Yeomen were skilled warriors and landowners serving medieval lords, often acting as reliable archers on the battlefield. Knights embodied the highest social rank of mounted warriors, bound by chivalry and responsible for protecting realms and upholding justice. Discover how the distinct roles of Yeoman and Knight shaped medieval society and influenced your understanding of historical warfare in the full article.
Table of Comparison
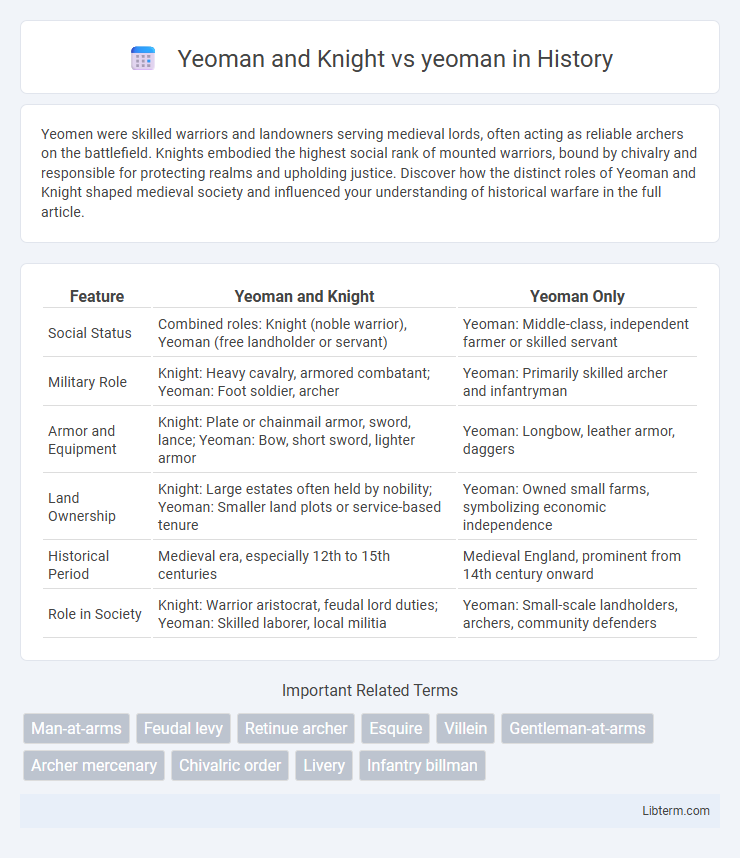
| Feature | Yeoman and Knight | Yeoman Only |
|---|---|---|
| Social Status | Combined roles: Knight (noble warrior), Yeoman (free landholder or servant) | Yeoman: Middle-class, independent farmer or skilled servant |
| Military Role | Knight: Heavy cavalry, armored combatant; Yeoman: Foot soldier, archer | Yeoman: Primarily skilled archer and infantryman |
| Armor and Equipment | Knight: Plate or chainmail armor, sword, lance; Yeoman: Bow, short sword, lighter armor | Yeoman: Longbow, leather armor, daggers |
| Land Ownership | Knight: Large estates often held by nobility; Yeoman: Smaller land plots or service-based tenure | Yeoman: Owned small farms, symbolizing economic independence |
| Historical Period | Medieval era, especially 12th to 15th centuries | Medieval England, prominent from 14th century onward |
| Role in Society | Knight: Warrior aristocrat, feudal lord duties; Yeoman: Skilled laborer, local militia | Yeoman: Small-scale landholders, archers, community defenders |
Defining Yeoman: Historical Context and Roles
Yeoman historically referred to a class of freeholders in medieval England who owned and cultivated their land, often serving as skilled archers in military contexts. As agricultural workers and minor landowners, yeomen played a crucial role in local economies and were distinguished from knights by their lower social status and lack of noble titles. The distinction between knight and yeoman involved differences in land ownership, military duties, and social hierarchy, with knights typically serving as heavily armored cavalry and holding significant feudal power.
Who Were the Knights? Social Status and Duties
Knights were medieval warriors of noble birth who held a higher social status than yeomen, serving as heavily armored cavalry sworn to protect their lord's lands and uphold chivalric codes. They underwent rigorous training from a young age and were often granted lands in exchange for military service, distinguishing them from yeomen, who were free peasants or skilled farmers with fewer privileges. Knights' duties included battlefield combat, administering justice, and participating in tournaments, reflecting their elite role within the feudal hierarchy.
Yeoman vs. Knight: Distinguishing Key Characteristics
Yeoman and Knight differ primarily in social status and military role, with Knights serving as elite armored cavalry and Yeomen as skilled foot soldiers or archers. Knights wore heavy armor, rode horses, and adhered to chivalric codes, while Yeomen typically fought with longbows or spears and held lower social rank. Economic resources, training, and battlefield function distinguish Knights' noble class from Yeoman's middling military status in medieval society.
Land Ownership: Yeoman and Knight Comparisons
Yeoman typically owned small to medium-sized land parcels, granting them economic independence and a middle-tier status in the medieval feudal hierarchy. Knights held larger estates often granted by the crown or noble lords in exchange for military service, reflecting their upper-tier social and economic power. The disparity in land ownership between yeomen and knights underscores the broader feudal system, where land was a primary source of wealth and authority.
Military Responsibilities: Yeoman and Knight in Warfare
Yeomen served as skilled infantry soldiers responsible for archery, reconnaissance, and maintaining communication lines during medieval warfare, playing a crucial role in supporting knights and ensuring battlefield coordination. Knights, heavily armored cavalry, led charges, engaged in direct combat, and often commanded troops, embodying the elite fighting force with strategic battlefield roles. The distinct military responsibilities of yeomen and knights complemented each other, with yeomen providing tactical support and ranged attacks while knights executed decisive melee engagements.
Societal Importance: How Yeomen and Knights Shaped Communities
Yeomen and knights played distinct yet complementary roles in medieval communities, with yeomen serving as skilled, land-owning farmers who provided economic stability and local governance, while knights upheld military defense and upheld feudal order. Yeomen's agricultural productivity and participation in local courts reinforced social cohesion and economic resilience within villages. Knights, through their martial responsibilities and patronage, fostered regional security and influenced the hierarchical structure critical to maintaining societal order.
Legal Rights and Privileges: Yeoman versus Knight
Yeomen held legal rights that allowed them to own land and participate in local courts, whereas knights enjoyed extensive privileges including military command and exemption from certain taxes. Knights possessed higher social status with hereditary titles and feudal duties, granting them greater influence in medieval legal and political systems. Yeomen, as free commoners, had limited legal protections compared to the noble privileges that knights could leverage within feudal hierarchies.
Economic Standing: Wealth and Lifestyle Differences
Yeomen were typically small landowners or prosperous farmers with moderate wealth, enabling a comfortable but modest rural lifestyle centered on agricultural productivity and community involvement. Knights held significantly higher economic standing, possessing extensive lands, greater income from manorial rents, and the financial means to support a chivalric lifestyle involving armor, horses, and participation in military campaigns. The wealth disparity between knights and yeomen shaped their distinct social roles and lifestyle choices, with knights enjoying privileges and status tied to nobility, while yeomen maintained independent, hardworking middle-class lives.
Symbolism and Representation in Literature
Yeoman in literature symbolizes loyalty, diligence, and the common man's role within feudal and medieval societies, often representing grounded virtue and practical service. The Knight vs Yeoman dynamic highlights contrasting social hierarchies and values: the Knight embodies chivalry, honor, and nobility, while the Yeoman emphasizes hardworking reliability and connection to the land. This juxtaposition serves to explore themes of class distinction, duty, and individual identity within literary narratives.
Yeoman and Knight: Lasting Legacies in Modern Culture
Yeoman and Knight embody enduring symbols of medieval hierarchy, with yeomen representing skilled commoners and knights symbolizing noble warriors bound by chivalry. The legacy of knights endures in modern culture through literature, film, and ceremonial orders that highlight ideals of honor and bravery. Yeomen contribute to cultural heritage by reflecting the rise of the common man, influencing contemporary narratives of social mobility and grassroots valor.
Yeoman and Knight Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com