engraved in stone or metal to withstand environmental degradation. Written tradition relies on manuscripts, scrolls, and later printed materials, which require continuous copying and transmission across generations, making them more vulnerable to loss, alteration, or decay. The preservation quality of monumental inscriptions inherently supports reliable knowledge transmission over centuries, whereas written tradition offers flexibility and detail but depends heavily on custodianship and reproduction fidelity.
Reliability and Authenticity of Sources
Monumental inscriptions provide a highly reliable and authentic source for historical research due to their contemporaneous nature and physical permanence, often carved in stone or metal to ensure durability. Written traditions, while rich in cultural and narrative value, may incorporate interpolations, oral transmission errors, and ideological biases, which can affect their accuracy and require critical analysis. The direct materiality of inscriptions serves as a primary evidence base, offering verifiable dates, official records, and linguistic data that enhance historical authenticity.
Influence on Collective Memory and Identity
Monumental inscriptions, etched in durable materials and placed in public spaces, serve as tangible anchors for collective memory by preserving authoritative narratives that reinforce community identity over time. Written traditions, through manuscripts and oral transcriptions, offer a dynamic and interpretive record that allows societies to adapt and reinterpret their histories to maintain cultural continuity. The interplay between these forms shapes collective identity by balancing permanence and adaptability in the transmission of cultural values and historical consciousness.
Interpretative Challenges: Deciphering Inscriptions vs Manuscripts
Monumental inscriptions often present interpretative challenges due to weathering, incomplete texts, and contextual ambiguity, contrasting with manuscripts that typically offer more complete and continuous narratives. Deciphering inscriptions requires expertise in epigraphy and paleography to reconstruct damaged or eroded characters, while manuscripts demand linguistic analysis to understand historical language evolution and scribal variations. Both sources complement each other, but inscriptions provide tangible, public records that are often more fragmented, making their interpretation a complex task requiring cross-disciplinary methods.
Modern Relevance: Digitalization and Heritage Conservation
Monumental inscriptions provide irreplaceable primary data for heritage conservation, capturing historical information in durable materials that digitalization helps preserve and analyze without loss of authenticity. Digital archives of these inscriptions enable global accessibility and advanced semantic searches, enhancing research and education beyond the limits of written traditions often confined to fragile manuscripts. Integrating digital tools with conservation efforts supports the safeguarding of cultural identity by ensuring that monumental texts remain accessible despite environmental or human threats.
monumental inscriptions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com