The Uniform Securities Act provides a standardized framework for regulating securities transactions to protect investors from fraud and ensure market integrity. It outlines registration requirements, exemptions, and enforcement mechanisms for securities offerings and professionals. Explore the article to understand how this act impacts your investments and financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
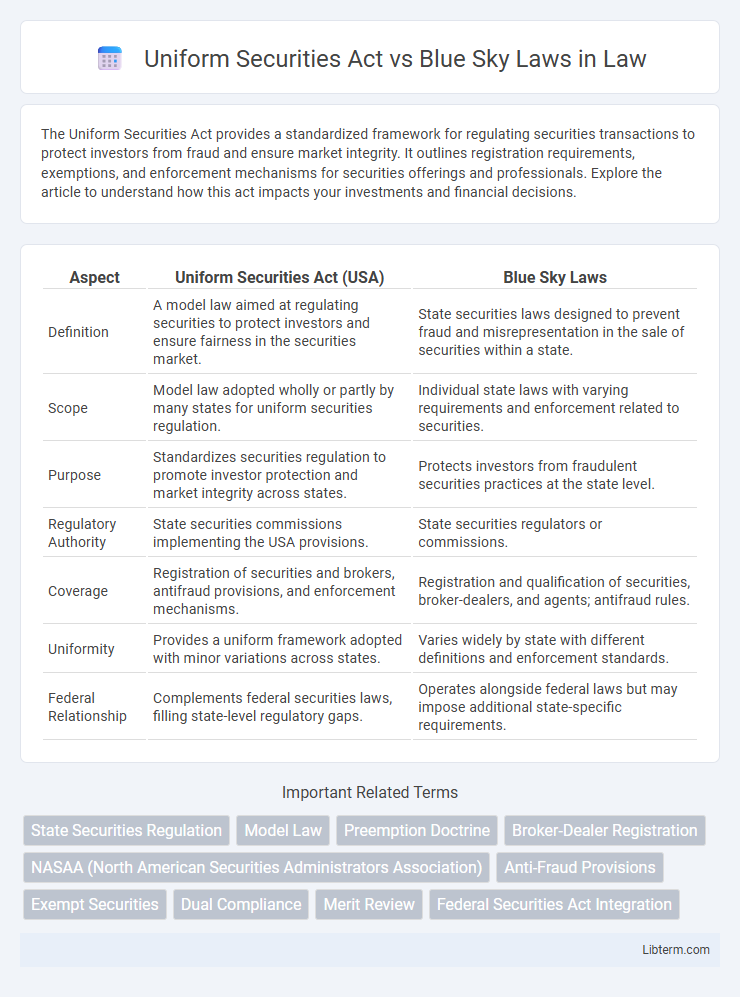
| Aspect | Uniform Securities Act (USA) | Blue Sky Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A model law aimed at regulating securities to protect investors and ensure fairness in the securities market. | State securities laws designed to prevent fraud and misrepresentation in the sale of securities within a state. |
| Scope | Model law adopted wholly or partly by many states for uniform securities regulation. | Individual state laws with varying requirements and enforcement related to securities. |
| Purpose | Standardizes securities regulation to promote investor protection and market integrity across states. | Protects investors from fraudulent securities practices at the state level. |
| Regulatory Authority | State securities commissions implementing the USA provisions. | State securities regulators or commissions. |
| Coverage | Registration of securities and brokers, antifraud provisions, and enforcement mechanisms. | Registration and qualification of securities, broker-dealers, and agents; antifraud rules. |
| Uniformity | Provides a uniform framework adopted with minor variations across states. | Varies widely by state with different definitions and enforcement standards. |
| Federal Relationship | Complements federal securities laws, filling state-level regulatory gaps. | Operates alongside federal laws but may impose additional state-specific requirements. |
Overview of the Uniform Securities Act
The Uniform Securities Act (USA) serves as a model legislation designed to regulate securities transactions and protect investors by standardizing state securities laws across the United States. It outlines key regulatory provisions including registration requirements for brokers, dealers, and advisers, as well as anti-fraud measures to prevent deceptive securities practices. The USA aims to provide consistent oversight while complementing federal securities regulations, distinguishing it from individual state Blue Sky laws, which vary in scope and enforcement.
Understanding Blue Sky Laws
Blue Sky Laws are state-level securities regulations designed to protect investors from fraudulent sales practices and ensure transparency in investment offerings. These laws require companies to register their securities offerings and provide detailed disclosures, aiming to prevent fraud and misrepresentation in local markets. The Uniform Securities Act serves as a model law to help states standardize their Blue Sky Laws, promoting consistency across jurisdictions.
Historical Development of State Securities Regulation
The historical development of state securities regulation began with Blue Sky Laws, enacted in the early 20th century to protect investors from fraudulent securities practices by requiring registration and disclosure at the state level. The Uniform Securities Act (USA), first introduced in 1956 by the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws, aimed to standardize and modernize these diverse state laws, providing a consistent framework for securities regulation across the United States. Over time, the USA served as a model statute that many states adopted or adapted, enhancing investor protection and streamlining enforcement against securities fraud.
Key Provisions in the Uniform Securities Act
The Uniform Securities Act establishes comprehensive regulatory frameworks including registration requirements for securities, broker-dealers, and investment advisers to protect investors from fraud and ensure transparency in securities transactions. It mandates detailed disclosures through prospectuses, antifraud provisions, and enforcement powers such as cease and desist orders and penalties, forming a standardized legal foundation across adopting states. Unlike Blue Sky Laws, which vary individually by state, the Uniform Securities Act promotes uniformity, simplifying compliance and enforcement in state securities regulation.
Variations in Blue Sky Laws Across States
Blue Sky Laws vary significantly across states, creating a complex regulatory environment compared to the more standardized Uniform Securities Act (USA). Each state implements its own registration requirements, disclosure obligations, and exemptions under its Blue Sky Law, leading to differences in investor protection and enforcement practices. These variations challenge issuers and brokers seeking multi-state compliance, emphasizing the importance of understanding specific state regulations alongside the broader framework provided by the USA.
Registration Requirements: Uniform Securities Act vs Blue Sky Laws
The Uniform Securities Act establishes standardized registration requirements for securities offerings and broker-dealer activities, promoting consistency across states by requiring filings, disclosure documents, and exemptions from registration. Blue Sky Laws vary significantly by state but generally mandate registration of securities and brokers to protect investors from fraud, often imposing unique local filing fees and disclosure standards. The Uniform Securities Act aims to harmonize these registration requirements, reducing duplicative filings and enhancing regulatory efficiency compared to the diverse and sometimes burdensome mandates of individual Blue Sky Laws.
Exemptions under Both Regulatory Frameworks
Exemptions under the Uniform Securities Act primarily include transactions involving government securities, certain non-profit organizations, and private placements that restrict resale to protect investors. Blue Sky Laws offer exemptions tailored by each state, often covering small offerings, intrastate offerings, and sales to accredited investors to reduce regulatory burdens while maintaining investor protection. Both frameworks aim to balance efficient capital formation with fraud prevention by delineating clear exemption categories aligned with federal securities laws.
Enforcement Mechanisms and Authorities
The Uniform Securities Act (USA) provides a standardized framework for regulating securities transactions and enforcement across states, empowering state securities administrators with the authority to investigate, prosecute fraud, and impose penalties. Blue Sky Laws, varying by state, establish specific state-level regulations and enforcement mechanisms, typically administered by state securities commissions or attorney generals with powers to pursue civil and criminal actions against violators. Enforcement under both frameworks includes cease and desist orders, fines, license revocations, and coordination with federal agencies like the SEC to enhance regulatory compliance and investor protection.
Investor Protections: Comparing Effectiveness
The Uniform Securities Act provides a standardized framework for state securities regulation, enhancing investor protections through clear registration requirements and antifraud provisions. Blue Sky Laws, although varying by state, also focus heavily on preventing fraudulent activities and ensuring transparency in securities offerings, but their effectiveness depends on the rigor of each state's enforcement. Comparing the two, the Uniform Securities Act offers a more consistent and comprehensive approach to investor protection, while Blue Sky Laws may offer stronger localized oversight in states with more aggressive regulatory practices.
Harmonization Efforts and Current Challenges
Harmonization efforts between the Uniform Securities Act (USA) and Blue Sky Laws aim to create consistent regulatory standards across U.S. states to streamline securities registration and protect investors. Despite these efforts, states maintain variations in definitions, exemptions, and enforcement practices, posing challenges for nationwide compliance and increasing costs for issuers. Current challenges include technological advancements, such as digital assets, which demand adaptable frameworks while balancing state sovereignty and investor protection.
Uniform Securities Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com