Exploring the science behind REM sleep reveals its crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation. During this sleep phase, your brain processes information and resets itself for optimal function. Discover how maximizing REM sleep can enhance your well-being by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
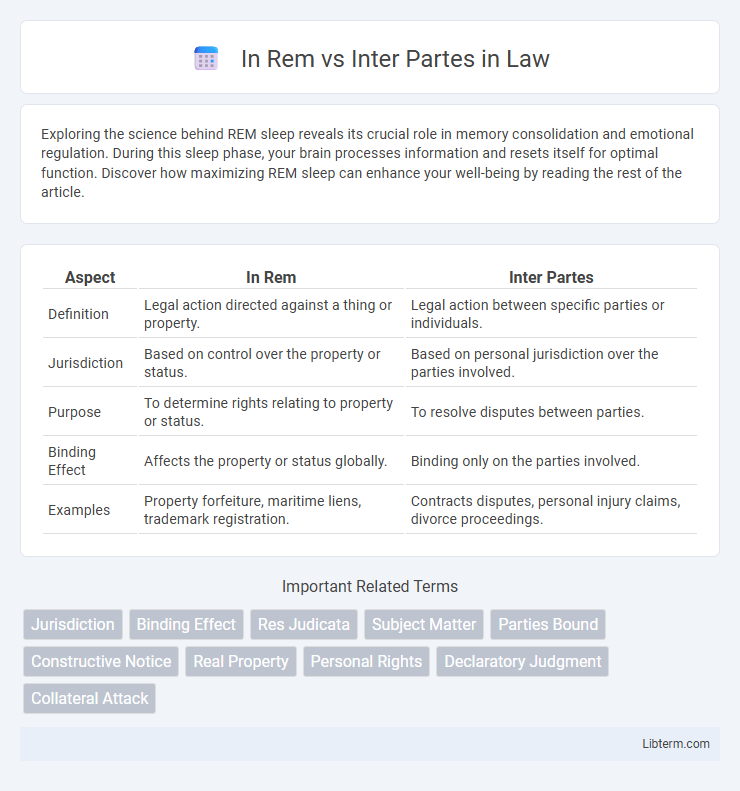
| Aspect | In Rem | Inter Partes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action directed against a thing or property. | Legal action between specific parties or individuals. |
| Jurisdiction | Based on control over the property or status. | Based on personal jurisdiction over the parties involved. |
| Purpose | To determine rights relating to property or status. | To resolve disputes between parties. |
| Binding Effect | Affects the property or status globally. | Binding only on the parties involved. |
| Examples | Property forfeiture, maritime liens, trademark registration. | Contracts disputes, personal injury claims, divorce proceedings. |
Understanding In Rem and Inter Partes: Definitions
In rem refers to legal actions directed against a specific property rather than a person, allowing courts to determine rights concerning that property itself. Inter partes actions involve disputes between specific parties, focusing on their rights and obligations under the law. Understanding the distinction between in rem, which targets property, and inter partes, which targets parties, is crucial in legal contexts such as intellectual property and property law.
Historical Evolution of In Rem and Inter Partes Proceedings
In rem proceedings originated in Roman law as remedies directed at property, allowing courts to assert jurisdiction based on the location of the subject matter rather than the parties involved. Inter partes proceedings evolved later, emphasizing disputes between specific parties with rights or obligations directly affected, facilitating adversarial engagement and detailed examination of claims. Historical evolution reflects the shift from property-focused legal actions to more structured dispute resolution between parties, shaping modern procedural frameworks in civil and property law.
Key Differences Between In Rem and Inter Partes Actions
In rem actions focus on rights against a specific property, allowing courts to determine control or ownership irrespective of the owner's identity. Inter partes actions involve disputes between specific parties, where the court resolves conflicts based on individual claims and liabilities. The key difference lies in in rem's jurisdiction over the property itself versus inter partes' jurisdiction over the parties involved.
Jurisdictional Scope in In Rem vs Inter Partes Cases
In rem jurisdiction focuses on the status of a specific property or thing within the territory of the court, allowing courts to exercise authority over the property itself rather than the parties involved. Inter partes jurisdiction involves the court's power over the parties to a dispute, requiring personal jurisdiction to adjudicate rights and obligations between individuals. The key distinction lies in in rem cases resolving rights related to the property universally, whereas inter partes cases affect only the parties before the court.
Legal Implications of In Rem Proceedings
In rem proceedings establish jurisdiction over property rather than a person, enabling courts to adjudicate rights related directly to the property itself, often in cases such as maritime liens or real estate disputes. Legal implications include the ability to bind absent parties with interests in the property, facilitating resolution when the parties are unknown or outside the court's personal jurisdiction. This approach contrasts with inter partes actions, where personal jurisdiction over the parties is required, and rulings typically affect only those specific parties involved in the litigation.
Rights and Obligations in Inter Partes Actions
Inter Partes actions involve direct disputes between parties, where rights and obligations are actively contested and defined through adversarial proceedings. The parties engage in a legal process that requires presenting evidence, arguments, and defenses related to the trademark's use, registration, or infringement claims. This mechanism ensures both claimants and respondents have procedural rights, including the right to be heard, to submit documents, and to receive a binding decision affecting their legal standing.
Examples of In Rem vs Inter Partes in Law
In rem cases involve disputes over property or status affecting the whole world, such as cases of maritime salvage or ownership of abandoned property, where the court's judgment binds all potential claimants. Inter partes cases focus on rights and obligations between specific parties, exemplified by contract disputes, litigation between two businesses over intellectual property infringement, or tenant-landlord disagreements. For instance, an in rem maritime lien action targets a vessel itself, while an inter partes contract dispute involves suing a specific party for breach.
Advantages and Disadvantages: In Rem vs Inter Partes
In rem proceedings offer the advantage of targeting property directly, simplifying enforcement and ensuring broader jurisdictional reach, but they can be limited by the need for tangible assets and may not address personal liabilities. Inter partes procedures provide the benefit of engaging all interested parties, facilitating dispute resolution through direct participation and comprehensive evidence presentation, though they often involve longer timelines and higher litigation costs. Choosing between in rem and inter partes depends on the case specifics, such as the nature of the dispute, asset availability, and desired enforceability scope.
Choosing the Right Action: Factors to Consider
Choosing between In Rem and Inter Partes actions depends on jurisdictional scope, with In Rem actions targeting property rights against the world, while Inter Partes actions address disputes between specific parties. Consider factors such as the nature of the interest (property vs. personal rights), the desired enforcement outcome, and procedural efficiency in litigation. Evaluating whether the dispute requires binding third parties or simply resolves conflicts between involved parties guides the optimal legal strategy.
Case Law: Landmark Decisions on In Rem and Inter Partes
Landmark decisions in In Rem cases, such as Shaffer v. Heitner, emphasized the necessity of minimum contacts for jurisdiction over property located within the forum state. In contrast, landmark Inter Partes cases like International Shoe Co. v. Washington established the foundation for personal jurisdiction based on sufficient contacts between the defendant and the forum state. These rulings collectively shaped the modern jurisdictional analysis distinguishing property-based claims from party-based claims.
In Rem Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com