A complainant is an individual or party who formally initiates a legal action or files a complaint to address a grievance or seek remedy. Understanding the role and rights of a complainant is essential in navigating legal procedures effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how being a complainant impacts your legal journey and the steps involved.
Table of Comparison
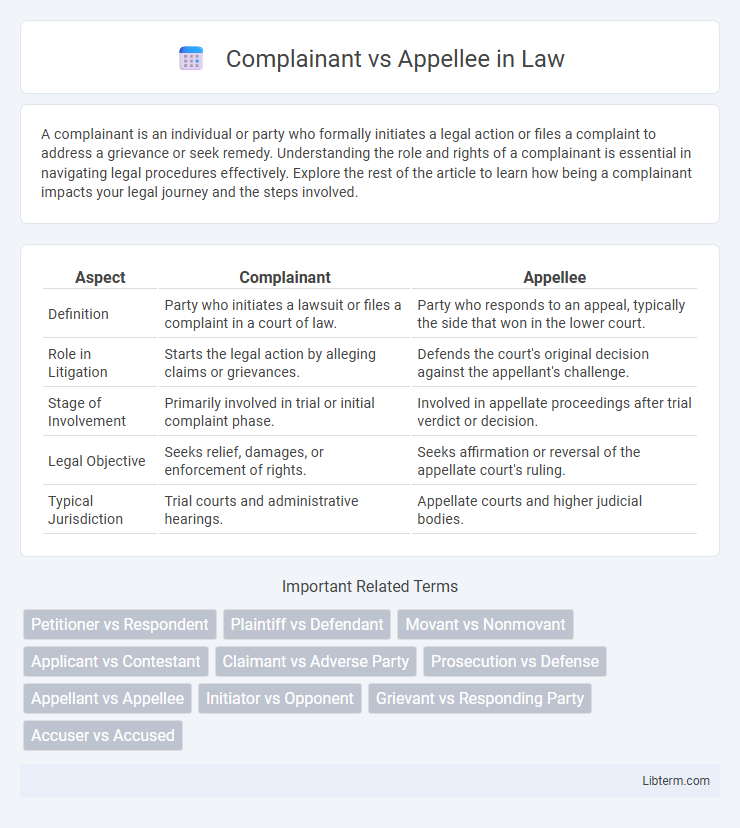
| Aspect | Complainant | Appellee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party who initiates a lawsuit or files a complaint in a court of law. | Party who responds to an appeal, typically the side that won in the lower court. |
| Role in Litigation | Starts the legal action by alleging claims or grievances. | Defends the court's original decision against the appellant's challenge. |
| Stage of Involvement | Primarily involved in trial or initial complaint phase. | Involved in appellate proceedings after trial verdict or decision. |
| Legal Objective | Seeks relief, damages, or enforcement of rights. | Seeks affirmation or reversal of the appellate court's ruling. |
| Typical Jurisdiction | Trial courts and administrative hearings. | Appellate courts and higher judicial bodies. |
Introduction to Legal Terms: Complainant vs Appellee
The complainant is the party who initiates a lawsuit by filing a complaint, seeking legal remedy for an alleged wrong. The appellee, on the other hand, is the party responding to an appeal, defending the original court's decision after the case is reviewed by a higher court. Understanding the distinction between complainant and appellee is essential in navigating civil litigation and appellate procedures.
Definition of Complainant in Legal Context
The complainant in a legal context refers to the individual or party who initiates a lawsuit or legal action by filing a formal complaint or accusation against another party. This entity alleges wrongdoing or harm caused by the appellee or defendant and seeks legal remedy or relief through the judicial system. The role of the complainant is critical in civil and criminal cases as they set the litigation process in motion by presenting their claims to a court.
Definition of Appellee in Legal Proceedings
An appellee is the party against whom an appeal is filed in a legal proceeding, typically the winner in the lower court who seeks to uphold the decision. Unlike the complainant, who initiates the case at the trial level, the appellee responds to the appellant's challenge by defending the original judgment. The appellee plays a crucial role in appellate courts by providing arguments and evidence to maintain the verdict or order being contested.
Key Differences Between Complainant and Appellee
The complainant initiates a lawsuit by filing a complaint, alleging wrongdoing and seeking legal remedy, whereas the appellee is the party responding to an appeal, typically defending the lower court's decision. The complainant's role is pivotal in the trial court phase, while the appellee becomes relevant during appellate proceedings. Understanding this distinction clarifies procedural positions and responsibilities within the judicial system.
Legal Roles and Responsibilities: Complainant vs Appellee
The complainant initiates a legal action by filing a complaint, setting forth allegations and seeking remedies in the trial court, while the appellee is the party responding to an appeal, defending the trial court's decision. The complainant holds the responsibility to prove their claims with sufficient evidence during the initial trial phase, whereas the appellee must demonstrate that the lower court's judgment was legally sound during the appellate review. Both roles involve distinct procedural duties: the complainant frames the dispute and pursues relief, and the appellee counters the appeal, aiming to uphold the original ruling.
Situations Where “Complainant” is Used
The term "complainant" is primarily used in criminal and administrative proceedings to designate the individual or party who initiates a complaint or alleges wrongdoing. Situations where a complainant is involved include reporting a criminal offense to law enforcement or filing a formal grievance with a regulatory agency. Unlike an appellee, the complainant is the originator of the complaint rather than the respondent appealing a court decision.
Cases Involving an “Appellee”
In cases involving an appellee, this party is the respondent who prevailed in the lower court and is responding to an appeal filed by the complainant or appellant. The appellee's role includes submitting briefs and oral arguments to defend the original court ruling. Courts primarily assess whether the appellee's position upholds the trial court's legal findings and procedural correctness.
Complainant and Appellee in Civil vs Criminal Law
In civil law, the complainant is typically referred to as the plaintiff, who initiates the lawsuit seeking remedies for grievances such as breach of contract or property disputes, while the appellee is the party responding to an appeal, defending a lower court's decision. In criminal law, the complainant is often the prosecution or state representing the public interest in pursuing charges against the defendant, whereas the appellee is the government or prosecution defending a conviction or sentence on appeal. The roles highlight the distinction between private party disputes in civil cases and public interest enforcement in criminal proceedings.
Process Flow: From Complainant to Appellee
The process flow begins with the complainant filing a formal complaint outlining grievances or claims against an opposing party. Once the complaint is submitted, the appellee, typically the party who won in the lower court but is responding to an appeal, receives notification and is required to file a response or brief addressing the issues raised. The appellate court reviews the submissions from both the complainant and appellee before making a final determination on the appeal.
Importance of Understanding Legal Party Terminology
Understanding the distinction between Complainant and Appellee is crucial in legal contexts to accurately interpret court documents and proceedings. The Complainant initiates a lawsuit by filing a complaint, while the Appellee is the party responding to an appeal after a trial court decision. Clear comprehension of these terms enhances effective legal communication and ensures proper procedural adherence during litigation and appeals.
Complainant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com