Stare decisis is a fundamental legal principle ensuring courts follow precedents established in previous rulings to maintain consistency and stability in the law. This doctrine promotes predictability in judicial decisions, guiding judges to respect established case law unless compelling reasons justify departure. Explore the rest of the article to understand how stare decisis impacts your legal rights and the justice system.
Table of Comparison
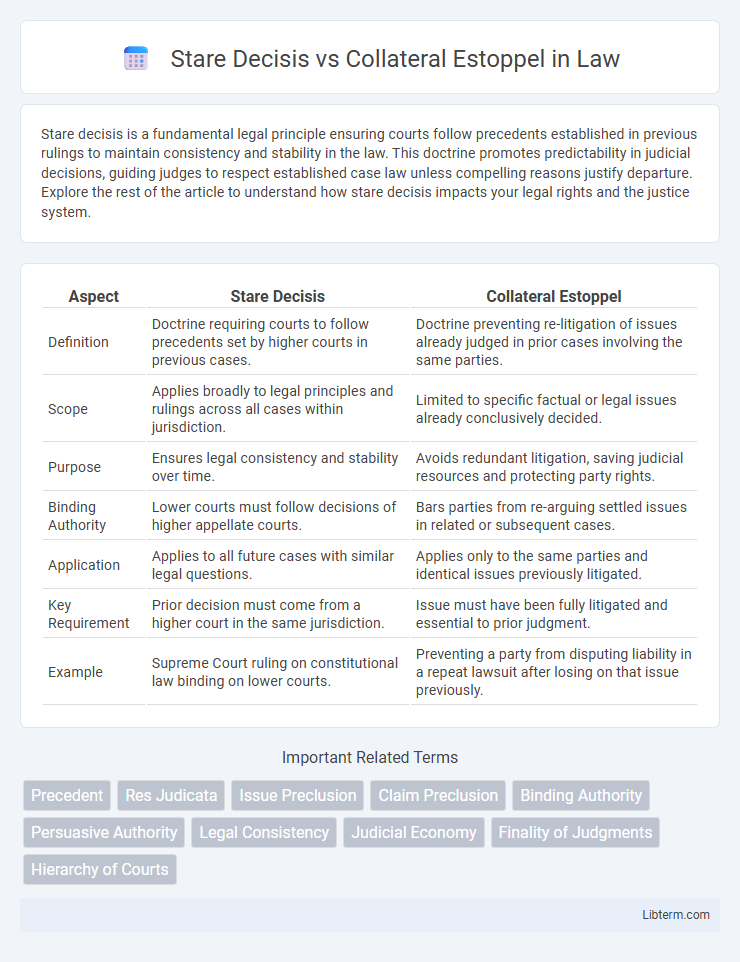
| Aspect | Stare Decisis | Collateral Estoppel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Doctrine requiring courts to follow precedents set by higher courts in previous cases. | Doctrine preventing re-litigation of issues already judged in prior cases involving the same parties. |
| Scope | Applies broadly to legal principles and rulings across all cases within jurisdiction. | Limited to specific factual or legal issues already conclusively decided. |
| Purpose | Ensures legal consistency and stability over time. | Avoids redundant litigation, saving judicial resources and protecting party rights. |
| Binding Authority | Lower courts must follow decisions of higher appellate courts. | Bars parties from re-arguing settled issues in related or subsequent cases. |
| Application | Applies to all future cases with similar legal questions. | Applies only to the same parties and identical issues previously litigated. |
| Key Requirement | Prior decision must come from a higher court in the same jurisdiction. | Issue must have been fully litigated and essential to prior judgment. |
| Example | Supreme Court ruling on constitutional law binding on lower courts. | Preventing a party from disputing liability in a repeat lawsuit after losing on that issue previously. |
Introduction to Stare Decisis and Collateral Estoppel
Stare Decisis is a fundamental legal principle that mandates courts to follow precedents set by higher courts within the same jurisdiction to ensure consistency and predictability in the law. Collateral Estoppel, also known as issue preclusion, prevents parties from re-litigating issues that have been conclusively resolved in previous legal proceedings between the same parties. Both doctrines promote judicial efficiency but operate differently: Stare Decisis binds courts to established legal rules, while Collateral Estoppel binds parties to previously determined factual or legal issues.
Defining Stare Decisis: Legal Precedent Explained
Stare decisis, a foundational principle in common law, mandates that courts follow established legal precedents to ensure consistency and predictability in judicial decisions. This doctrine requires judges to adhere to prior rulings from higher courts within the same jurisdiction when deciding cases with similar facts or legal issues. Unlike collateral estoppel, which prevents re-litigation of specific issues between the same parties, stare decisis governs the broader application of legal principles across different cases, reinforcing stability in the law.
Understanding Collateral Estoppel: Issue Preclusion
Collateral estoppel, also known as issue preclusion, prevents parties from relitigating an issue that has already been conclusively decided in a previous case involving the same parties. This doctrine ensures judicial efficiency by binding courts to prior determinations of factual or legal issues, provided the issue was actually litigated and essential to the prior judgment. Unlike stare decisis, which binds courts to precedent decisions on legal principles, collateral estoppel applies specifically to factual or legal issues between the same litigants, promoting finality in litigation.
Key Differences Between Stare Decisis and Collateral Estoppel
Stare decisis mandates courts to follow precedent in future cases with similar facts and legal issues, ensuring consistency in judicial decisions. Collateral estoppel, or issue preclusion, prevents re-litigation of specific factual or legal issues already resolved between the same parties in prior cases. Unlike stare decisis, which applies broadly to legal principles across cases, collateral estoppel restricts only particular issues in subsequent suits involving identical parties.
Historical Development of Stare Decisis and Collateral Estoppel
Stare decisis, rooted in English common law since the 14th century, mandates courts to follow precedent to ensure legal consistency and predictability. Collateral estoppel, emerging from 19th-century American jurisprudence, prevents re-litigation of issues already decided in prior cases involving the same parties. Both doctrines evolved to promote judicial efficiency and fairness, with stare decisis emphasizing adherence to precedent and collateral estoppel focusing on issue preclusion.
Application of Stare Decisis in Judicial Decisions
Stare Decisis ensures judicial consistency by requiring courts to follow precedents established in previous rulings, thereby promoting legal stability and predictability. It is primarily applied in higher courts, where decisions bind lower courts within the same jurisdiction, reinforcing uniform interpretations of the law. This doctrine differs from collateral estoppel, which prevents the re-litigation of specific factual or legal issues already decided between the same parties in prior cases.
Role of Collateral Estoppel in Litigation
Collateral estoppel, also known as issue preclusion, prevents parties from relitigating an issue already decided in a previous case, promoting judicial efficiency and consistency. In litigation, collateral estoppel plays a critical role by barring reexamination of facts or legal questions that were conclusively resolved, thereby conserving court resources and avoiding contradictory judgments. Unlike stare decisis, which binds courts to precedent on broad legal principles, collateral estoppel applies to specific factual or legal issues between the same parties in subsequent proceedings.
Practical Implications for Legal Practitioners
Stare decisis ensures legal consistency by requiring courts to follow established precedents, allowing legal practitioners to predict case outcomes and advise clients effectively. Collateral estoppel prevents parties from relitigating issues already decided in previous cases, streamlining litigation and reducing legal costs. Understanding the interplay between these doctrines enables attorneys to strategically navigate case law, manage risk, and optimize courtroom efficiency.
Landmark Cases on Stare Decisis and Collateral Estoppel
Landmark cases on stare decisis include *Marbury v. Madison* (1803), which firmly established judicial review and the principle that courts must follow precedent to ensure legal consistency. For collateral estoppel, *Parklane Hosiery Co. v. Shore* (1979) stands out by clarifying that once an issue is litigated and decided, it cannot be re-litigated between the same parties in future lawsuits. Both doctrines serve to maintain judicial economy and fairness, with stare decisis ensuring continuity in legal rulings and collateral estoppel preventing repetitive litigation on established facts or issues.
Conclusion: Navigating Legal Consistency and Finality
Stare decisis ensures legal consistency by requiring courts to follow precedent, promoting predictable and stable law development. Collateral estoppel enforces finality by preventing re-litigation of issues already decided, reducing judicial burden and protecting parties from redundant lawsuits. Balancing these doctrines is essential for maintaining both the reliability of legal rulings and the efficient administration of justice.
Stare Decisis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com